Testicular Cancers - UCSF | Department of Medicine
... o Intermediate: testicular or RP primary, nonpulmonary visceral mets, intermediate lab values • Both -> Poor: mediastinal primary site, nonpulmonary visceral mets, AFP>10,000, B hCG >50,000, LDH >10X upper normal • 5 year survival: 91% good, 79% intermediate, 48% poor prognosis Extragonal GCTs • Mid ...
... o Intermediate: testicular or RP primary, nonpulmonary visceral mets, intermediate lab values • Both -> Poor: mediastinal primary site, nonpulmonary visceral mets, AFP>10,000, B hCG >50,000, LDH >10X upper normal • 5 year survival: 91% good, 79% intermediate, 48% poor prognosis Extragonal GCTs • Mid ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... c) Cristae membrane d) Stroma 11. At the end of Glycolysis, the original glucose molecule has been broken down into _____________________ molecules. a) 2 glyceraldehyde – 3 - phosphate b) 3 pyruvate c) 2 phosphoenol pyruvate d) 2 pyruvate 12. The transformation of fumarate into malate requires the u ...
... c) Cristae membrane d) Stroma 11. At the end of Glycolysis, the original glucose molecule has been broken down into _____________________ molecules. a) 2 glyceraldehyde – 3 - phosphate b) 3 pyruvate c) 2 phosphoenol pyruvate d) 2 pyruvate 12. The transformation of fumarate into malate requires the u ...
Cell Respiration ch. 9
... 2 pyruvate molecules Energy investment phase: cell uses ATP to phosphorylate fuel Energy payoff phase: ATP is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation and NAD+ is reduced to NADH by food oxidation Net energy yield per glucose molecule: 2 ATP plus 2 NADH; no CO2 is released; occurs aerobically or ...
... 2 pyruvate molecules Energy investment phase: cell uses ATP to phosphorylate fuel Energy payoff phase: ATP is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation and NAD+ is reduced to NADH by food oxidation Net energy yield per glucose molecule: 2 ATP plus 2 NADH; no CO2 is released; occurs aerobically or ...
Document
... Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) is an important cofactor of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, or PDC a critical enzyme in glucose metabolism. Thiamine is neither synthesized nor stored in good amounts by most vertebrates. It is required in the diets of most vertebrates. Thiamine deficiency ultimately cau ...
... Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) is an important cofactor of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, or PDC a critical enzyme in glucose metabolism. Thiamine is neither synthesized nor stored in good amounts by most vertebrates. It is required in the diets of most vertebrates. Thiamine deficiency ultimately cau ...
The Aerobic Fate of Pyruvate
... I could tell that some of you were not impressed by the mere 2 ATPs produced per glucose by glycolysis. The 2 ATP’s produced are only a small fraction of the potential energy available from glucose. Under anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potentia ...
... I could tell that some of you were not impressed by the mere 2 ATPs produced per glucose by glycolysis. The 2 ATP’s produced are only a small fraction of the potential energy available from glucose. Under anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potentia ...
fates of pyruvate
... 1)alcohol fermentation – pyruvate converted to ethyl alcohol 2)lactic acid fermentation - pyruvate converted to lactic acid (cheese, yogurt) - Aerobic conditions: Pyruvate enter the mitochondria where it is completely oxidized Pyruvate -> enzyme -> acetyl group + CO2 + NADH ...
... 1)alcohol fermentation – pyruvate converted to ethyl alcohol 2)lactic acid fermentation - pyruvate converted to lactic acid (cheese, yogurt) - Aerobic conditions: Pyruvate enter the mitochondria where it is completely oxidized Pyruvate -> enzyme -> acetyl group + CO2 + NADH ...
Oxidative degradation of glucose File
... Glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, chemical energy in the form of ATP is produced, and NADH- reduced coenzymes are produced. This metabolic pathway takes place in almost all cells. All of the enzymes of the glycolysis pathway are found in the extramitochondrial soluble fraction of ...
... Glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, chemical energy in the form of ATP is produced, and NADH- reduced coenzymes are produced. This metabolic pathway takes place in almost all cells. All of the enzymes of the glycolysis pathway are found in the extramitochondrial soluble fraction of ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 12 Notes
... Succinate dehydrogenase- uses FAD and generates FADH2. This enzyme is not in matrix but in inner mitochondrial membrane and hands FADH2 directly to the electron transport ...
