HLA typing of renal patients and investigation of disease
... Amplification of DNA takes place in a thermal cycler. The process involves a series of up to thirty cycles consisting of three steps. 1) The double stranded DNA is heated to 95ºC breaking the hydrogen bonds between them and separating the two strands. 2) As the temperature is reduced, the primers an ...
... Amplification of DNA takes place in a thermal cycler. The process involves a series of up to thirty cycles consisting of three steps. 1) The double stranded DNA is heated to 95ºC breaking the hydrogen bonds between them and separating the two strands. 2) As the temperature is reduced, the primers an ...
Genetics 1. What do the letters DNA stand for? 2. Two scientists are
... 7. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimides. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. ...
... 7. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimides. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. ...
What are the three steps in PCR?
... It is often used in DNA fingerprinting It requires gel electrophoresis which separates DNA by size ...
... It is often used in DNA fingerprinting It requires gel electrophoresis which separates DNA by size ...
Biotech unit Objectives
... stem cells RFLP analysis sticky ends restriction endonucleases hybridization plasmid mapping primer tracking dye lane marker genetically modified foods electroporation ...
... stem cells RFLP analysis sticky ends restriction endonucleases hybridization plasmid mapping primer tracking dye lane marker genetically modified foods electroporation ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... Questions 3-4 pertain to the following experiment. Four pairs of PCR primers were used to amplify DNA isolated from one man's somatic cells, and from 21 single sperm that he donated for this study. Each primer pair amplifies a different region of the human genome, referred to as genes A, B, C and D. ...
... Questions 3-4 pertain to the following experiment. Four pairs of PCR primers were used to amplify DNA isolated from one man's somatic cells, and from 21 single sperm that he donated for this study. Each primer pair amplifies a different region of the human genome, referred to as genes A, B, C and D. ...
Ross - Tree Improvement Program
... (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/variation). Two genes are shown – the vertical lines are “exons” that encode proteins; the “introns” between exons are discarded. ...
... (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/variation). Two genes are shown – the vertical lines are “exons” that encode proteins; the “introns” between exons are discarded. ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
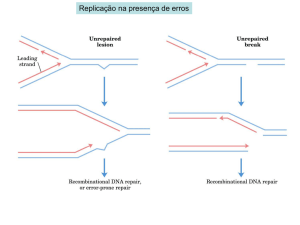
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
DNA Test Review
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
Jatropha genotyping In Gh Pu QR In Gh Pu QR 13 primer pairs
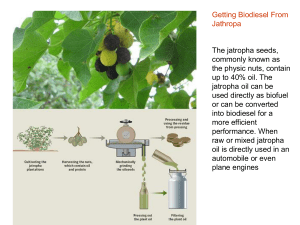
... commonly known as the physic nuts, contain up to 40% oil. The jatropha oil can be used directly as biofuel or can be converted into biodiesel for a more efficient performance. When raw or mixed jatropha oil is directly used in an automobile or even plane engines ...
... commonly known as the physic nuts, contain up to 40% oil. The jatropha oil can be used directly as biofuel or can be converted into biodiesel for a more efficient performance. When raw or mixed jatropha oil is directly used in an automobile or even plane engines ...
MCAS BIOLOGY REVIEW GENETICS AND EVOLUTION
... from DNA Translation takes place at the ribosome in the cytoplasm; translates mRNA to tRNA to amino acid ...
... from DNA Translation takes place at the ribosome in the cytoplasm; translates mRNA to tRNA to amino acid ...
ap biology review guide big idea #2
... millions of copies of DNA can be made from one original copy. In this method, the target DNA molecule is subjected to temperatures over 95 degrees C to make the double-stranded DNA separate. The temperature is then lowered slightly to allow primers to anneal before the Taq polymerase catalyzes the r ...
... millions of copies of DNA can be made from one original copy. In this method, the target DNA molecule is subjected to temperatures over 95 degrees C to make the double-stranded DNA separate. The temperature is then lowered slightly to allow primers to anneal before the Taq polymerase catalyzes the r ...
