Econ 101, sections 2 and 6, S06 - Iowa State University Department
... c. are the leaders of industry who own and manage the largest manufacturing firms. * are inputs into the production process. 8. In a production possibility graph, an output combination is said to be efficient if a. it lies beyond the production possibility frontier. b. it involves production of the ...
... c. are the leaders of industry who own and manage the largest manufacturing firms. * are inputs into the production process. 8. In a production possibility graph, an output combination is said to be efficient if a. it lies beyond the production possibility frontier. b. it involves production of the ...
When Supply and Demand Just Won`t Do: Using
... Figures 2 and 3 show demand curves that make parallel shifts, but this is not the only possibility. Consider for example, a change in tastes (or income or the availability of other goods) that has little effect on the demand for that vehicle by potential buyers with the highest reservation values, b ...
... Figures 2 and 3 show demand curves that make parallel shifts, but this is not the only possibility. Consider for example, a change in tastes (or income or the availability of other goods) that has little effect on the demand for that vehicle by potential buyers with the highest reservation values, b ...
Suggested solutions for Quiz #1
... b. Find the new equilibrium price and the new equilibrium quantity. Explain how the market adjusts to the new equilibrium. The new equilibrium is pe $.37 and q e 600 . At the old equilibrium price of $.36 there is a temporary shortage. Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied by 400 units. So ...
... b. Find the new equilibrium price and the new equilibrium quantity. Explain how the market adjusts to the new equilibrium. The new equilibrium is pe $.37 and q e 600 . At the old equilibrium price of $.36 there is a temporary shortage. Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied by 400 units. So ...
price ceiling
... Consumers who cannot obtain supplies (even though they are willing to purchase at the equilibrium price ) ...
... Consumers who cannot obtain supplies (even though they are willing to purchase at the equilibrium price ) ...
Scarcity and Resource Allocation
... The basic economic problem is that of scarcity – the competition between unlimited wants and limited resources. Hence, resources have to be allocated in such a way to promote the two main microeconomic aims – efficiency and equity. The three basic economic questions that arise out of the problem of ...
... The basic economic problem is that of scarcity – the competition between unlimited wants and limited resources. Hence, resources have to be allocated in such a way to promote the two main microeconomic aims – efficiency and equity. The three basic economic questions that arise out of the problem of ...
What are consumers` and producers` surplus?
... Pe , the consumer demands Qe units and the producer is willing to supply Qe units. The subscript e refers to equilibrium on each letter. We can find the values algebraically by setting the demand and supply function equal. We may also estimate the values by examining a graph. ...
... Pe , the consumer demands Qe units and the producer is willing to supply Qe units. The subscript e refers to equilibrium on each letter. We can find the values algebraically by setting the demand and supply function equal. We may also estimate the values by examining a graph. ...
Existence of an Equilibrium for a Competitive Economy
... L. WALRAS[24] first formulated the state of the economic system a t any point of time as the solution of a system of simultaneous equations representing the demand for goods by consumers, the supply of goods by producers, and the equilibrium condition that supply equal demand on every market. I t wa ...
... L. WALRAS[24] first formulated the state of the economic system a t any point of time as the solution of a system of simultaneous equations representing the demand for goods by consumers, the supply of goods by producers, and the equilibrium condition that supply equal demand on every market. I t wa ...
Chapter 14
... Find new short-run equilibrium using new short-run supply curve of initially active firms Find new long-run equilibrium using new long-run supply curve which reflects free entry ...
... Find new short-run equilibrium using new short-run supply curve of initially active firms Find new long-run equilibrium using new long-run supply curve which reflects free entry ...
EconS425 - Homework #2 (Due on February 18 , 2015)
... of cA = $6 whereas firm B (less efficient) at a unit cost of cB = $8. a. Suppose that the aggregate market demand for boxes of paper clips is p = 12 – Q/2, where p is the price per box and Q is the number of boxes sold. Solve for the Nash-Bertrand equilibrium prices pbA and pbB, and the equilibrium ...
... of cA = $6 whereas firm B (less efficient) at a unit cost of cB = $8. a. Suppose that the aggregate market demand for boxes of paper clips is p = 12 – Q/2, where p is the price per box and Q is the number of boxes sold. Solve for the Nash-Bertrand equilibrium prices pbA and pbB, and the equilibrium ...
The Free Enterprise System
... Monopolies • When there is no COMPETITION and one firm controls the whole market. • U.S. Government allows only a few, such as utility companies. ...
... Monopolies • When there is no COMPETITION and one firm controls the whole market. • U.S. Government allows only a few, such as utility companies. ...
