Slide 1
... cell survival under nonselective conditions. Episome no longer in use. They usually occur in bacteria, sometimes in eukaryotic organisms (e.g., the 2um-ring in yeast S. cerevisiae). Sizes: 1 to over 400 kb. Copy numbers: 1 - hundreds in a single cell, or even thousands of copies. Every plasmid conta ...
... cell survival under nonselective conditions. Episome no longer in use. They usually occur in bacteria, sometimes in eukaryotic organisms (e.g., the 2um-ring in yeast S. cerevisiae). Sizes: 1 to over 400 kb. Copy numbers: 1 - hundreds in a single cell, or even thousands of copies. Every plasmid conta ...
PDF
... You are studying mechanisms used by bacterial cells to avoid accumulating mutations. Using a reversion assay similar to the Ames test, you identify a mutant strain that has a 20 to 50-fold higher spontaneous mutation rate. You find that this strain carries a mutation that destroys the activity of th ...
... You are studying mechanisms used by bacterial cells to avoid accumulating mutations. Using a reversion assay similar to the Ames test, you identify a mutant strain that has a 20 to 50-fold higher spontaneous mutation rate. You find that this strain carries a mutation that destroys the activity of th ...
Paper 2
... Use a genetic cross to show the phenotypic ratio of their offspring if one of the males of the F 1 generation was mated with an albino female. ...
... Use a genetic cross to show the phenotypic ratio of their offspring if one of the males of the F 1 generation was mated with an albino female. ...
Exercise 10 - DNA Fingerprinting - Lake
... Because these repetitive sequences are short (4-6 bases) and occur side-by-side (in tandem) they are termed short tandem repeats (STR’s). The objective of DNA fingerprinting is to determine how many times a sequence of an STR is repeated in a DNA sample. How many times does the STR “TTTC” repeat its ...
... Because these repetitive sequences are short (4-6 bases) and occur side-by-side (in tandem) they are termed short tandem repeats (STR’s). The objective of DNA fingerprinting is to determine how many times a sequence of an STR is repeated in a DNA sample. How many times does the STR “TTTC” repeat its ...
slg mock midterm – for practice only
... 31. Which of the following statements describes the concept of “semi-conservative” DNA replication? a. The two parental strands reassociate after acting as templates for new strands, thus restoring the parental double helix. b. Each strand of both daughter molecules contains a mixture of old and ne ...
... 31. Which of the following statements describes the concept of “semi-conservative” DNA replication? a. The two parental strands reassociate after acting as templates for new strands, thus restoring the parental double helix. b. Each strand of both daughter molecules contains a mixture of old and ne ...
(OR) – case-control study - Computer Science
... There are different causes and each of these causes can be result of interaction of several genes Each cause explains certain percentage of cases ...
... There are different causes and each of these causes can be result of interaction of several genes Each cause explains certain percentage of cases ...
Probability Practice
... BI2. c. Students know how random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele will be in a gamete. BI2. g. Students know how to predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents. BI3. a. Students know how to predict the prob ...
... BI2. c. Students know how random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele will be in a gamete. BI2. g. Students know how to predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents. BI3. a. Students know how to predict the prob ...
RNA PP
... to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • So, RNA is making a single-stranded copy from DNA that takes information out of the nucleus. ...
... to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • So, RNA is making a single-stranded copy from DNA that takes information out of the nucleus. ...
MB207Jan2010
... • Chromosome must synapse (pair) in order for chiasmata to form where crossing-over occurs – DNA synapsis: base pairing between complementary strands from 2 DNA molecules – Chiasmata: regions where paired homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis, a cross-shaped structure • Onl ...
... • Chromosome must synapse (pair) in order for chiasmata to form where crossing-over occurs – DNA synapsis: base pairing between complementary strands from 2 DNA molecules – Chiasmata: regions where paired homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis, a cross-shaped structure • Onl ...
Phenotype versus genotype reporting for DNA polymorphisms
... mutation, causing a lack of amplification with one of two manufacturer’s kits. The sample did not achieve consensus as 39 laboratories reported two alleles, while 31 reported a single allele. It is clear from the results that the child was heterozygous for 6 and 9.3. The mother’s phenotype was 8,9.3 ...
... mutation, causing a lack of amplification with one of two manufacturer’s kits. The sample did not achieve consensus as 39 laboratories reported two alleles, while 31 reported a single allele. It is clear from the results that the child was heterozygous for 6 and 9.3. The mother’s phenotype was 8,9.3 ...
Activating the MSH2/MSH6 Apoptotic Pathway in Cancer Cells
... concentrations needed for anti-tumour activity causes dangerous hypotension in vivo, and it is therefore not a viable chemotherapeutic agent in humans. Reserpine’s ability to effectively induce MMR-dependent apoptosis in cancer cells is, however, a proof-ofconcept that virtual analysis of molecular ...
