Goal 8: Analyze features of the economic system of the US
... 17. A local newspaper reports that eating broccoli will increase strength, stamina, and performance in sports. This will most likely cause a ___________________ for broccoli. A. Supply increase B. Supply decrease C. Demand increase D. Demand decrease 18. An equilibrium price is best defined as: A. T ...
... 17. A local newspaper reports that eating broccoli will increase strength, stamina, and performance in sports. This will most likely cause a ___________________ for broccoli. A. Supply increase B. Supply decrease C. Demand increase D. Demand decrease 18. An equilibrium price is best defined as: A. T ...
Supply and Demand - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... actual purchases, rather only what consumers are willing and able to purchase. LO-2 ...
... actual purchases, rather only what consumers are willing and able to purchase. LO-2 ...
Lec15.pdf
... Close substitutes (or complements), matter of degree 2. Why is number of firms in industry small? Large fixed costs or scale economies 3. Forms of strategic interactions a. Choice variables — quantities or prices Others — investment, R-and-D, advertising, ... b. Simultaneous vs. sequential actions l ...
... Close substitutes (or complements), matter of degree 2. Why is number of firms in industry small? Large fixed costs or scale economies 3. Forms of strategic interactions a. Choice variables — quantities or prices Others — investment, R-and-D, advertising, ... b. Simultaneous vs. sequential actions l ...
Answers to Practice Questions 2
... 2) b. The elasticity of supply is identical in both markets but demand in Japan is more elastic. Therefore, the deadweight loss in Japan is larger. Next, in the United States, a demand curve is less elastic than a supply one; therefore, the tax incidence falls more heavily on consumers. Finally, tax ...
... 2) b. The elasticity of supply is identical in both markets but demand in Japan is more elastic. Therefore, the deadweight loss in Japan is larger. Next, in the United States, a demand curve is less elastic than a supply one; therefore, the tax incidence falls more heavily on consumers. Finally, tax ...
Economic Survey
... technology and methods of production change shifting supply curve to increase or decrease ...
... technology and methods of production change shifting supply curve to increase or decrease ...
Federal Urdu University
... b, Find Elasticity of demand at each possible point c, Find Elasticity of Supply at each possible point d, Find point elasticity of demand and supply where price equal to 11 Q#9: Define consumer surplus, producer surplus with the help of an example? Q#10 Multiple Choice Questions. Select any one ans ...
... b, Find Elasticity of demand at each possible point c, Find Elasticity of Supply at each possible point d, Find point elasticity of demand and supply where price equal to 11 Q#9: Define consumer surplus, producer surplus with the help of an example? Q#10 Multiple Choice Questions. Select any one ans ...
Demand, Supply & Price
... Reverse is true if the is a decrease in expectations (demand will decrease). ...
... Reverse is true if the is a decrease in expectations (demand will decrease). ...
Demand & Supply
... What Is Demand? Demand is a relationship between a product’s price and quantity demanded. Demand is shown using a schedule or curve. The law of demand states that price and quantity demanded are inversely related. Market demand is the sum of quantities demanded by all consumers in a market. ...
... What Is Demand? Demand is a relationship between a product’s price and quantity demanded. Demand is shown using a schedule or curve. The law of demand states that price and quantity demanded are inversely related. Market demand is the sum of quantities demanded by all consumers in a market. ...
Supply and Demand Together
... The FREE MARKET system automatically pushes the price toward equilibrium. Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd ...
... The FREE MARKET system automatically pushes the price toward equilibrium. Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd ...
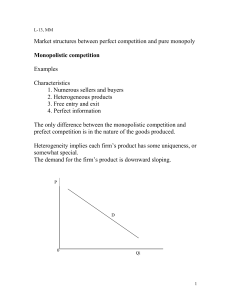
Market structures between perfect competition and pure monopoly
... 3. Yet it provides a variety of goods and offer a wide range of choice, which benefits consumers. ...
... 3. Yet it provides a variety of goods and offer a wide range of choice, which benefits consumers. ...
SECTION 2: Supply and Demand Need to Know: 1. Other things being equal, as the price increases, the corresponding quantity demanded falls.
... 1. Other things being equal, as the price increases, the corresponding quantity demanded falls. 2. Restated, there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. ...
... 1. Other things being equal, as the price increases, the corresponding quantity demanded falls. 2. Restated, there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. ...
Practice Questions for Midterm 1
... good x and good y, the consumer should consume until the ratio of marginal utilities over price is the same across both goods. Marginal Utility is an additional utility gained from consuming an additional unit of good. It is the same as marginal benefit. If the marginal utility per dollar is not the ...
... good x and good y, the consumer should consume until the ratio of marginal utilities over price is the same across both goods. Marginal Utility is an additional utility gained from consuming an additional unit of good. It is the same as marginal benefit. If the marginal utility per dollar is not the ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