DNA Fingerprinting: The Code to Identification
... bones found in a shared grave in Russia. The victims turned out to be members of the royal family, the Romanovs, who had been executed in 1918. Because the Y chromosome, part of the nuclear genome, is passed largely intact from father to son for many generations, DNA fingerprinting of the Y chromoso ...
... bones found in a shared grave in Russia. The victims turned out to be members of the royal family, the Romanovs, who had been executed in 1918. Because the Y chromosome, part of the nuclear genome, is passed largely intact from father to son for many generations, DNA fingerprinting of the Y chromoso ...
A Critical Review of the Identification of Mass Disaster Remains
... two definitions that can explain what is considered a mass disaster: The first tradition definition is any event resulting in six or more deaths at the same time and in the same place from one basic cause, and the second more recent is an event that causes such a number of essentially simultaneous d ...
... two definitions that can explain what is considered a mass disaster: The first tradition definition is any event resulting in six or more deaths at the same time and in the same place from one basic cause, and the second more recent is an event that causes such a number of essentially simultaneous d ...
lecture5
... restoring the correct C. This is done without the need to break the DNA backbone (in contrast to the mechanisms of excision repair described below). Some of the drugs used in cancer chemotherapy ("chemo") also damage DNA by alkylation. Some of the methyl groups can be removed by a protein encoded by ...
... restoring the correct C. This is done without the need to break the DNA backbone (in contrast to the mechanisms of excision repair described below). Some of the drugs used in cancer chemotherapy ("chemo") also damage DNA by alkylation. Some of the methyl groups can be removed by a protein encoded by ...
AWC Summer Studentship Report_Will Stovall
... relationships among individuals within populations. Although this experiment imparted some understanding of the genetic structure of extant populations, and was able to assign bycaught individuals to broad geographic regions, it is likely that more modern genetic analysis methods could reveal furthe ...
... relationships among individuals within populations. Although this experiment imparted some understanding of the genetic structure of extant populations, and was able to assign bycaught individuals to broad geographic regions, it is likely that more modern genetic analysis methods could reveal furthe ...
MCDB 1041 3/9/12 Activity 6: Central Dogma Continued PART I
... extent of the gene. Thus, you will notice that only the sequence in part A begins with ATG, the required start codon. The promoter would be just to the left of this ATG sequence (ie, the top strand is the coding strand). Your tasks: * Find and mark where the nucleotide change has occurred between th ...
... extent of the gene. Thus, you will notice that only the sequence in part A begins with ATG, the required start codon. The promoter would be just to the left of this ATG sequence (ie, the top strand is the coding strand). Your tasks: * Find and mark where the nucleotide change has occurred between th ...
Recitation Section 7 Answer Key Molecular Biology—DNA as
... Observations of heritable traits indicate that genetic information must be recorded somehow and also must be passed on to offspring. In addition, change over time indicates that there must also be a mechanism that allows the information to be changed. 3. Given what you now know about DNA structure, ...
... Observations of heritable traits indicate that genetic information must be recorded somehow and also must be passed on to offspring. In addition, change over time indicates that there must also be a mechanism that allows the information to be changed. 3. Given what you now know about DNA structure, ...
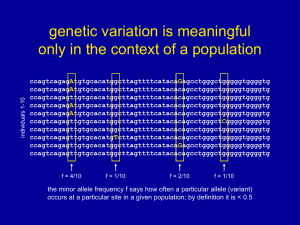
lecture26_Polymorphi..
... Edwards AW. 2003. Human genetic diversity: Lewontin's fallacy. Bioessays 25: 798-801 even if the probability of misclassifying an individual’s race based on a single locus is as high as 30%, the misclassification probability based on 10 loci can drop to a few percent ...
... Edwards AW. 2003. Human genetic diversity: Lewontin's fallacy. Bioessays 25: 798-801 even if the probability of misclassifying an individual’s race based on a single locus is as high as 30%, the misclassification probability based on 10 loci can drop to a few percent ...
Study questions - Pre-lab
... d. What do we mean when we say a SNP is associated with a certain phenotypic trait? We mean that it’s not necessarily causal to the phenotypic trait. The SNP segregates with the trait, but it may or may not be its underlying cause (for example, the SNP DNA may be in very close proximity to the DNA u ...
... d. What do we mean when we say a SNP is associated with a certain phenotypic trait? We mean that it’s not necessarily causal to the phenotypic trait. The SNP segregates with the trait, but it may or may not be its underlying cause (for example, the SNP DNA may be in very close proximity to the DNA u ...
DNA sequencing
... Molecules which differ by only one nucleotide in their length can be separated. ...
... Molecules which differ by only one nucleotide in their length can be separated. ...
More Basic Biotechnology Tools Many uses of restriction enzymes
... need to know a bit of sequence to make proper primers primers can bracket target sequence ▪ start with long piece of DNA & ...
