Key to Microeconomics Test 1 Short answer essay and/or graph (55
... Absolute advantage: refers to a producer having higher efficiency of production. Efficiency refers to ability to produce more output with same resources. Comparative advantage: between two(or more) producers, a comparative advantage indicates lower relative opportunity costs. b) Why would a country ...
... Absolute advantage: refers to a producer having higher efficiency of production. Efficiency refers to ability to produce more output with same resources. Comparative advantage: between two(or more) producers, a comparative advantage indicates lower relative opportunity costs. b) Why would a country ...
Recursive Competitive Equilibrium: The Case of Homogeneous
... uncertainty. Optimality of recursive equilibria and supportability of Pareto optima by recursive equilibria is established in a simpler and more direct way which does not rely upon the equivalence of recursive and state-contingent equilibrium allocations. The homogeneity of consumers is admittedly n ...
... uncertainty. Optimality of recursive equilibria and supportability of Pareto optima by recursive equilibria is established in a simpler and more direct way which does not rely upon the equivalence of recursive and state-contingent equilibrium allocations. The homogeneity of consumers is admittedly n ...
Topic Priority Checklist
... equilibria of the purely competitive firm. 33. In words and using graphical analysis, show the profit scenario of a single price monopolist and a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist. 34. Identify the government policies employed when a firm exercises monopoly power or is a natural monopoly. 35 ...
... equilibria of the purely competitive firm. 33. In words and using graphical analysis, show the profit scenario of a single price monopolist and a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist. 34. Identify the government policies employed when a firm exercises monopoly power or is a natural monopoly. 35 ...
Part I
... helpful). “If a firm has a production function, Q L0.4 K 0.6 and factor prices are constant, then long-run marginal cost equals long-run average cost.” b. True or False or Uncertain. Please explain in less than 40 words (add a diagram if you think helpful). “If the demand curve for a monopolist is ...
... helpful). “If a firm has a production function, Q L0.4 K 0.6 and factor prices are constant, then long-run marginal cost equals long-run average cost.” b. True or False or Uncertain. Please explain in less than 40 words (add a diagram if you think helpful). “If the demand curve for a monopolist is ...
Please review and make sure that you understand
... Please review and make sure that you understand these key terms. Do not just memorize them! What you make on the test is up to you and you will receive the grade you earn. The exam is 48 multiple choice questions and 1 essay. You will have all class period to take this exam. ...
... Please review and make sure that you understand these key terms. Do not just memorize them! What you make on the test is up to you and you will receive the grade you earn. The exam is 48 multiple choice questions and 1 essay. You will have all class period to take this exam. ...
The Road Less Travelled - University College Dublin
... Bhagwati et al. (1998, p. 382) and Kreps (1990, p. 727).) In this paper, I draw on recent work (Neary (2002a, b, c)) where I argue that they can all be avoided in a simple way. This is to allow firms to be "large" in their own sector, but to require them to be "small" in the economy as a whole. Tech ...
... Bhagwati et al. (1998, p. 382) and Kreps (1990, p. 727).) In this paper, I draw on recent work (Neary (2002a, b, c)) where I argue that they can all be avoided in a simple way. This is to allow firms to be "large" in their own sector, but to require them to be "small" in the economy as a whole. Tech ...
Answers
... +6: slope parameter on technology: If technology improves by one unit then output will increase by 6 units. -32 = Slope parameter on price of related good. If the price of the related good increases by $1, production of the good of interest will decrease by 32 units. -20 = Slope parameter on price ...
... +6: slope parameter on technology: If technology improves by one unit then output will increase by 6 units. -32 = Slope parameter on price of related good. If the price of the related good increases by $1, production of the good of interest will decrease by 32 units. -20 = Slope parameter on price ...
Chapter 3 / Individual Markets: Demand and Supply
... b. The supply curve is a graphic representation of supply and the law of supply; the market supply of a good or service is the sum of the supplies of all sellers of the good or service. c. The supply of a good or service depends on the techniques used to produce it, the prices of the resources emplo ...
... b. The supply curve is a graphic representation of supply and the law of supply; the market supply of a good or service is the sum of the supplies of all sellers of the good or service. c. The supply of a good or service depends on the techniques used to produce it, the prices of the resources emplo ...
Price - Gore High School
... When the market is not in equilibrium we call this a disequilibrium. When the market is in a disequilibrium, there will be pressure on the market. These pressures are from the needs of consumers for goods and services (demand) and the need of producers to sell their goods and services (supply) These ...
... When the market is not in equilibrium we call this a disequilibrium. When the market is in a disequilibrium, there will be pressure on the market. These pressures are from the needs of consumers for goods and services (demand) and the need of producers to sell their goods and services (supply) These ...
GCE January 2003 Question Paper Economics
... OBJECTIVE TEST QUESTIONS You are advised to spend no more than 30 minutes on these questions. Each item consists of a question or an incomplete statement followed by four suggested answers or completions. You are to select the most appropriate answer in each case. ...
... OBJECTIVE TEST QUESTIONS You are advised to spend no more than 30 minutes on these questions. Each item consists of a question or an incomplete statement followed by four suggested answers or completions. You are to select the most appropriate answer in each case. ...
