+ 2
... Question: Is fermentation a catabolic process or is it an anabolic process? Fermentation may be considered as two metabolic pathways, glycolysis and the extending reactions. It may also be considered as a single metabolic pathway from glucose to the final fermentation products. ...
... Question: Is fermentation a catabolic process or is it an anabolic process? Fermentation may be considered as two metabolic pathways, glycolysis and the extending reactions. It may also be considered as a single metabolic pathway from glucose to the final fermentation products. ...
7.2 Glycolysis
... Glycolysis occurs with or without oxygen (during both aerobic and anaerobic respiration) Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell During glycolysis glucose is split in two to form 2 pyruvate molecules ...
... Glycolysis occurs with or without oxygen (during both aerobic and anaerobic respiration) Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell During glycolysis glucose is split in two to form 2 pyruvate molecules ...
classification of enzymes
... act as acids or bases. In “specific acid or base catalysis” rate of reaction is sensitive to changes in protons , but is independent of conc of other acids or bases present in the solution or at active site. In “general acid or base catalysis” reaction rates are sensitive to ...
... act as acids or bases. In “specific acid or base catalysis” rate of reaction is sensitive to changes in protons , but is independent of conc of other acids or bases present in the solution or at active site. In “general acid or base catalysis” reaction rates are sensitive to ...
Lecture_5_Control_of_glycolysis
... Exercise training also stimulates HIF-1, which enhances the ability to generate ATP anaerobically and stimulates new blood vessel growth. ...
... Exercise training also stimulates HIF-1, which enhances the ability to generate ATP anaerobically and stimulates new blood vessel growth. ...
Document
... and that makes some ATP (without needing Kreb’s and ETC) • This decreases pH and reduces cells’ ability to ...
... and that makes some ATP (without needing Kreb’s and ETC) • This decreases pH and reduces cells’ ability to ...
Lecture 15 (Parker) - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... ATP, instead it removes electrons from Acetyl CoA forming NADH and FADH2. These electron carriers yield nine ATP molecules when oxidized by oxidative phosphorylation. Electrons released in the re-oxidation of NADH and FADH2 flow through a series of membrane proteins to generate a proton gradient acr ...
... ATP, instead it removes electrons from Acetyl CoA forming NADH and FADH2. These electron carriers yield nine ATP molecules when oxidized by oxidative phosphorylation. Electrons released in the re-oxidation of NADH and FADH2 flow through a series of membrane proteins to generate a proton gradient acr ...
Hexokinase
... Glycolysis is an anaerobic pathway—it does not require oxygen 1.The TCA (tricarboxylic acid) cycle is aerobic. When oxygen is abundant, cells prefer to combine these pathways in aerobic metabolism 2.When oxygen is limiting, cells adapt to carry out more glycolysis ...
... Glycolysis is an anaerobic pathway—it does not require oxygen 1.The TCA (tricarboxylic acid) cycle is aerobic. When oxygen is abundant, cells prefer to combine these pathways in aerobic metabolism 2.When oxygen is limiting, cells adapt to carry out more glycolysis ...
Fermentation
... substrate, glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and ATP production will all come to a stop. The NAD+ produced by the oxidation of pyruvate during fermentation rapidly cycles back to participate again in glycolysis. In this way, cells can still perform glycolysis, and gain the ATP it produces, even in the ab ...
... substrate, glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and ATP production will all come to a stop. The NAD+ produced by the oxidation of pyruvate during fermentation rapidly cycles back to participate again in glycolysis. In this way, cells can still perform glycolysis, and gain the ATP it produces, even in the ab ...
Alcohol Metabolism
... amount/unit time) EtOH oxidation requires NAD+ and its availability: o is rate-limiting factor (limits EtOH metabolism to about 8g/h) o leads to competition between EtOH and other metabolic substrates for available NAD+, which may be factor in EtOH-induced liver damage accumulation of acetaldehy ...
... amount/unit time) EtOH oxidation requires NAD+ and its availability: o is rate-limiting factor (limits EtOH metabolism to about 8g/h) o leads to competition between EtOH and other metabolic substrates for available NAD+, which may be factor in EtOH-induced liver damage accumulation of acetaldehy ...
