Climate Change: Is It Becoming A Reality In South Africa?
... At each time-step (5-30 min) the full set of atmospheric equations (momentum, continuity, thermodynamic, moisture) as well as all physical parameterization schemes are solved for each model grid point point. This is done on the world’s strongest supercomputers ...
... At each time-step (5-30 min) the full set of atmospheric equations (momentum, continuity, thermodynamic, moisture) as well as all physical parameterization schemes are solved for each model grid point point. This is done on the world’s strongest supercomputers ...
weather quiz - Travelling across time
... B. Biologists C. 15. Which pressure system brings rain/stormy weather? High pressure A. Low pressure B. 16. __________ is used to photograph and track large scale air movements such as typhoons etc. 17. The process in which liquid water changes into a gas or water vapor Transpiration A. Evaporation ...
... B. Biologists C. 15. Which pressure system brings rain/stormy weather? High pressure A. Low pressure B. 16. __________ is used to photograph and track large scale air movements such as typhoons etc. 17. The process in which liquid water changes into a gas or water vapor Transpiration A. Evaporation ...
20100921144515309-152610
... • For 11 of the 17 atmosphere fully coupled oceanatmosphere runs, use 6-hourly boundary conditions to drive 25km regional climate model for ...
... • For 11 of the 17 atmosphere fully coupled oceanatmosphere runs, use 6-hourly boundary conditions to drive 25km regional climate model for ...
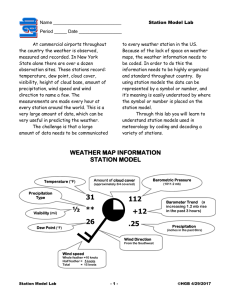
Station Model Lab
... State alone there are over a dozen observation sites. These stations record: temperature, dew point, cloud cover, visibility, height of cloud base, amount of precipitation, wind speed and wind direction to name a few. The measurements are made every hour at every station around the world. This is a ...
... State alone there are over a dozen observation sites. These stations record: temperature, dew point, cloud cover, visibility, height of cloud base, amount of precipitation, wind speed and wind direction to name a few. The measurements are made every hour at every station around the world. This is a ...
Additional Reading Notes (WORD document)
... b. Problem. The model world is not reality. For example, the North American Monsoon, which has previously been mentioned due to its influence on the weather and climate of the southwestern U.S. and happens every year, does not happen in the models. Hard for me to believe that if the model is missing ...
... b. Problem. The model world is not reality. For example, the North American Monsoon, which has previously been mentioned due to its influence on the weather and climate of the southwestern U.S. and happens every year, does not happen in the models. Hard for me to believe that if the model is missing ...
The Earth`s Atmosphere
... an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather occurs. The boundary that divides the troposphere from the stratosphere is called the "tropo ...
... an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather occurs. The boundary that divides the troposphere from the stratosphere is called the "tropo ...
Does the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Threaten our Future?
... 0.54oC since 1881, and we know that equivalent CO2 levels rose by 40% over that period. When the warming trend is analysed it is noted that nearly 70% of the warming occurred in the first half of the record, while the bulk of the greenhouse gas build up clearly occurred in the second half of the rec ...
... 0.54oC since 1881, and we know that equivalent CO2 levels rose by 40% over that period. When the warming trend is analysed it is noted that nearly 70% of the warming occurred in the first half of the record, while the bulk of the greenhouse gas build up clearly occurred in the second half of the rec ...
Providing seamless seasonal to centennial projections for
... with impacts models (and society) for health (food security and water). Climate Services agenda. ...
... with impacts models (and society) for health (food security and water). Climate Services agenda. ...
Lecture 1
... All kinds of tutorials on the web on how to convert units using ‘dimensional analysis’ or ‘factor label’ For example: http://www.ncsu.edu/felder-public/kenny/papers/units.html ...
... All kinds of tutorials on the web on how to convert units using ‘dimensional analysis’ or ‘factor label’ For example: http://www.ncsu.edu/felder-public/kenny/papers/units.html ...
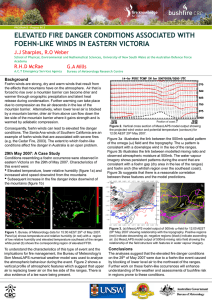
Foehn winds and effect on fire weather: Victorian Case Study File
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
Meteorology_Study_Guide
... ______ 36. Warm air displaces cold air; the warm air is pushed up a gradual slope ______ 37. A front in which neither air mass is moving ______ 38. A large body of air with the characteristics of the area over which it forms ______ 39. The temperature at which water vapor in the air condenses into l ...
... ______ 36. Warm air displaces cold air; the warm air is pushed up a gradual slope ______ 37. A front in which neither air mass is moving ______ 38. A large body of air with the characteristics of the area over which it forms ______ 39. The temperature at which water vapor in the air condenses into l ...
