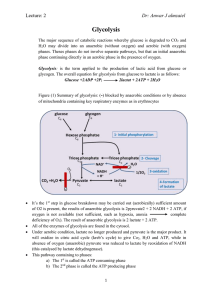
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
... In the normal fed state PEPCK mRNA in the liver is rapidly turned over. This is typical for a sequence which is regulated at the level of gene expression. Why? In the fed state insulin is released by the pancreas and this suppresses transcription of PEPCK, the mRNA is unstable so very little PEPCK p ...
... In the normal fed state PEPCK mRNA in the liver is rapidly turned over. This is typical for a sequence which is regulated at the level of gene expression. Why? In the fed state insulin is released by the pancreas and this suppresses transcription of PEPCK, the mRNA is unstable so very little PEPCK p ...
Cellular Respiration
... in the ABSENCE of oxygen, NADH generated from glycolysis passes its H atoms to either acetaldehyde to produce ethanol or to pyruvate to produce lactic acid. Products of fermentation include: – wine – beer – soy sauce – bread – carbonated beverages – cheese ...
... in the ABSENCE of oxygen, NADH generated from glycolysis passes its H atoms to either acetaldehyde to produce ethanol or to pyruvate to produce lactic acid. Products of fermentation include: – wine – beer – soy sauce – bread – carbonated beverages – cheese ...
Lecture 26
... Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from these non-carbohydrate precursors. Most precursors must enter the Krebs cycle at some point to be ...
... Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from these non-carbohydrate precursors. Most precursors must enter the Krebs cycle at some point to be ...
TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE
... carbon dioxide, reduced NAD, reduced FAD and GTP • There are negative and positive controls for the TCA cycle ...
... carbon dioxide, reduced NAD, reduced FAD and GTP • There are negative and positive controls for the TCA cycle ...
BCH 3033 General Biochemistry EXAM 5 Name: Fall, 2012
... 9.Which of the following is not true of the reaction catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex? a. Biotin participates in the decarboxylation. b. Both NAD+ and a flavin nucleotide act as electron carriers. c The reaction occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. d.The substrate is held by the lipoyl ...
... 9.Which of the following is not true of the reaction catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex? a. Biotin participates in the decarboxylation. b. Both NAD+ and a flavin nucleotide act as electron carriers. c The reaction occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. d.The substrate is held by the lipoyl ...
LIP Lactate inflection point
... acid concentration increases • Beyond the LIP the athlete has to stop or reduce muscle effort • Trained athletes can and aim to increase their tolerance to lactic acid accumulation • Scientific testing in labs (eg: AIS) is the best method, but a rough estimates describes it as ...
... acid concentration increases • Beyond the LIP the athlete has to stop or reduce muscle effort • Trained athletes can and aim to increase their tolerance to lactic acid accumulation • Scientific testing in labs (eg: AIS) is the best method, but a rough estimates describes it as ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... +FAD+GDP+Pi+2H2O→2CO2+3NADH+FADH2+G TP+2H++CoA • One Acetyl-CoA through the cycle produces two CO2, one ATP, four reduced coenzymes • Two H2Os are used as substrates • Absolutely depends on O2 ...
... +FAD+GDP+Pi+2H2O→2CO2+3NADH+FADH2+G TP+2H++CoA • One Acetyl-CoA through the cycle produces two CO2, one ATP, four reduced coenzymes • Two H2Os are used as substrates • Absolutely depends on O2 ...
Test 1
... F26BP gets dephosphorylated so [F26BP]9 As [F26BP]9, PFK-1 activity9,& FBPase-1activity 8 so glycolysis 9 and neogenesis8 so sugar build up in liver cell Insulin 8 A signal that the blood sugar level is too high Insulin binding to a cell surface receptor starts a series of phophorylation events that ...
... F26BP gets dephosphorylated so [F26BP]9 As [F26BP]9, PFK-1 activity9,& FBPase-1activity 8 so glycolysis 9 and neogenesis8 so sugar build up in liver cell Insulin 8 A signal that the blood sugar level is too high Insulin binding to a cell surface receptor starts a series of phophorylation events that ...
Dr: Anwar J almzaiel Glycolysis
... Glycolysis is not only the principle route for glucose metabolism, but it also provides the main pathway for the metabolism of fructose and galactose derived from the diet. The ability of glycolysis to provide energy in the absence of oxygen allows muscle contraction in which oxygen supply insuffici ...
... Glycolysis is not only the principle route for glucose metabolism, but it also provides the main pathway for the metabolism of fructose and galactose derived from the diet. The ability of glycolysis to provide energy in the absence of oxygen allows muscle contraction in which oxygen supply insuffici ...
Study Guide - PEP 535 Exam#1
... What is the source of the increasing concentration of Pi during intense exercise? Glycogenolysis and Glycolysis Is phosphorylase the only enzyme needed during glycogenolysis? If not, why? Explain the multifaceted biochemical regulation of glycogenolysis. Why is the regulation of glycogenolysis impor ...
... What is the source of the increasing concentration of Pi during intense exercise? Glycogenolysis and Glycolysis Is phosphorylase the only enzyme needed during glycogenolysis? If not, why? Explain the multifaceted biochemical regulation of glycogenolysis. Why is the regulation of glycogenolysis impor ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration STAGE 1: Glycolysis
... 1. Bacteria that live in oxygen-free places ...
... 1. Bacteria that live in oxygen-free places ...
Fermentation - Peoria Public Schools
... respiration to produce energy. However when there is an absence of oxygen, an organism will go through a process called fermentation. ...
... respiration to produce energy. However when there is an absence of oxygen, an organism will go through a process called fermentation. ...