Markets--NEW - Cal Poly Pomona
... Please limit your answers to the spaces provided. If necessary, write on the back of the page. Do not attach printout or additional pages. All questions pertain to the Markets module in SimEcon. Make sure you have read the “Markets Manual” which may be found on the ClassWeb site prior to beginning ...
... Please limit your answers to the spaces provided. If necessary, write on the back of the page. Do not attach printout or additional pages. All questions pertain to the Markets module in SimEcon. Make sure you have read the “Markets Manual” which may be found on the ClassWeb site prior to beginning ...
Chap002
... the independent variable is on the vertical axis rather than on the horizontal axis.) d. When put together these functions show an equilibrium price and output as well as the surpluses and shortages that will come from disequilibrium prices. 2. An equilibrium price brings maximum welfare to the syst ...
... the independent variable is on the vertical axis rather than on the horizontal axis.) d. When put together these functions show an equilibrium price and output as well as the surpluses and shortages that will come from disequilibrium prices. 2. An equilibrium price brings maximum welfare to the syst ...
Law of Demand - MsDozierSocialStudies
... Elasticity of Demand- is the measure of how consumers will react to a change in price. 1. Inelastic Demand- A decrease in price will lead to only a small change in demand, or no change at all. Also can be your personal choice that makes something inelastic. ...
... Elasticity of Demand- is the measure of how consumers will react to a change in price. 1. Inelastic Demand- A decrease in price will lead to only a small change in demand, or no change at all. Also can be your personal choice that makes something inelastic. ...
Name: Date: Section
... C) occurs when a seller charges two or more prices for the same good or service. D) occurs when the seller charges different prices for different quality products. 14. Which statement is true? A) All monopolies are good. B) All monopolies are bad. C) Most natural monopolies are government regulated ...
... C) occurs when a seller charges two or more prices for the same good or service. D) occurs when the seller charges different prices for different quality products. 14. Which statement is true? A) All monopolies are good. B) All monopolies are bad. C) Most natural monopolies are government regulated ...
Price Controls
... Sometimes a minimum price is set in a market above the equilibrium as it is seen as being unfair to the suppliers in that particular market. In a market where there are a combination of very high and very low prices, a minimum price may be set which it cannot fall below. This price must be above equ ...
... Sometimes a minimum price is set in a market above the equilibrium as it is seen as being unfair to the suppliers in that particular market. In a market where there are a combination of very high and very low prices, a minimum price may be set which it cannot fall below. This price must be above equ ...
Solutions 3 - Emilio Cuilty
... 5) What should the state government do if they want to guarantee that pumpkin planters can earn a higher profit? Is that good or bad for the entire society? It’s an open question. The answer could be price floor, price support system or subsidy. I think it might be good time to introduce these conce ...
... 5) What should the state government do if they want to guarantee that pumpkin planters can earn a higher profit? Is that good or bad for the entire society? It’s an open question. The answer could be price floor, price support system or subsidy. I think it might be good time to introduce these conce ...
Mathematics in Economics
... framework—constitute what might be called the operating conditions of the particular economic system. These are the "data" which in verbal analysis are used to explain the "unknown" outputs, employment, prices, investments, and so on. Translated into mathematical language this means that the availab ...
... framework—constitute what might be called the operating conditions of the particular economic system. These are the "data" which in verbal analysis are used to explain the "unknown" outputs, employment, prices, investments, and so on. Translated into mathematical language this means that the availab ...
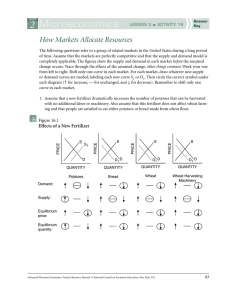
How Markets Allocate Resources
... The following questions refer to a group of related markets in the United States during a long period of time. Assume that the markets are perfectly competitive and that the supply and demand model is completely applicable. The figures show the supply and demand in each market before the assumed cha ...
... The following questions refer to a group of related markets in the United States during a long period of time. Assume that the markets are perfectly competitive and that the supply and demand model is completely applicable. The figures show the supply and demand in each market before the assumed cha ...
module 6 supply and equilibrium
... 1. Change in input prices The cost of the resources that are used in production of finished goods increase or decrease. This makes the production of the final good more costly for those who produce and sell it. Producers are less willing to supply the final good at any given price. ...
... 1. Change in input prices The cost of the resources that are used in production of finished goods increase or decrease. This makes the production of the final good more costly for those who produce and sell it. Producers are less willing to supply the final good at any given price. ...