Word - NIEHS SNPs Program - University of Washington
... PolyPhen predicts the potential consequence of an amino acid substitution on the structure and function of a human protein using physical and comparative considerations. 1. Enter the amino acid sequence for BRCA1 from the fasta file available at http://egp.gs.washington.edu/workshop/BRCA1.protein.fs ...
... PolyPhen predicts the potential consequence of an amino acid substitution on the structure and function of a human protein using physical and comparative considerations. 1. Enter the amino acid sequence for BRCA1 from the fasta file available at http://egp.gs.washington.edu/workshop/BRCA1.protein.fs ...
... Many mutations in Neurospora crassa are only known by a morphological or other visible phenotype. For many of these, the actual open reading frame responsible remains unknown. Among these are several temperature-sensitive lethal mutations known as unknown (Inoue and Ishikawa, 1970; Ishikawa and Perk ...
ALE 7 - Biol 100
... The number of times a cell is capable of dividing is called the Hayflick limit—named after Leonard Hayflick, the biologist that discovered it in 1961. It’s intriguing to note that the cells of longer-lived species of animals have a larger Hayflick limit (e.g. Human fibroblast cells have a Hayflick l ...
... The number of times a cell is capable of dividing is called the Hayflick limit—named after Leonard Hayflick, the biologist that discovered it in 1961. It’s intriguing to note that the cells of longer-lived species of animals have a larger Hayflick limit (e.g. Human fibroblast cells have a Hayflick l ...
20161108101511001
... •Defendant is “included” as a possible contributor; •Statistics offered on CPI (Cumulative probability of inclusion) ...
... •Defendant is “included” as a possible contributor; •Statistics offered on CPI (Cumulative probability of inclusion) ...
Rapid sequencing of DNA based on single molecule detection
... photostability. We have been able to utilize the increased photon yield of R6G in EtOH to observe the bursts of photons from individual molecules of R6G using cW excitation as indicated from non-random correlations in the autocorrelation function and tails in the Poisson distributions (13). For TRIT ...
... photostability. We have been able to utilize the increased photon yield of R6G in EtOH to observe the bursts of photons from individual molecules of R6G using cW excitation as indicated from non-random correlations in the autocorrelation function and tails in the Poisson distributions (13). For TRIT ...
Repression of E-cadherin by the Polycomb Group Protein
... PCR amplification was done using 200 ng of bisulfite modified DNA as template, with forward pimer 5’- ATTTTAGTAATTTTAGGTTAGAGGGTTA -3’ and reverse primer 5’- ACCACAACCAATCAACAAC -3’ which is biotinylated. Bisulfite-modified DNA was amplified in a 24-µL reaction with the primer set and HotStarTaq DN ...
... PCR amplification was done using 200 ng of bisulfite modified DNA as template, with forward pimer 5’- ATTTTAGTAATTTTAGGTTAGAGGGTTA -3’ and reverse primer 5’- ACCACAACCAATCAACAAC -3’ which is biotinylated. Bisulfite-modified DNA was amplified in a 24-µL reaction with the primer set and HotStarTaq DN ...
Substrate
... buffer (2 mM, pH 8.0), 4 µL of phenol red (0.5 % in ethanol), an appropriate amount of enzyme, and the reaction was started by adding 2 µl of BnLAE substrate. Either pure enantiomers or a racemic mixture were used. Due to the release of free acid by an active esterase, a drop of pH leading to a colo ...
... buffer (2 mM, pH 8.0), 4 µL of phenol red (0.5 % in ethanol), an appropriate amount of enzyme, and the reaction was started by adding 2 µl of BnLAE substrate. Either pure enantiomers or a racemic mixture were used. Due to the release of free acid by an active esterase, a drop of pH leading to a colo ...
white - UWL faculty websites
... of ethanol. Prior to sequencing, the denatured plasmid was further purified using the Geneclean I1 kit, omitting the agarose gel electrophoresis step. This final step was found to improve the quality and consistency of the sequence data. The sequencing strategies for the white and brown alleles are ...
... of ethanol. Prior to sequencing, the denatured plasmid was further purified using the Geneclean I1 kit, omitting the agarose gel electrophoresis step. This final step was found to improve the quality and consistency of the sequence data. The sequencing strategies for the white and brown alleles are ...
Molecular Basis of Polymorphisms of Human Complement
... C3 S alleles are commonly HAV 4-1 negative, while C3 F alleles are commonly HAV 4-1 positive. We studied 45 normal individuals (three Chinese and 42 Caucasoids with the following gene frequency : C3 S = 0.81 ; C3 F = 0.19) by immunoblotting. We found two C3 S HAV 4-1-positive alleles, but no C3 F HA ...