... Succinate dehydrogenase- uses FAD and generates FADH2. This enzyme is not in matrix but in inner mitochondrial membrane and hands FADH2 directly to the electron transport ...
Citric Acid cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid cycle or Krebs Cycle
... Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) is an important cofactor of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, or PDC a critical enzyme in glucose metabolism. Thiamine is neither synthesized nor stored in good amounts by most vertebrates. It is required in the diets of most vertebrates. Thiamine deficiency ultimate ...
... Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) is an important cofactor of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, or PDC a critical enzyme in glucose metabolism. Thiamine is neither synthesized nor stored in good amounts by most vertebrates. It is required in the diets of most vertebrates. Thiamine deficiency ultimate ...
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM - UNAIR | E
... respiratory chain to oxygen is prevented - Pyruvate is reduced by the NADH to lactate, by Lactate dehidrogenase enzyme Lactate dehydrogenase ...
... respiratory chain to oxygen is prevented - Pyruvate is reduced by the NADH to lactate, by Lactate dehidrogenase enzyme Lactate dehydrogenase ...
Quiz - Columbus Labs
... LDH regenerates NAD+ from NADH converting pyruvate to lactate so glycolysis can continue. The lactate produced is released into the blood. The muscle LDH isozyme (A4) works best in the NAD+-regenerating direction. Heart tissue is aerobic and uses lactate as a fuel, converting it to pyruvate via LDH ...
... LDH regenerates NAD+ from NADH converting pyruvate to lactate so glycolysis can continue. The lactate produced is released into the blood. The muscle LDH isozyme (A4) works best in the NAD+-regenerating direction. Heart tissue is aerobic and uses lactate as a fuel, converting it to pyruvate via LDH ...
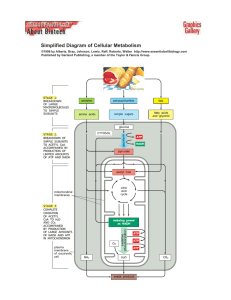
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
PowerPoint - 2014 Science Interns
... cooled before enzymes that break down sugars into lactic acid can be added. If A acidocaldarius is used, the liquid from the acid pretreatment will not have to be cooled or neutralized as extensively and the bacteria will break down the sugars directly into lactic acid, cutting out intermediate step ...
... cooled before enzymes that break down sugars into lactic acid can be added. If A acidocaldarius is used, the liquid from the acid pretreatment will not have to be cooled or neutralized as extensively and the bacteria will break down the sugars directly into lactic acid, cutting out intermediate step ...
carbohydrate metabolism
... NET= +9-2= 7ATPs, when 1 glucose is oxidized up to pyruvate *this is calculated as 2.5ATP per NADH ...
... NET= +9-2= 7ATPs, when 1 glucose is oxidized up to pyruvate *this is calculated as 2.5ATP per NADH ...
Student notes in ppt
... Two Major Roles of Glucokinase Role in liver cells When blood glucose levels are high, both hexokinase I and glucokinase are active in liver cells, whereas, other tissues only have hexokinase 1 and their ability to take up glucose after a meal is unchanged. Since phosphorylation traps glucose insid ...
... Two Major Roles of Glucokinase Role in liver cells When blood glucose levels are high, both hexokinase I and glucokinase are active in liver cells, whereas, other tissues only have hexokinase 1 and their ability to take up glucose after a meal is unchanged. Since phosphorylation traps glucose insid ...
The Citric acid cycle - University of Houston
... Why such a complex set of enzymes? 1 Enzymatic reactions rates are limited by diffusion, with shorter distance between subunits a enzyme can almost direct the substrate from one subunit (catalytic site) to another. 2. Channeling metabolic intermediates between ...
... Why such a complex set of enzymes? 1 Enzymatic reactions rates are limited by diffusion, with shorter distance between subunits a enzyme can almost direct the substrate from one subunit (catalytic site) to another. 2. Channeling metabolic intermediates between ...
Enzymes of Clinical Significance
... Lactate + NAD+ ---LD (pH 8.3-8.9) Pyruvate + NADH + H+ (Increased ABS at 340 nm) ...
