A Mesoscale Tour of the Pacific Northwest
... being driven by latent heating in the ascending air columns. • Such heating forces the isobaric surfaces above the storm to rise, resulting in mass outflow at upper levels and the diminution of pressure at the surface. • Espy did not indicate any circulation around midlatitude cyclones, but noted on ...
... being driven by latent heating in the ascending air columns. • Such heating forces the isobaric surfaces above the storm to rise, resulting in mass outflow at upper levels and the diminution of pressure at the surface. • Espy did not indicate any circulation around midlatitude cyclones, but noted on ...
Section 2 Models in Science
... Figure 3 Supercomputers help scientists create very complex models that predict the results of climate change. To model climate change, researchers use information about current and past land and ocean-water temperatures around Earth. They also use information about weather patterns, ocean currents, ...
... Figure 3 Supercomputers help scientists create very complex models that predict the results of climate change. To model climate change, researchers use information about current and past land and ocean-water temperatures around Earth. They also use information about weather patterns, ocean currents, ...
Meteorologist - Science with Ms. C
... • When they are darker, they may signal rain or thunderstorms, as they develop into cumulonimbus clouds (thunderheads). ...
... • When they are darker, they may signal rain or thunderstorms, as they develop into cumulonimbus clouds (thunderheads). ...
Storm Risk Mitigation through Improved Prediction and
... Storms have had an increasing social and economic cost over recent years and are likely to be the main cause of loss of life or assets in the UK over the next few decades. The negative societal impacts caused by adverse weather are disproportionately influenced by extremes. Furthermore, with climate ...
... Storms have had an increasing social and economic cost over recent years and are likely to be the main cause of loss of life or assets in the UK over the next few decades. The negative societal impacts caused by adverse weather are disproportionately influenced by extremes. Furthermore, with climate ...
Science Scientific Method - SOEST
... For nearly 2000 Years we have a Big Blank in progress Why? ...
... For nearly 2000 Years we have a Big Blank in progress Why? ...
CHAPTER 11 DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS Learning Objectives
... • The inference engine performs reasoning by using the contents of the knowledge base • During the consultation, the engine examines the rules of the knowledge base one by one. When a rule’s condition is true, the specified action is taken • The process of examining the rules continues until a pass ...
... • The inference engine performs reasoning by using the contents of the knowledge base • During the consultation, the engine examines the rules of the knowledge base one by one. When a rule’s condition is true, the specified action is taken • The process of examining the rules continues until a pass ...
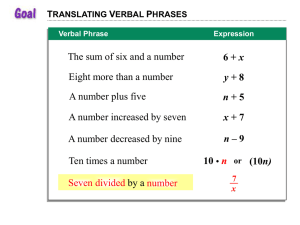
Translating Expressions (1.6)
... Using a Verbal Model JET PILOT A jet pilot is flying from Los Angeles, CA to Chicago, IL at a speed of 500 miles per hour. When the plane is 600 miles from Chicago, an air traffic controller tells the pilot that it will be 2 hours before the plane can get clearance to land. The pilot knows the spee ...
... Using a Verbal Model JET PILOT A jet pilot is flying from Los Angeles, CA to Chicago, IL at a speed of 500 miles per hour. When the plane is 600 miles from Chicago, an air traffic controller tells the pilot that it will be 2 hours before the plane can get clearance to land. The pilot knows the spee ...
The Environmental Apocalypse - Silverhill Institute of Environmental
... LIMITATIONS OF MODELS/SCENARIOS According to the National Centre for Policy Analysis–a non-profit, non-partisan public policy research organization–there are many limitations of the current scientific models including General Circulation Models or Global Climate Models (GCMs), which are used to dete ...
... LIMITATIONS OF MODELS/SCENARIOS According to the National Centre for Policy Analysis–a non-profit, non-partisan public policy research organization–there are many limitations of the current scientific models including General Circulation Models or Global Climate Models (GCMs), which are used to dete ...
Tuesday 26 October, 2010 – by Laurens Bouwer
... evidence that anthropogenic changes in extreme weather is the main driver for the observed trend. A review of the literature shows that the observed loss increase is caused primarily by increasing exposure and value of capital at risk. The PhD thesis of Laurens Bouwer proposes a comprehensive approa ...
... evidence that anthropogenic changes in extreme weather is the main driver for the observed trend. A review of the literature shows that the observed loss increase is caused primarily by increasing exposure and value of capital at risk. The PhD thesis of Laurens Bouwer proposes a comprehensive approa ...
Your Weather Knowledge Study Guide
... Two causes of wind are the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface and differences in air pressure. ...