... C3 S alleles are commonly HAV 4-1 negative, while C3 F alleles are commonly HAV 4-1 positive. We studied 45 normal individuals (three Chinese and 42 Caucasoids with the following gene frequency : C3 S = 0.81 ; C3 F = 0.19) by immunoblotting. We found two C3 S HAV 4-1-positive alleles, but no C3 F HA ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis - Liceo da Vinci
... molecules containing anywhere from several hundred to several thousand ribonucleotides, depending on the size of the protein to be made. Each of the 100,000 or so proteins in the human body is synthesized from a different mRNA that has been transcribed from a specific gene on DNA. "Why do we need mR ...
... molecules containing anywhere from several hundred to several thousand ribonucleotides, depending on the size of the protein to be made. Each of the 100,000 or so proteins in the human body is synthesized from a different mRNA that has been transcribed from a specific gene on DNA. "Why do we need mR ...
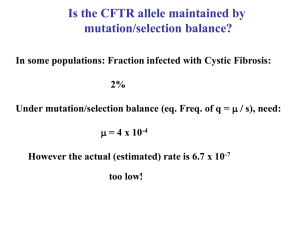
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... Polymorphism is simply a snapshot of a continuous process of mutational input and subsequent random extinction or fixation of alleles. ...
... Polymorphism is simply a snapshot of a continuous process of mutational input and subsequent random extinction or fixation of alleles. ...
Practice Benchmark I Page 1 of 12 Directions: Please choose the
... 30. Scientists are studying an inherited disease in which cells make an inactive protein that is too small. Which statement MOST LIKELY explains why the cells make an inactive protein? A. Only introns were used to create the protein. B. ...
... 30. Scientists are studying an inherited disease in which cells make an inactive protein that is too small. Which statement MOST LIKELY explains why the cells make an inactive protein? A. Only introns were used to create the protein. B. ...
495-Ze15
... The model suggests the mechanism of DNA replication, namely, strand separation and synthesis of new chains using parent chains as templates. The information containing in DNA molecule is transcribed into base sequence of RNA single chain macromolecule, than (during translation) this information is u ...
... The model suggests the mechanism of DNA replication, namely, strand separation and synthesis of new chains using parent chains as templates. The information containing in DNA molecule is transcribed into base sequence of RNA single chain macromolecule, than (during translation) this information is u ...
A Variable Number of Tandem Repeats Locus with!, the Human
... have been detected, characterized by SstI fragments of 2.75, 2.70, 2.65, 2.60, or 2.50 kb corresponding to BamHI fragments of 3.45, 3.40, 3.35, 3.30, or 3.20 kb (3, 5). The distribution of these alleles among 143 unrelated individuals was found to be skewed with 250 (87.4%) chromosomes having 2.70/3 ...
... have been detected, characterized by SstI fragments of 2.75, 2.70, 2.65, 2.60, or 2.50 kb corresponding to BamHI fragments of 3.45, 3.40, 3.35, 3.30, or 3.20 kb (3, 5). The distribution of these alleles among 143 unrelated individuals was found to be skewed with 250 (87.4%) chromosomes having 2.70/3 ...
Answer Key (up to 3/21)
... molecule, assign the 3’ to 5’ polarity of each strand and then label the direction in which DNA synthesis will proceed for each strand. I guarantee this will be addressed in some way on the exam. What does dNTP stand for? Why is DNA polymerization, specifically during replication, considered an exer ...
... molecule, assign the 3’ to 5’ polarity of each strand and then label the direction in which DNA synthesis will proceed for each strand. I guarantee this will be addressed in some way on the exam. What does dNTP stand for? Why is DNA polymerization, specifically during replication, considered an exer ...
Minimum SNPs version 2043 user manual
... assigned as distinct alleles and, for each isolate, the alleles at each of the seven loci define the allelic profile or sequence type (ST). Each isolate of a species is therefore unambiguously characterised by a series of seven integers which correspond to the alleles at the seven house-keeping loci ...
... assigned as distinct alleles and, for each isolate, the alleles at each of the seven loci define the allelic profile or sequence type (ST). Each isolate of a species is therefore unambiguously characterised by a series of seven integers which correspond to the alleles at the seven house-keeping loci ...
Lecture 1 09-23-2016
... Tandem = In a line AGGCTAGGCTAGGCTA GGCT Multiple repeats of same sequence; number of repeats is variable = allele! ...
... Tandem = In a line AGGCTAGGCTAGGCTA GGCT Multiple repeats of same sequence; number of repeats is variable = allele! ...
laid the foundation of genetics through his work on garden peas
... Types of alleles 1.Dominant allele – the expressed trait or the observable trait. Ex. RR or Rr 2. Recessive allele – the trait which is not expressed when the dominant allele is present. Ex. rr ...
... Types of alleles 1.Dominant allele – the expressed trait or the observable trait. Ex. RR or Rr 2. Recessive allele – the trait which is not expressed when the dominant allele is present. Ex. rr ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.