Q4 Describe the body`s mechanisms for regulating
... pyruvate and lactate, using the pyruvate for the Krebs cycle and transporting the lactate to the liver for gluconeogenesis via the Cori cycle Inhibits cellular utilization of glucose during hypoglycaemia, cau ...
... pyruvate and lactate, using the pyruvate for the Krebs cycle and transporting the lactate to the liver for gluconeogenesis via the Cori cycle Inhibits cellular utilization of glucose during hypoglycaemia, cau ...
CHM 20 EXAM 3 – REVIEW Name Ms Dang Indicate whether each
... At first, one might expect the inhibition of phosphorylase action by caffeine to be a case of traditional noncompetitive inhibition because the inhibitor apparently does not bind at the active site. However, glycogen phosphorylase is known to be an allosteric enzyme and the classical terms competiti ...
... At first, one might expect the inhibition of phosphorylase action by caffeine to be a case of traditional noncompetitive inhibition because the inhibitor apparently does not bind at the active site. However, glycogen phosphorylase is known to be an allosteric enzyme and the classical terms competiti ...
Chemistry: Biological Molecules (GPC)
... for individuals in various settings. They often work with patients in health-care facilities, designing nutrition plans to prevent and treat diseases. For example, dietitians may teach a patient with diabetes how to manage blood-sugar levels by eating the correct types and amounts of carbohydrates. ...
... for individuals in various settings. They often work with patients in health-care facilities, designing nutrition plans to prevent and treat diseases. For example, dietitians may teach a patient with diabetes how to manage blood-sugar levels by eating the correct types and amounts of carbohydrates. ...
see previous week 3 link
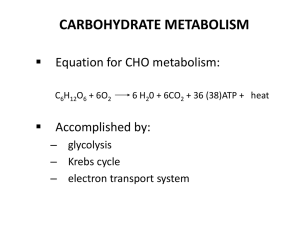
... • Citric acid cycle – a cyclical series of oxidation reactions that give off CO2 and produce one ATP per cycle; occurs twice per glucose molecule • Electron transport system – a series of carriers that accept electrons removed from glucose and pass them from one carrier to the next until the final ...
... • Citric acid cycle – a cyclical series of oxidation reactions that give off CO2 and produce one ATP per cycle; occurs twice per glucose molecule • Electron transport system – a series of carriers that accept electrons removed from glucose and pass them from one carrier to the next until the final ...
Import Settings
... E) the amino acid carries no net electrical charge 18. Amino acid side-chain residues have: A) a positive charge in every situation B) pKs that assure the solubility of every protein C) constant pKs no matter what aqueous environment they are found in D) different pKs in peptides as compared to the ...
... E) the amino acid carries no net electrical charge 18. Amino acid side-chain residues have: A) a positive charge in every situation B) pKs that assure the solubility of every protein C) constant pKs no matter what aqueous environment they are found in D) different pKs in peptides as compared to the ...
Read the passage. (i) Name the substance in cells which carries
... of producing drip dry shirts made from natural fibres. Other cotton plants are being genetically engineered to produce their own insecticides. When they have perfected these new types of cotton plants, the scientists will use cloning techniques to produce large numbers of them. ...
... of producing drip dry shirts made from natural fibres. Other cotton plants are being genetically engineered to produce their own insecticides. When they have perfected these new types of cotton plants, the scientists will use cloning techniques to produce large numbers of them. ...
1 - SMIC Nutrition Science
... Answer (key points): Oxidative phosphorylation accounts for approximately 90% of ATP production and involves a series of linked chemical reactions that make up the electron transport chain. If the body could not generate ATP via the electron transport chain, death would result. (pp. 278-279) ...
... Answer (key points): Oxidative phosphorylation accounts for approximately 90% of ATP production and involves a series of linked chemical reactions that make up the electron transport chain. If the body could not generate ATP via the electron transport chain, death would result. (pp. 278-279) ...
CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF MACROMOLECULES
... • The repeated units are small molecules called monomers (mono = one). – Some monomers have other functions of their own. ...
... • The repeated units are small molecules called monomers (mono = one). – Some monomers have other functions of their own. ...
Microbial Metabolism
... • Oxidation is the removal of electrons. • Reduction is the gain of electrons. • Redox reaction is an oxidation reaction paired with a reduction reaction. ...
... • Oxidation is the removal of electrons. • Reduction is the gain of electrons. • Redox reaction is an oxidation reaction paired with a reduction reaction. ...
outlines
... Facilitated Diffusion – diffusion of ions/polar solutes via a carrier protein (channel protein) (ex. glucose) Active Transport - works against the concentration gradient and requires energy (ATP hydrolysis) 1) Primary (ex. Na/K pump—3Na+ pumped out and 2K+ pumped into cell fueled by ATP hydrolysis) ...