Fermentation
... away from a lion ) will not use anaerobic respiration but will start fermentation ...
... away from a lion ) will not use anaerobic respiration but will start fermentation ...
Patrick, An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e Chapter 3
... The Lineweaver-Burke plot has 1/initial rate on the y-axis and 1/substrate concentration on the x-axis. This should give a straight line having an intercept of 0.00400 on the y-axis and a slope of 0.00155 Therefore, the maximum rate of reaction = 1/intercept = 250.2 mol dm-3 s-1 KM = slope x (maximu ...
... The Lineweaver-Burke plot has 1/initial rate on the y-axis and 1/substrate concentration on the x-axis. This should give a straight line having an intercept of 0.00400 on the y-axis and a slope of 0.00155 Therefore, the maximum rate of reaction = 1/intercept = 250.2 mol dm-3 s-1 KM = slope x (maximu ...
Energy Systems
... - high concentrations of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) - flushed out of body ...
... - high concentrations of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) - flushed out of body ...
ch3b_SP13x
... – Yield raw materials (amino acids, etc) and chemical energy (NADH, ATP) – Convergent: diverse starting materials broken down to conserved set of ...
... – Yield raw materials (amino acids, etc) and chemical energy (NADH, ATP) – Convergent: diverse starting materials broken down to conserved set of ...
Document
... pyruvate continues in the formation of Acetyl CoA and NADH that follows into the Krebs cycle and ETC ...
... pyruvate continues in the formation of Acetyl CoA and NADH that follows into the Krebs cycle and ETC ...
Why does lactic acid build up in muscles?
... pyruvate through a series of steps. When the body has plenty of oxygen, pyruvate is shuttled to an aerobic pathway to be further broken down for more energy. But when oxygen is limited, the body temporarily converts pyruvate into a substance called lactate, which allows glucose breakdown--and thus e ...
... pyruvate through a series of steps. When the body has plenty of oxygen, pyruvate is shuttled to an aerobic pathway to be further broken down for more energy. But when oxygen is limited, the body temporarily converts pyruvate into a substance called lactate, which allows glucose breakdown--and thus e ...
Slide 1
... and anaerobic (B) glycolysis. Glucose is phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate and subsequently to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate via fructose-6-phosphate and phosphofructokinase 1, the main regulatory enzymes in brain glycolysis. NADH is produced in the conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bi ...
... and anaerobic (B) glycolysis. Glucose is phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate and subsequently to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate via fructose-6-phosphate and phosphofructokinase 1, the main regulatory enzymes in brain glycolysis. NADH is produced in the conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bi ...
Computer Lab - Advanced Chimera
... Two structures of LF, together, are able to help biochemists figure out how this enzyme works. In the same chimera window, load 1JKY and 1J7N. Explore the structure of each of these. You’ll notice that one has the substrate peptide bound while the other does not. What does the other structure have i ...
... Two structures of LF, together, are able to help biochemists figure out how this enzyme works. In the same chimera window, load 1JKY and 1J7N. Explore the structure of each of these. You’ll notice that one has the substrate peptide bound while the other does not. What does the other structure have i ...
The ATP-PCr energy system can operate with or without oxygen but
... system can sustain all-out exercise for about 10 seconds and during this time, the potential rate for power output is at its greatest. If activity continues beyond this initial period, the body must rely on another energy system to produce ATP ...
... system can sustain all-out exercise for about 10 seconds and during this time, the potential rate for power output is at its greatest. If activity continues beyond this initial period, the body must rely on another energy system to produce ATP ...
Citric Acid Cycle Overview
... small increase in [pyruvate] an a large increase in [lactate] so that the [lactate]/[pyruvate] ratio is many times larger than normal. Explain. ...
... small increase in [pyruvate] an a large increase in [lactate] so that the [lactate]/[pyruvate] ratio is many times larger than normal. Explain. ...
lect11
... ketone bodies are synthesised from acetyl-CoA they represent a means of using the energy available in fatty acids for tissues that may not be able to use fatty acids themselves ...
... ketone bodies are synthesised from acetyl-CoA they represent a means of using the energy available in fatty acids for tissues that may not be able to use fatty acids themselves ...
Enzyme_Classificn
... ENZYME CLASSIFICATION ANSWERS TO IN-CLASS EXERCISE (1) TRANSFERASE (HEXOKINASE) (2) OXIDOREDUCTASE (ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE) (3) HYDROLASE (ATPase) (4) LYASE (PYRUVATE DECARBOXYLASE) (5) LIGASE (PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE) (6) ISOMERASE (MALEATE ISOMERASE) (7) HYDROLASE (PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVATE ...
... ENZYME CLASSIFICATION ANSWERS TO IN-CLASS EXERCISE (1) TRANSFERASE (HEXOKINASE) (2) OXIDOREDUCTASE (ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE) (3) HYDROLASE (ATPase) (4) LYASE (PYRUVATE DECARBOXYLASE) (5) LIGASE (PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE) (6) ISOMERASE (MALEATE ISOMERASE) (7) HYDROLASE (PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVATE ...
Lactate dehydrogenase

A lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells (animals, plants, and prokaryotes). LDH catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate and back, as it converts NADH to NAD+ and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another.LDH exist in four distinct enzyme classes. This article is about the common NAD(P)-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase. Other LDHs act on D-lactate and/or are dependent on cytochrome c: D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)) and L-lactate (L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)). LDH has been of medical significance because it is found extensively in body tissues, such as blood cells and heart muscle. Because it is released during tissue damage, it is a marker of common injuries and disease such as heart failure.