Classification of Enzymes - Lectures For UG-5
... “a” is the class, “b” is the subclass, “c” is the subsubclass, and “d” is the sub-sub-subclass. The “b” and “c” digits describe the reaction, while the “d” digit is used to distinguish between different enzymes of the same function based on the actual substrate in the reaction. • Example: for Alcoho ...
... “a” is the class, “b” is the subclass, “c” is the subsubclass, and “d” is the sub-sub-subclass. The “b” and “c” digits describe the reaction, while the “d” digit is used to distinguish between different enzymes of the same function based on the actual substrate in the reaction. • Example: for Alcoho ...
Analysis of Cell Ageing
... FeCl3. The Guthrie test uses a bacterial inhibition. Now we use electrospray tandem mass spectrometry which tests for many enzyme deficiencies with small amount of blood with high accuracy and speed. Q1 – PKU is a autosomal recessive condition. Q2 – Most common enzyme deficiency is phenylalanine hyd ...
... FeCl3. The Guthrie test uses a bacterial inhibition. Now we use electrospray tandem mass spectrometry which tests for many enzyme deficiencies with small amount of blood with high accuracy and speed. Q1 – PKU is a autosomal recessive condition. Q2 – Most common enzyme deficiency is phenylalanine hyd ...
SG 7,8,9,10
... List the energy transforming pathways of carbohydrate metabolism and their interconnections. Describe the 2 stages of glycolysis step by step, include enzymes, products, type of reaction, net energy production. Describe the 3 fates of pyruvate in detail, reactions, control, enzymes, importance of pa ...
... List the energy transforming pathways of carbohydrate metabolism and their interconnections. Describe the 2 stages of glycolysis step by step, include enzymes, products, type of reaction, net energy production. Describe the 3 fates of pyruvate in detail, reactions, control, enzymes, importance of pa ...
Pre AP Bio Nov 8 2016
... and that makes some ATP (without needing Kreb’s and ETC) • This decreases pH and reduces cells’ ability to ...
... and that makes some ATP (without needing Kreb’s and ETC) • This decreases pH and reduces cells’ ability to ...
ch 9 Cellular_Respiration
... coenzyme that transports electrons from glucose to the electron transport chain to make ATP • NAD+ is reduced (electrons are added) to NADH + H+ using the enzyme dehydrogenase (2 electrons and 2 protons, but one proton is released) ...
... coenzyme that transports electrons from glucose to the electron transport chain to make ATP • NAD+ is reduced (electrons are added) to NADH + H+ using the enzyme dehydrogenase (2 electrons and 2 protons, but one proton is released) ...
Step 1: Hexokinase
... • Reading for Friday, Feb. 23 on integration of metabolism: 258-262 • Reading for Monday, Feb. 26 on respiration: 265-271 • Homework due Monday, Feb. 26: Problem 9-5 – Convert all concentrations to M, and your answer will be in M. – Don’t worry about [H+] – use equations as given in problem. – Deter ...
... • Reading for Friday, Feb. 23 on integration of metabolism: 258-262 • Reading for Monday, Feb. 26 on respiration: 265-271 • Homework due Monday, Feb. 26: Problem 9-5 – Convert all concentrations to M, and your answer will be in M. – Don’t worry about [H+] – use equations as given in problem. – Deter ...
Chem331 Krebs Cycle
... Think of why this is a cycle vs. pathway - not because it is written that way. Oxaloacetate - only a small amount is needed - catalytic role Anapleurotic - “filling up” cycle can be used as entry and exit for production of other essential metabolites The TCA ...
... Think of why this is a cycle vs. pathway - not because it is written that way. Oxaloacetate - only a small amount is needed - catalytic role Anapleurotic - “filling up” cycle can be used as entry and exit for production of other essential metabolites The TCA ...
Nucleic Acids
... What you need to know! • The difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. ...
... What you need to know! • The difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. ...
Gluconeogenesis
... - Include all intermediates of glycolysis and citric acid cycle, glycerol, lactate and the α-keto acids obtained from deamination of glucogenic amino acids. -Glycerol: obtained from the hydrolysis of the triglycerides in adipose tissue, travels to liver which is phosphorylated and metabolized - Lact ...