... concentrations needed for anti-tumour activity causes dangerous hypotension in vivo, and it is therefore not a viable chemotherapeutic agent in humans. Reserpine’s ability to effectively induce MMR-dependent apoptosis in cancer cells is, however, a proof-ofconcept that virtual analysis of molecular ...
slg mock midterm – for practice only
... 31. Which of the following statements describes the concept of “semi-conservative” DNA replication? a. The two parental strands reassociate after acting as templates for new strands, thus restoring the parental double helix. b. Each strand of both daughter molecules contains a mixture of old and ne ...
... 31. Which of the following statements describes the concept of “semi-conservative” DNA replication? a. The two parental strands reassociate after acting as templates for new strands, thus restoring the parental double helix. b. Each strand of both daughter molecules contains a mixture of old and ne ...
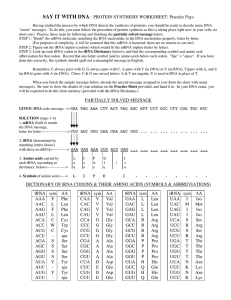
SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
Genetic Notes
... • With incomplete dominance, a cross between organisms with two different phenotypes produces offspring with a third phenotype that is a blending of the parental traits. ...
... • With incomplete dominance, a cross between organisms with two different phenotypes produces offspring with a third phenotype that is a blending of the parental traits. ...
STATION 1: Nucleic acids
... 13) What is the most likely explanation for this base composition? 14) A mutant of E. coli with a heat-sensitive DNA ligase (25°C permissive, 37°C nonpermissive) has been used to show that DNA synthesis is discontinuous. Examination of DNA replication in the presence of [3H]-thymidine in the mutant ...
... 13) What is the most likely explanation for this base composition? 14) A mutant of E. coli with a heat-sensitive DNA ligase (25°C permissive, 37°C nonpermissive) has been used to show that DNA synthesis is discontinuous. Examination of DNA replication in the presence of [3H]-thymidine in the mutant ...
simultaneous detection of four food borne bacterial pathogens by
... concern in establishment of Multiplex PCR protocols. The primers used in this study were tested for their specificities. The sensitivity of the detection depends on the condition of the PCR reaction such as, primer annealing temperature, primer concentration, Mg2+ concentration, extension time and c ...
... concern in establishment of Multiplex PCR protocols. The primers used in this study were tested for their specificities. The sensitivity of the detection depends on the condition of the PCR reaction such as, primer annealing temperature, primer concentration, Mg2+ concentration, extension time and c ...
Lesson Plans Teacher: Robinson Dates: 2/6
... I can describe the concepts and principles within Mendelian Genetics, and solve for simple genetic problems, sex linked problems, genetic diseases in both Punnett’s square form and pedigree form. Use a Punnetts Square to solve the problems on the board. “Solve in Reverse” activity. If given one pare ...
... I can describe the concepts and principles within Mendelian Genetics, and solve for simple genetic problems, sex linked problems, genetic diseases in both Punnett’s square form and pedigree form. Use a Punnetts Square to solve the problems on the board. “Solve in Reverse” activity. If given one pare ...
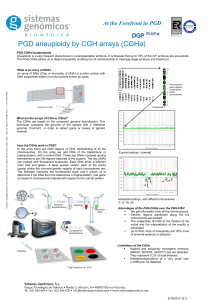
At the Forefront in PGD
... provide information of the rest of chromosomes. Combined chromosomal PGD is based on CGH arrays technology. It allows to identify the altered embryos (unbalanced) in relation to the translocation/inversion and it also allows us to study aneuploidy for 24 chromosomes, simultaniously and in the same c ...
... provide information of the rest of chromosomes. Combined chromosomal PGD is based on CGH arrays technology. It allows to identify the altered embryos (unbalanced) in relation to the translocation/inversion and it also allows us to study aneuploidy for 24 chromosomes, simultaniously and in the same c ...
Genotyping BoLA-DRB3 alleles in Brazilian Dairy Gir cattle (Bos
... studies, genotyping was carried out using polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism of the amplified fragments (PCR-RFLP) for assignment of alleles. This methodology cannot accurately determine differences between all current alleles, and this may have led to the differe ...
... studies, genotyping was carried out using polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism of the amplified fragments (PCR-RFLP) for assignment of alleles. This methodology cannot accurately determine differences between all current alleles, and this may have led to the differe ...
12) Inheritance, genes and chromosomes • 13) DNA
... DNA polymerases make mistakes in replication, and DNA can be damaged in living cells. Cells have three repair mechanisms: • Proofreading (error rate 10-4 • Mismatch repair • Excision repair ...
... DNA polymerases make mistakes in replication, and DNA can be damaged in living cells. Cells have three repair mechanisms: • Proofreading (error rate 10-4 • Mismatch repair • Excision repair ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.