Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 101
... 14. Which of the following situations certainly leads to a lower equilibrium price? a. An increase in demand accompanied by an increase in supply. b. A decrease in demand accompanied by an increase in supply. c. A decrease in supply accompanied by an increase in demand. d. An increase in demand, wit ...
... 14. Which of the following situations certainly leads to a lower equilibrium price? a. An increase in demand accompanied by an increase in supply. b. A decrease in demand accompanied by an increase in supply. c. A decrease in supply accompanied by an increase in demand. d. An increase in demand, wit ...
Formative Quiz on Supply and Demand 1. The law of demand states
... A. consumers will buy more of a product as the price increases. B. consumers will buy more of a product as the price decreases. C. suppliers will produce more of a product as the price increases. D. suppliers will produce more of a product as the price decreases. 2. As the quantity of goods consumed ...
... A. consumers will buy more of a product as the price increases. B. consumers will buy more of a product as the price decreases. C. suppliers will produce more of a product as the price increases. D. suppliers will produce more of a product as the price decreases. 2. As the quantity of goods consumed ...
Market Equilibrium
... much producers want to sell include input prices, technology, expectations, and the number of sellers. If one of these factors changes, the supply curve shifts. ...
... much producers want to sell include input prices, technology, expectations, and the number of sellers. If one of these factors changes, the supply curve shifts. ...
Understanding Supply and Demand
... • In addition to price, other determinants of how much consumers want to buy include income, the prices of complements and substitutes, tastes, expectations, and the number of buyers. • If one of these factors changes, the demand curve shifts. ...
... • In addition to price, other determinants of how much consumers want to buy include income, the prices of complements and substitutes, tastes, expectations, and the number of buyers. • If one of these factors changes, the demand curve shifts. ...
AP Micro Concepts
... Price takers Demand = MR = Price Graph: Firm vs. Industry/Market Short-Run vs. Long-Run (Graphs) Short-Run (Profit or Loss) Long-Run Equilibrium New Firms Enter and Exit ...
... Price takers Demand = MR = Price Graph: Firm vs. Industry/Market Short-Run vs. Long-Run (Graphs) Short-Run (Profit or Loss) Long-Run Equilibrium New Firms Enter and Exit ...
Price Controls Practice Exam
... A) inefficiency because it causes too much job search B) efficiency because few workers lose their jobs C) efficiency because it increases most workers’ wages D) inefficiency because it decreases productive unemployment 6. Price ceilings are primarily target to help ____________, while price floors ...
... A) inefficiency because it causes too much job search B) efficiency because few workers lose their jobs C) efficiency because it increases most workers’ wages D) inefficiency because it decreases productive unemployment 6. Price ceilings are primarily target to help ____________, while price floors ...
Combining Supply and Demand Section 1: Guided Reading and Review
... a. by assisting the centrally planned economy b. by serving as a tool for distributing goods and services c. by limiting the market to people who have the most money d. by preventing inflation or deflation from affecting the supply of goods _ _ 10. Why did the former Soviet Union use a command econo ...
... a. by assisting the centrally planned economy b. by serving as a tool for distributing goods and services c. by limiting the market to people who have the most money d. by preventing inflation or deflation from affecting the supply of goods _ _ 10. Why did the former Soviet Union use a command econo ...
quantity supplied - Effingham County Schools
... • Graphically, individual supply curves are summed horizontally to obtain the market supply curve • Change in Qs - Caused by a change in anything that alters the quantity supplied at each price. ...
... • Graphically, individual supply curves are summed horizontally to obtain the market supply curve • Change in Qs - Caused by a change in anything that alters the quantity supplied at each price. ...
Short Run Market Equilibrium
... Long Run Equilibrium In the long run, ¯rms can adjust all inputs. More importantly, new ¯rms can enter the market in search of pro¯t opportunities, and existing ¯rms can exit the market if they are receiving negative pro¯ts. To make things simple, we will assume that there is free entry and exit, a ...