Lecture 13 slides
... – In LR, to maximize π =PQTC • need to discuss price • price depends on market structure ...
... – In LR, to maximize π =PQTC • need to discuss price • price depends on market structure ...
Chapter 6
... Since markets tend toward equilibrium, a change in supply will set market forces in motion that lead the market to a new equilibrium price and quantity sold. ...
... Since markets tend toward equilibrium, a change in supply will set market forces in motion that lead the market to a new equilibrium price and quantity sold. ...
market equilibrium
... How is market competition different from competition in sports and in games? Why do car dealers usually locate together on the outskirts of town? What’s the difference between making stuff right and making the right stuff? Why do government efforts to keep rents low usually lead to a housing ...
... How is market competition different from competition in sports and in games? Why do car dealers usually locate together on the outskirts of town? What’s the difference between making stuff right and making the right stuff? Why do government efforts to keep rents low usually lead to a housing ...
Chapter 4: Markets in Action
... Listen to the “Ask the Instructor Video Clip” titled “Why Do Some Prices Adjust More Slowly?” You will learn how equilibrium prices adjust in the market for stocks and nurses. ...
... Listen to the “Ask the Instructor Video Clip” titled “Why Do Some Prices Adjust More Slowly?” You will learn how equilibrium prices adjust in the market for stocks and nurses. ...
Economics
... 2. Kites are manufactured by identical firms. Eac firm’s long-run average and marginal costs of production are given by AC= Q + 100/Q and MC=2Q where Q is the number of kites produced. a. In long-run equilibrium, how many kites can each firm produce? ...
... 2. Kites are manufactured by identical firms. Eac firm’s long-run average and marginal costs of production are given by AC= Q + 100/Q and MC=2Q where Q is the number of kites produced. a. In long-run equilibrium, how many kites can each firm produce? ...
First Midterm (Afternoon Lecture) with answers
... Fill in the blanks for the next 3 questions: 1. ______ is a study of firms, markets, and pricing decisions. a. Microeconomics b. Macroeconomics 2. Economists use economic models for _____________. a. Normative economics b. Both normative and positive economics 3. The statement, “the major problem no ...
... Fill in the blanks for the next 3 questions: 1. ______ is a study of firms, markets, and pricing decisions. a. Microeconomics b. Macroeconomics 2. Economists use economic models for _____________. a. Normative economics b. Both normative and positive economics 3. The statement, “the major problem no ...
Handout 3 Solutions
... Assume there is a downward sloping demand curve and an upward sloping supply curve for Frosted Flakes. In the following scenarios, explain whether there will be a shift in demand, a shift in supply, a movement along the demand curve, or a movement along the supply curve. If there ...
... Assume there is a downward sloping demand curve and an upward sloping supply curve for Frosted Flakes. In the following scenarios, explain whether there will be a shift in demand, a shift in supply, a movement along the demand curve, or a movement along the supply curve. If there ...
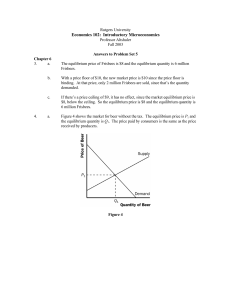
Answers to Problem set 5 - rci.rutgers.edu
... If the government imposes a $500 tax on luxury cars, the price paid by consumers will rise less than $500, in general. The burden of any tax is shared by both producers and consumersthe price paid by consumers rises and the price received by producers falls, with the difference between the two equa ...
... If the government imposes a $500 tax on luxury cars, the price paid by consumers will rise less than $500, in general. The burden of any tax is shared by both producers and consumersthe price paid by consumers rises and the price received by producers falls, with the difference between the two equa ...
File
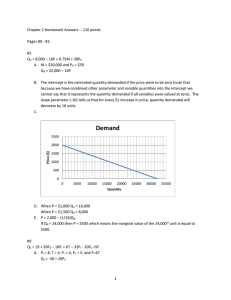
... Explain the parameters of the linear demand function, Qd = a – bP. Plot a given linear demand function. (Assume Qd = 14 – 2P.) Explain the implications of changes in parameters a and b and how such changes would be reflected on a graph. Explain the parameters of the linear supply function, Qs = c – ...
... Explain the parameters of the linear demand function, Qd = a – bP. Plot a given linear demand function. (Assume Qd = 14 – 2P.) Explain the implications of changes in parameters a and b and how such changes would be reflected on a graph. Explain the parameters of the linear supply function, Qs = c – ...
1 Unit 6. Firm behaviour and market structure: perfect competition
... A growth of output in an increasing-cost industry expands the demand for factors of production and pushes up their prices. As a result a firm’s average total cost curve shifts upward (see the figure below). Entrance of new firms shifts down short-run supply curve. In the long run equilibrium moves ...
... A growth of output in an increasing-cost industry expands the demand for factors of production and pushes up their prices. As a result a firm’s average total cost curve shifts upward (see the figure below). Entrance of new firms shifts down short-run supply curve. In the long run equilibrium moves ...