... need to know a bit of sequence to make proper primers primers can bracket target sequence ▪ start with long piece of DNA & ...
幻灯片 1
... ligation cycles join oligonucleotides into increasingly larger strands. A final PCR step is often employed to amplify the full-length target from the incomplete products. ...
... ligation cycles join oligonucleotides into increasingly larger strands. A final PCR step is often employed to amplify the full-length target from the incomplete products. ...
1. Chromosome structure a. Nucleosome
... 4. Electrophoresis- Used to look at unique pattern created by fragments of DNA; cut DNA using enzyme; load into a gel that is covered with buffer; turn on electricity; DNA runs from negative to positive; larger chunks move less; unique for each person if testing variable areas of DNA; can be used fo ...
... 4. Electrophoresis- Used to look at unique pattern created by fragments of DNA; cut DNA using enzyme; load into a gel that is covered with buffer; turn on electricity; DNA runs from negative to positive; larger chunks move less; unique for each person if testing variable areas of DNA; can be used fo ...
Modern Genetics Meets the Dodo and the Solitaire
... particular amino acid 13. The main goal of the Human Genome Project was to a. find cures for genetic diseases b. find all mutations in human DNA c. count the number of genes in human DNA d. sequence all DNA on human chromosomes 14. Genetic engineering involves a. inserting changed DNA into an organi ...
... particular amino acid 13. The main goal of the Human Genome Project was to a. find cures for genetic diseases b. find all mutations in human DNA c. count the number of genes in human DNA d. sequence all DNA on human chromosomes 14. Genetic engineering involves a. inserting changed DNA into an organi ...
Name Period _____ Date ______ SPRING MULTIPLE CHOICE
... DNA’s double strand is held together by weak ____________________ bonds Each nucleotide (containing a ________________________ base, ___________________ and ____________________) is held together between the sugar and phosphate by strong ________________ bonds 12. Describe how RNA is different than ...
... DNA’s double strand is held together by weak ____________________ bonds Each nucleotide (containing a ________________________ base, ___________________ and ____________________) is held together between the sugar and phosphate by strong ________________ bonds 12. Describe how RNA is different than ...
Things to Know for the Test – Honors
... processes are read the way they are, where they occur in the cell, etc. DNA is the blueprint of life. It is made of nucleotides that contain the code to make proteins. Proteins control everything that an organism does. They control hair color, acts as hormones such as insulin, etc. DNA is so importa ...
... processes are read the way they are, where they occur in the cell, etc. DNA is the blueprint of life. It is made of nucleotides that contain the code to make proteins. Proteins control everything that an organism does. They control hair color, acts as hormones such as insulin, etc. DNA is so importa ...
Biofuel phyto-forensics case resolved through PCR
... Step 3: This step is called DNA Synthesis. The complementary nature of the DNA bases allows us to construct a new double stranded DNA molecule from a single strand. When the primers were added to the DNA sample, we also added additional bases (A’s, T’s, C’s, G’s) and an enzyme called DNA polymerase. ...
... Step 3: This step is called DNA Synthesis. The complementary nature of the DNA bases allows us to construct a new double stranded DNA molecule from a single strand. When the primers were added to the DNA sample, we also added additional bases (A’s, T’s, C’s, G’s) and an enzyme called DNA polymerase. ...
Biotech 2 - Explore Biology
... Copy DNA without plasmids? PCR! Polymerase Chain Reaction method for making many, many copies of a specific segment of DNA ~only need 1 cell of DNA to start ...
... Copy DNA without plasmids? PCR! Polymerase Chain Reaction method for making many, many copies of a specific segment of DNA ~only need 1 cell of DNA to start ...
NAME Date DNA Structure Review Figure 1 The untwisted form of
... there is a relationship between DNA and _________________________. 20. Only the bases, which form the steps of the DNA ladder, control inheritance. There are thousands of genes in any one organism, such as a human being. Since there are only four bases, then one base ______________________ (could / ...
... there is a relationship between DNA and _________________________. 20. Only the bases, which form the steps of the DNA ladder, control inheritance. There are thousands of genes in any one organism, such as a human being. Since there are only four bases, then one base ______________________ (could / ...
Biotechnology 2
... Copy DNA without plasmids? PCR! Polymerase Chain Reaction method for making many, many copies of a specific segment of DNA ~only need 1 cell of DNA to start ...
... Copy DNA without plasmids? PCR! Polymerase Chain Reaction method for making many, many copies of a specific segment of DNA ~only need 1 cell of DNA to start ...
Lecture 9 - Bacterial Genetics Chpt. 8
... What are mutations? • Change in the base sequence of the DNA • Do they always change the genetic code? ...
... What are mutations? • Change in the base sequence of the DNA • Do they always change the genetic code? ...
agarose gel - Bio
... vacuum filtration or column separation. The purified DNA fragments are of high quality and are ...
... vacuum filtration or column separation. The purified DNA fragments are of high quality and are ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.