... Facilitated Diffusion – diffusion of ions/polar solutes via a carrier protein (channel protein) (ex. glucose) Active Transport - works against the concentration gradient and requires energy (ATP hydrolysis) 1) Primary (ex. Na/K pump—3Na+ pumped out and 2K+ pumped into cell fueled by ATP hydrolysis) ...
EXPECTATIONS for Do Now
... cell are proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Food energy is measured in calories. If one consumes more calories than the body uses, then they will gain weight. ...
... cell are proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Food energy is measured in calories. If one consumes more calories than the body uses, then they will gain weight. ...
KEY Biochemistry Macromolecules – POGIL
... 3. In Figure 10, within your nucleotide cirlces, please circle all the phosphate groups and box the nitrogenous bases. How many of each of these do you see in Figure 10? SEE FIGURE 7 AND 8 FOR LOCATION OF SUGAR AND PHOSPHATES ...
... 3. In Figure 10, within your nucleotide cirlces, please circle all the phosphate groups and box the nitrogenous bases. How many of each of these do you see in Figure 10? SEE FIGURE 7 AND 8 FOR LOCATION OF SUGAR AND PHOSPHATES ...
CHAPTER 8 OBJECTIVES
... 3. Describe the formation of a glycosidic linkage. 4. Distinguish between the glycosidic linkages found in starch and cellulose. Explain why the difference is biologically important. 5. Develop a table that shows the storage and structural form of carbs (rows) in plants and animals (columns). ...
... 3. Describe the formation of a glycosidic linkage. 4. Distinguish between the glycosidic linkages found in starch and cellulose. Explain why the difference is biologically important. 5. Develop a table that shows the storage and structural form of carbs (rows) in plants and animals (columns). ...
(pt=2) What is an acid?
... What are three, clear characteristics that can distinguish between something that is living or ...
... What are three, clear characteristics that can distinguish between something that is living or ...
slib Human Biochemistry
... Digestion of triglycerides [508] • Fats must be broken down into glycerol and fatty acids to be transported in blood • Fats undergo hydrolysis using enzymes – Lipases ...
... Digestion of triglycerides [508] • Fats must be broken down into glycerol and fatty acids to be transported in blood • Fats undergo hydrolysis using enzymes – Lipases ...
FES 100 - Introduction to Forest Biology Exam 1: 100 points October
... What are three, clear characteristics that can distinguish between something that is living ...
... What are three, clear characteristics that can distinguish between something that is living ...
Cellular Respiration 3 Parts Glycolysis Kreb`s Cycle
... the energy of the carbohydrate as it is. Both types of organisms must convert the carbohydrate to ATP, the energy currency of the cell, in order to carry out metabolic activity. ...
... the energy of the carbohydrate as it is. Both types of organisms must convert the carbohydrate to ATP, the energy currency of the cell, in order to carry out metabolic activity. ...
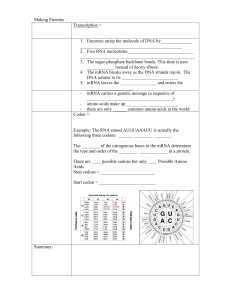
DNA Transcription
... The ________ of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA determines the type and order of the ________ ____________ in a protein. There are ____ possible codons but only ____ Possible Amino Acids Stop codons = ________________________ Start codon = _________________________ ...
... The ________ of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA determines the type and order of the ________ ____________ in a protein. There are ____ possible codons but only ____ Possible Amino Acids Stop codons = ________________________ Start codon = _________________________ ...
Simulating Protein Synthesis
... List at least 3 differences between transcription and translation? (3) Transcription ...
... List at least 3 differences between transcription and translation? (3) Transcription ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Polymers (macromolecules) - “many units” • Formed when two or more small units called ...
... Polymers (macromolecules) - “many units” • Formed when two or more small units called ...
to find the lecture notes for lecture 1 click here
... through food = essential fatty acids e.g omega-3 fatty acids -polyunsaturated fatty acids -important in regulating cholesterol levels -lower LDL levels in the ...
... through food = essential fatty acids e.g omega-3 fatty acids -polyunsaturated fatty acids -important in regulating cholesterol levels -lower LDL levels in the ...
University of North Carolina researchers provide evidence for how
... launch a selection process that we can envision creating the first life on Earth.” Thus, Carter said, RNA did not have to invent itself from the primordial soup. Instead, even before there were cells, it seems more likely that there were interactions between amino acids and nucleotides that led to t ...
... launch a selection process that we can envision creating the first life on Earth.” Thus, Carter said, RNA did not have to invent itself from the primordial soup. Instead, even before there were cells, it seems more likely that there were interactions between amino acids and nucleotides that led to t ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.