... Long Run Equilibrium In the long run, ¯rms can adjust all inputs. More importantly, new ¯rms can enter the market in search of pro¯t opportunities, and existing ¯rms can exit the market if they are receiving negative pro¯ts. To make things simple, we will assume that there is free entry and exit, a ...
3-9-Week-6-Answers-Price-Ch-6-
... It is a government set maximum price that can be charged for a good or service such as rent. ...
... It is a government set maximum price that can be charged for a good or service such as rent. ...
Supply and Demand
... consumer remain unchanged, then the change in quantity of good demanded by the consumer will be negatively correlated to the change in the price of the good. ...
... consumer remain unchanged, then the change in quantity of good demanded by the consumer will be negatively correlated to the change in the price of the good. ...
Net Surplus
... Rations scarce resources to those who “value” goods the most (however, do note that value depends on income!) Provide allocative signals, telling those with factors of production how those factors will be valued in alternate uses. ...
... Rations scarce resources to those who “value” goods the most (however, do note that value depends on income!) Provide allocative signals, telling those with factors of production how those factors will be valued in alternate uses. ...
First Midterm
... b. Decrease in demand for videos. 2) A university considers re-painting crosswalks in the campus. In a social sense, the opportunity cost of doing this is greater: a. When the university employs teenagers not enrolled in school and otherwise unemployed in order to paint crosswalks than when it emplo ...
... b. Decrease in demand for videos. 2) A university considers re-painting crosswalks in the campus. In a social sense, the opportunity cost of doing this is greater: a. When the university employs teenagers not enrolled in school and otherwise unemployed in order to paint crosswalks than when it emplo ...
ECON 3070-001 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory
... a) Monthly income is 1000, the price of pizza is 8 and the price · of record albums i s 10. b) Same conditions as in a, except that income is 500. c) same conditions as in a, except that income is 2000 and pizza i s 16 d) Same conditions as in a , except that record albums cost 5 . e) Compare the bu ...
... a) Monthly income is 1000, the price of pizza is 8 and the price · of record albums i s 10. b) Same conditions as in a, except that income is 500. c) same conditions as in a, except that income is 2000 and pizza i s 16 d) Same conditions as in a , except that record albums cost 5 . e) Compare the bu ...
Equilibrium
... Law of Supply and Demand: the claim that the price of any good adjusts to bring the supply and demand for that good into balance. ...
... Law of Supply and Demand: the claim that the price of any good adjusts to bring the supply and demand for that good into balance. ...
Net Surplus
... Rations scarce resources to those who “value” goods the most (however, do note that value depends on income!) Provide allocative signals, telling those with factors of production how those factors will be valued in alternate uses. ...
... Rations scarce resources to those who “value” goods the most (however, do note that value depends on income!) Provide allocative signals, telling those with factors of production how those factors will be valued in alternate uses. ...
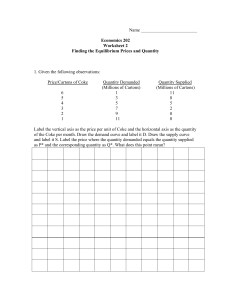
Name Economics 202 Worksheet 2 Finding the Equilibrium Prices
... shortage drawn above is only temporary. After a trial-and-error period of time the forces of surplus and shortage will automatically restore the equilibrium price and quantity as originally drawn in step one. Explain how this occurs. ...
... shortage drawn above is only temporary. After a trial-and-error period of time the forces of surplus and shortage will automatically restore the equilibrium price and quantity as originally drawn in step one. Explain how this occurs. ...
2-Page All Graph Summary Study Sheet
... When MR = 0 , demand is unit elastic and total revenue is maximized. Firms operate in Elastic range. Only if MC = ZERO, then firms would produce at unit elasticity ...
... When MR = 0 , demand is unit elastic and total revenue is maximized. Firms operate in Elastic range. Only if MC = ZERO, then firms would produce at unit elasticity ...