... - Include all intermediates of glycolysis and citric acid cycle, glycerol, lactate and the α-keto acids obtained from deamination of glucogenic amino acids. -Glycerol: obtained from the hydrolysis of the triglycerides in adipose tissue, travels to liver which is phosphorylated and metabolized - Lact ...
Biochem03 - Amit Kessel Ph.D
... reaction by negative feedback. D. the inhibitor binds only to the active site and increases the Km. 42. The tricarboxylic acid cycle is initiated by the condensation of acetylCoA and: A. malate. B. citrate. C. pyruvate. D. oxaloacetate. E. HCO3-. 43. Gluconeogenesis: A. is favored when insulin conce ...
... reaction by negative feedback. D. the inhibitor binds only to the active site and increases the Km. 42. The tricarboxylic acid cycle is initiated by the condensation of acetylCoA and: A. malate. B. citrate. C. pyruvate. D. oxaloacetate. E. HCO3-. 43. Gluconeogenesis: A. is favored when insulin conce ...
Citric Acid Cycle Overview
... Problem 55 • Animals lack a glyoxylate pathway and cannot convert fats to carbohydrates. However, if an animal is fed a fatty acid with all its carbons labelled by C‐14, some of the labeled carbons later appear in glucose. How is this possible? ...
... Problem 55 • Animals lack a glyoxylate pathway and cannot convert fats to carbohydrates. However, if an animal is fed a fatty acid with all its carbons labelled by C‐14, some of the labeled carbons later appear in glucose. How is this possible? ...
untitled file - Blue Earth Area Schools
... there is no O2 to be the final electron acceptor • NADH donates the high energy electron back to pyruvate to form either lactic acid or ethanol and CO2 • Then NAD+ is recycled and glycolysis can proceed ...
... there is no O2 to be the final electron acceptor • NADH donates the high energy electron back to pyruvate to form either lactic acid or ethanol and CO2 • Then NAD+ is recycled and glycolysis can proceed ...
Islamic University of Gaza Advanced Biochemistry Faculty of
... These three reactions of the cycle, citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase operate with large negative free energy changes under the concentrations of products and reactants in the matrix of the mitochondria. Because the citric acid cycle is linked to oxygen con ...
... These three reactions of the cycle, citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase operate with large negative free energy changes under the concentrations of products and reactants in the matrix of the mitochondria. Because the citric acid cycle is linked to oxygen con ...
Hereditary mitochondrial diseases disorders of mitochondrial fatty
... A defect of the mitochondrial respiratory chain should be considered in patients presenting with an unexplained combination of neuromuscular and/or nonneuromuscular symptoms, with a progressive course, involving seemingly unrelated organs or tissues. ...
... A defect of the mitochondrial respiratory chain should be considered in patients presenting with an unexplained combination of neuromuscular and/or nonneuromuscular symptoms, with a progressive course, involving seemingly unrelated organs or tissues. ...
Citric acid Cycle Remake - Study in Universal Science College
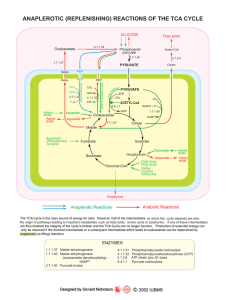
... If the CAC intermediate are used for synthetic reactions, they are replenished by anaplerotic reactions in the cells (indicated by red colours). ...
... If the CAC intermediate are used for synthetic reactions, they are replenished by anaplerotic reactions in the cells (indicated by red colours). ...
Lactate dehydrogenase

A lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells (animals, plants, and prokaryotes). LDH catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate and back, as it converts NADH to NAD+ and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another.LDH exist in four distinct enzyme classes. This article is about the common NAD(P)-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase. Other LDHs act on D-lactate and/or are dependent on cytochrome c: D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)) and L-lactate (L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)). LDH has been of medical significance because it is found extensively in body tissues, such as blood cells and heart muscle. Because it is released during tissue damage, it is a marker of common injuries and disease such as heart failure.