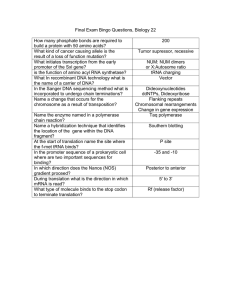
AT CG - Middletown Public Schools
... DNA and Mutations DNA is made up of nucleotides that each contain a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. The four possible bases are adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine. Remember that adenine and thymine are complementary and form pairs, and cytosine and guanine are complementary and form pairs. 1. B ...
... DNA and Mutations DNA is made up of nucleotides that each contain a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. The four possible bases are adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine. Remember that adenine and thymine are complementary and form pairs, and cytosine and guanine are complementary and form pairs. 1. B ...
notes
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
Different types of PCR
... is used to copy all of the mRNAs in an amplified by PCR using primers that ...
... is used to copy all of the mRNAs in an amplified by PCR using primers that ...
Webquests_files/Genes and DNA SWQ
... The four nucleotides Difference between dominant and recessive alleles ...
... The four nucleotides Difference between dominant and recessive alleles ...
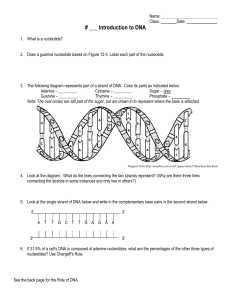
Use the diagram to match the letter (A-C) to the correct term(1
... 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen b ...
... 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen b ...
Using microsatellites as molecular markers
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
Cytosine – ______ Sugar
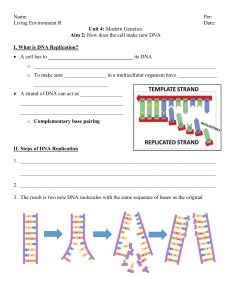
... 2. Draw a guanine nucleotide based on Figure 12-5. Label each part of the nucleotide. ...
... 2. Draw a guanine nucleotide based on Figure 12-5. Label each part of the nucleotide. ...
Name - OnCourse
... 3. The “backbones” of the DNA molecule is made up of two components, what are these? c. _______________________________ d. _______________________________ 5. There are four different bases that make up the “rungs.” What are the names of those bases? a. _______________________________ b. ____________ ...
... 3. The “backbones” of the DNA molecule is made up of two components, what are these? c. _______________________________ d. _______________________________ 5. There are four different bases that make up the “rungs.” What are the names of those bases? a. _______________________________ b. ____________ ...
Genetic Engineering - Duplin County Schools
... Selective Breeding • Allowing only those with desired character istics to produce the next generation ...
... Selective Breeding • Allowing only those with desired character istics to produce the next generation ...
Document
... within the human population—each variable position is termed a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) One specific combination of the three SNPs, termed a haplotype, correlates most strongly with tasting ability SNPs also predict adverse responses to PROZAC® and Paxil® ...
... within the human population—each variable position is termed a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) One specific combination of the three SNPs, termed a haplotype, correlates most strongly with tasting ability SNPs also predict adverse responses to PROZAC® and Paxil® ...
Molecular Pathology - Charles River Laboratories
... © 2013, Charles River Laboratories International, Inc. ...
... © 2013, Charles River Laboratories International, Inc. ...
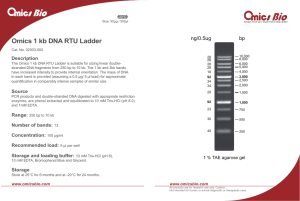
Omics 1 kb DNA RTU Ladder
... The Omics 1 kb DNA RTU Ladder is suitable for sizing linear doublestranded DNA fragments from 250 bp to 10 kb. The 1 kb and 3kb bands have increased intensity to provide internal orientation. The mass of DNA in each band is provided (assuming a 0.5 μg/ 5 μl load) for approximate quantification in co ...
... The Omics 1 kb DNA RTU Ladder is suitable for sizing linear doublestranded DNA fragments from 250 bp to 10 kb. The 1 kb and 3kb bands have increased intensity to provide internal orientation. The mass of DNA in each band is provided (assuming a 0.5 μg/ 5 μl load) for approximate quantification in co ...
Recitation 10 Solutions
... 1. How is a cDNA library different from a genomic library? A genomic library is a population of host bacteria, each of which carries a DNA fragment that was inserted into a cloning vector, such that the collection of cloned DNA fragment represents the entire genome of the source organism. The DNA fr ...
... 1. How is a cDNA library different from a genomic library? A genomic library is a population of host bacteria, each of which carries a DNA fragment that was inserted into a cloning vector, such that the collection of cloned DNA fragment represents the entire genome of the source organism. The DNA fr ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.