Probabilistic climate prediction/projection from the decadal to the
... determined by uncertainties in observations of historical climate. • Idea is to develop robust, well-understood transfer functions which link something we want to predict with some physically related observable. • Often termed the “ASK” approach – see, e.g., Allen et al (2000), Stott and Kettleborou ...
... determined by uncertainties in observations of historical climate. • Idea is to develop robust, well-understood transfer functions which link something we want to predict with some physically related observable. • Often termed the “ASK” approach – see, e.g., Allen et al (2000), Stott and Kettleborou ...
Draft 2016 National Research Infrastructure Roadmap
... The vision of Australia’s weather forecasting, atmospheric analysis, earth systems, climate and climate change research communities is to transform the investment-to-date on ACCESS into a national research platform/system that significantly enhances research collaboration, broadens services capabili ...
... The vision of Australia’s weather forecasting, atmospheric analysis, earth systems, climate and climate change research communities is to transform the investment-to-date on ACCESS into a national research platform/system that significantly enhances research collaboration, broadens services capabili ...
Stratospheric and tropospheric SSU/MSU temperature
... years in a “historical” climate simulation will rarely (and only by chance) coincide with years when El Niños have actually occurred. This is because the historical runs are initiated from an arbitrary point of a quasi-equilibrium control run, so internal variations (even if they were perfectly pred ...
... years in a “historical” climate simulation will rarely (and only by chance) coincide with years when El Niños have actually occurred. This is because the historical runs are initiated from an arbitrary point of a quasi-equilibrium control run, so internal variations (even if they were perfectly pred ...
IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON WATER - Asian G-WADI
... Presented by : Lama Masalha UNESCO Amman Office 17th July 2010 Beijing, China ...
... Presented by : Lama Masalha UNESCO Amman Office 17th July 2010 Beijing, China ...
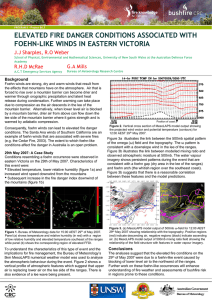
Foehn Winds in Eastern Victoria
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
Data in developing countries
... event would normally be as rare as or rarer than the 10th or 90th percentile. By definition, my rare is not necessarily your rare…. • An extreme climate event is an average of a number of weather events over a certain period of time, an average which is itself extreme (e.g. rainfall over a season). ...
... event would normally be as rare as or rarer than the 10th or 90th percentile. By definition, my rare is not necessarily your rare…. • An extreme climate event is an average of a number of weather events over a certain period of time, an average which is itself extreme (e.g. rainfall over a season). ...
Historical Survey - Atmospheric Sciences
... being driven by latent heating in the ascending air columns. • Such heating forces the isobaric surfaces above the storm to rise, resulting in mass outflow at upper levels and the diminution of pressure at the surface. • Espy did not indicate any circulation around midlatitude cyclones, but noted on ...
... being driven by latent heating in the ascending air columns. • Such heating forces the isobaric surfaces above the storm to rise, resulting in mass outflow at upper levels and the diminution of pressure at the surface. • Espy did not indicate any circulation around midlatitude cyclones, but noted on ...
Intro to (psycho)linguistics and n-gram models
... marginal statistics, you see, are going to become hugely dominated, you see, by the words you and see, with equal frequency, you see. ...
... marginal statistics, you see, are going to become hugely dominated, you see, by the words you and see, with equal frequency, you see. ...
The Advanced Hurricane WRF Ensemble Data Assimilation System
... – Have a “decent” estimate of TC structure (wave-0) – Does not lead to significant initialization problem ...
... – Have a “decent” estimate of TC structure (wave-0) – Does not lead to significant initialization problem ...
Atmospheric model
An atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, moist processes (clouds and precipitation), heat exchange, soil, vegetation, surface water, the kinematic effects of terrain, and convection. Most atmospheric models are numerical, i.e. they discretize equations of motion. They can predict microscale phenomena such as tornadoes and boundary layer eddies, sub-microscale turbulent flow over buildings, as well as synoptic and global flows. The horizontal domain of a model is either global, covering the entire Earth, or regional (limited-area), covering only part of the Earth. The different types of models run are thermotropic, barotropic, hydrostatic, and nonhydrostatic. Some of the model types make assumptions about the atmosphere which lengthens the time steps used and increases computational speed.Forecasts are computed using mathematical equations for the physics and dynamics of the atmosphere. These equations are nonlinear and are impossible to solve exactly. Therefore, numerical methods obtain approximate solutions. Different models use different solution methods. Global models often use spectral methods for the horizontal dimensions and finite-difference methods for the vertical dimension, while regional models usually use finite-difference methods in all three dimensions. For specific locations, model output statistics use climate information, output from numerical weather prediction, and current surface weather observations to develop statistical relationships which account for model bias and resolution issues.