Section 6-3
... • Having parents with desired traits produce offspring – Inbreeding • Crossing two individuals that have identical alleles ...
... • Having parents with desired traits produce offspring – Inbreeding • Crossing two individuals that have identical alleles ...
Genetic Markers
... polymorphisms (RFLPs) if in a restriction enzyme site • Tandem repeat sequences (or microsatellies), such as dinucleotides (CA)n, tri- and tetra-nucleotides, that are variable for the number of repeats. • Most polymorphisms are in non-coding DNA – there is more of it, and mutations are not selected ...
... polymorphisms (RFLPs) if in a restriction enzyme site • Tandem repeat sequences (or microsatellies), such as dinucleotides (CA)n, tri- and tetra-nucleotides, that are variable for the number of repeats. • Most polymorphisms are in non-coding DNA – there is more of it, and mutations are not selected ...
Name
... 2. How does reverse transcriptase make a single strand of DNA from a mRNA (2)? Reverse transcriptase creates DNA from mRNA by first isolating the mRNA, adding reverse transcriptase, which creates a complimentary strand of DNA- single stranded, then DNA polymerase adds the second complimentary strand ...
... 2. How does reverse transcriptase make a single strand of DNA from a mRNA (2)? Reverse transcriptase creates DNA from mRNA by first isolating the mRNA, adding reverse transcriptase, which creates a complimentary strand of DNA- single stranded, then DNA polymerase adds the second complimentary strand ...
CALF THYMUS DNA, ACTIVATED - Sigma
... of α- P-TTP (3000 Ci/mmol); and 20 units of DNA Polymerase (Sigma Catalog No. D 9380). 39% of the ...
... of α- P-TTP (3000 Ci/mmol); and 20 units of DNA Polymerase (Sigma Catalog No. D 9380). 39% of the ...
2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... 2 The members of a species are capable of _______________________________ with each other. ...
... 2 The members of a species are capable of _______________________________ with each other. ...
DNA Sequencing
... Once DNA amplified, its nucleotide sequence determined Today, DNA sequencing is automated Automated system originally based on Dideoxy Chain Termination Method Invented by Frederick Sanger - received Nobel Prize in 1980 ...
... Once DNA amplified, its nucleotide sequence determined Today, DNA sequencing is automated Automated system originally based on Dideoxy Chain Termination Method Invented by Frederick Sanger - received Nobel Prize in 1980 ...
DNA * History, Structure, and Functions
... happen if he crossed various pea plants He would carefully transfer the pollen from one plant to another He did this thousands of times ...
... happen if he crossed various pea plants He would carefully transfer the pollen from one plant to another He did this thousands of times ...
Document
... Agarose gel electrophoresis can be used to investigate an individual’s genotype directly. If two alleles have sequence differences that change a restriction enzyme recognition site, then the size differences of the DNA fragments from a restriction digest can tell the researcher which alleles an ind ...
... Agarose gel electrophoresis can be used to investigate an individual’s genotype directly. If two alleles have sequence differences that change a restriction enzyme recognition site, then the size differences of the DNA fragments from a restriction digest can tell the researcher which alleles an ind ...
Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers In the nucleus of the
... 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and determine the sequence of all genes found on the human chromosome. 5. The nucleus 6. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine 7. The phosphate groups give DNA its acidic properties. 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair follicular tissue, bone 9. Re ...
... 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and determine the sequence of all genes found on the human chromosome. 5. The nucleus 6. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine 7. The phosphate groups give DNA its acidic properties. 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair follicular tissue, bone 9. Re ...
PCR - Polymerase Chain Reaction
... from PCR product • T-RFLP (terminal-RFLP) is in most respects identical except for a marker on the end of the enzyme • Works as fingerprinting technique because different organisms with different DNA sequences will have different lengths of DNA between identical units targeted by the restriction enz ...
... from PCR product • T-RFLP (terminal-RFLP) is in most respects identical except for a marker on the end of the enzyme • Works as fingerprinting technique because different organisms with different DNA sequences will have different lengths of DNA between identical units targeted by the restriction enz ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.