... Two causes of wind are the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface and differences in air pressure. ...
Слайд 1 - Hydrograph Model
... parameters; the model requires minimum of calibration • To assess the possible effect of climate change on active layer depth the processes-based deterministic models are required. The Hydrograph model may be considered to be one of those models • The stochastic model of Weather was used here to dow ...
... parameters; the model requires minimum of calibration • To assess the possible effect of climate change on active layer depth the processes-based deterministic models are required. The Hydrograph model may be considered to be one of those models • The stochastic model of Weather was used here to dow ...
More knowledge, less certainty
... be devoted to assessing the skill of climate predictions for timescales out to about 30 years. These climate forecasts, which should help guide decision-makers on how to plan for and adapt to change, will no doubt receive much attention. Another chapter will deal with longerterm projections, to 2100 ...
... be devoted to assessing the skill of climate predictions for timescales out to about 30 years. These climate forecasts, which should help guide decision-makers on how to plan for and adapt to change, will no doubt receive much attention. Another chapter will deal with longerterm projections, to 2100 ...
ESSC - Earth and Environmental Systems Institute
... Mech., 2007, and J. Geophys. Res., in press). Model grids usually do not adequately resolve the narrow boundary layer at the grounding line where there is a sharp transition from sheet-like to shelf-like flow. However, accurate grounding-line migration is likely to be essential for the next generati ...
... Mech., 2007, and J. Geophys. Res., in press). Model grids usually do not adequately resolve the narrow boundary layer at the grounding line where there is a sharp transition from sheet-like to shelf-like flow. However, accurate grounding-line migration is likely to be essential for the next generati ...
Andy Modaff, Tony Schneider, Richie Moore, and
... receiving antenna which is then received by a computer. The information received determines the distance of precipitation relative to the location of the receiving antenna. A specific form of radar, called a Doppler radar, utilizes the Doppler effect. The Doppler effect is the change in pitch or fre ...
... receiving antenna which is then received by a computer. The information received determines the distance of precipitation relative to the location of the receiving antenna. A specific form of radar, called a Doppler radar, utilizes the Doppler effect. The Doppler effect is the change in pitch or fre ...
Model
... • Simulations of the climate of the last 1000 years show a larger amplitude in the temperature variability than the proxy reconstructions • The models predict a climate change between 1.4 and 5.8 K. If the uncertainty is taken into account, it might well extend beyond 8 K ...
... • Simulations of the climate of the last 1000 years show a larger amplitude in the temperature variability than the proxy reconstructions • The models predict a climate change between 1.4 and 5.8 K. If the uncertainty is taken into account, it might well extend beyond 8 K ...
Lab 6: Models for MOS Devices
... A more accurate model is the BSIM model used in programs such as SPICE and SPECTRE. The basic BSIM 3 model has 97 parameters but extreme values for the BSIM model parameters (often termed corner models) are often included resulting in a several-fold increase in the total number of parameters. Even t ...
... A more accurate model is the BSIM model used in programs such as SPICE and SPECTRE. The basic BSIM 3 model has 97 parameters but extreme values for the BSIM model parameters (often termed corner models) are often included resulting in a several-fold increase in the total number of parameters. Even t ...
Climate Change - University of Tasmania
... disciplines who can deal with this issue sensibly. • Reduce the emissions of climate change gases. • Facilitate adaptation to changes in weather patterns ...
... disciplines who can deal with this issue sensibly. • Reduce the emissions of climate change gases. • Facilitate adaptation to changes in weather patterns ...
Atmospheric model
An atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, moist processes (clouds and precipitation), heat exchange, soil, vegetation, surface water, the kinematic effects of terrain, and convection. Most atmospheric models are numerical, i.e. they discretize equations of motion. They can predict microscale phenomena such as tornadoes and boundary layer eddies, sub-microscale turbulent flow over buildings, as well as synoptic and global flows. The horizontal domain of a model is either global, covering the entire Earth, or regional (limited-area), covering only part of the Earth. The different types of models run are thermotropic, barotropic, hydrostatic, and nonhydrostatic. Some of the model types make assumptions about the atmosphere which lengthens the time steps used and increases computational speed.Forecasts are computed using mathematical equations for the physics and dynamics of the atmosphere. These equations are nonlinear and are impossible to solve exactly. Therefore, numerical methods obtain approximate solutions. Different models use different solution methods. Global models often use spectral methods for the horizontal dimensions and finite-difference methods for the vertical dimension, while regional models usually use finite-difference methods in all three dimensions. For specific locations, model output statistics use climate information, output from numerical weather prediction, and current surface weather observations to develop statistical relationships which account for model bias and resolution issues.