... Lactate + NAD+ ---LD (pH 8.3-8.9) Pyruvate + NADH + H+ (Increased ABS at 340 nm) ...
Lecture 26 - Glycolysis 2
... Two Major Roles of Glucokinase Role in liver cells When blood glucose levels are high, both hexokinase I and glucokinase are active in liver cells, whereas, other tissues only have hexokinase 1 and their ability to take up glucose after a meal is unchanged. Since phosphorylation traps glucose insid ...
... Two Major Roles of Glucokinase Role in liver cells When blood glucose levels are high, both hexokinase I and glucokinase are active in liver cells, whereas, other tissues only have hexokinase 1 and their ability to take up glucose after a meal is unchanged. Since phosphorylation traps glucose insid ...
Slide 1
... Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from glucogenic precursors which are not of carbohydrate origin (gluconeogenic precursors) It occurs during prolonged fasting to synthesize glucose for tissues requiring continuous supply of glucose as a source of energy: Brain, RBCs, Kidney medulla, Lens, ...
... Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from glucogenic precursors which are not of carbohydrate origin (gluconeogenic precursors) It occurs during prolonged fasting to synthesize glucose for tissues requiring continuous supply of glucose as a source of energy: Brain, RBCs, Kidney medulla, Lens, ...
Enzymes - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... not increase proportionately Zero Order kinetics (approaching Vmax) Enzyme is fully saturated with substrate ...
... not increase proportionately Zero Order kinetics (approaching Vmax) Enzyme is fully saturated with substrate ...
Met1 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... B) lipid metabolism disorders - carnitine palmitoyl transferase deficiencies see p. 750 >> C) purine metabolism disorders - myoadenylate deaminase deficiency see below >> D) mitochondrial myopathies - succinate dehydrogenase deficiency exercise intolerance in childhood; exertion-induced symptoms ( ...
... B) lipid metabolism disorders - carnitine palmitoyl transferase deficiencies see p. 750 >> C) purine metabolism disorders - myoadenylate deaminase deficiency see below >> D) mitochondrial myopathies - succinate dehydrogenase deficiency exercise intolerance in childhood; exertion-induced symptoms ( ...
Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) - LSU School of Medicine
... The Krebs Cycle Citric Acid Cycle; The TCA Cycle • Pyruvate (actually the acetyl group) from glycolysis is degraded to CO2 – The acetyl group is formed in stage II of metabolism from carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism ...
... The Krebs Cycle Citric Acid Cycle; The TCA Cycle • Pyruvate (actually the acetyl group) from glycolysis is degraded to CO2 – The acetyl group is formed in stage II of metabolism from carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism ...
Cellular Respiration
... NADH and FADH2 carry hydrogen atoms and electrons to a series of compounds in the mitochondria that pump H+ ions into the intermembrane space. As H+ ions move through channels down the concentration gradient, ATP is produced. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the ETC. Without it, electrons ca ...
... NADH and FADH2 carry hydrogen atoms and electrons to a series of compounds in the mitochondria that pump H+ ions into the intermembrane space. As H+ ions move through channels down the concentration gradient, ATP is produced. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the ETC. Without it, electrons ca ...
Problem Set 3 (Due February 4th) 1. In 1896, Christiaan Eijkman
... Please read the attached paper and discuss how this E. coli enzyme is regulated and how this mechanism relates to the ‘dietary’ carbon source. E. coli Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH) can be inhibited by the activity of another enzyme, IDH kinase/phosphorylase (gene aceK). This enzyme, which is part o ...
... Please read the attached paper and discuss how this E. coli enzyme is regulated and how this mechanism relates to the ‘dietary’ carbon source. E. coli Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH) can be inhibited by the activity of another enzyme, IDH kinase/phosphorylase (gene aceK). This enzyme, which is part o ...
Lactate dehydrogenase

A lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells (animals, plants, and prokaryotes). LDH catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate and back, as it converts NADH to NAD+ and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another.LDH exist in four distinct enzyme classes. This article is about the common NAD(P)-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase. Other LDHs act on D-lactate and/or are dependent on cytochrome c: D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)) and L-lactate (L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)). LDH has been of medical significance because it is found extensively in body tissues, such as blood cells and heart muscle. Because it is released during tissue damage, it is a marker of common injuries and disease such as heart failure.