Equilibrium Price and Prices
... Transaction Costs in Markets • The costs of time and information required for exchange • Example: You are looking for a summer job. One way is to go from employer to employer looking for openings. Both time consuming and could take extensive travel. A better strategy would be to pick up a couple of ...
... Transaction Costs in Markets • The costs of time and information required for exchange • Example: You are looking for a summer job. One way is to go from employer to employer looking for openings. Both time consuming and could take extensive travel. A better strategy would be to pick up a couple of ...
What was your hourly wage in your most recent job?
... A minimum wage rate is set 20% higher than the equilibrium wage. This causes total wages received by laborers to rise only if A) B) C) D) E) ...
... A minimum wage rate is set 20% higher than the equilibrium wage. This causes total wages received by laborers to rise only if A) B) C) D) E) ...
microecon
... ____ 15. Because a modest price increase has little or no effect, the demand for the product is: a. complementary c. elastic b. inelastic d. Unit elastic ____ 16. Consumers’ willingness to replace a costly item with a less costly item is an example of: a. The substitution effect c. Demand elasticity ...
... ____ 15. Because a modest price increase has little or no effect, the demand for the product is: a. complementary c. elastic b. inelastic d. Unit elastic ____ 16. Consumers’ willingness to replace a costly item with a less costly item is an example of: a. The substitution effect c. Demand elasticity ...
Chapter 3
... A change in a good’s own price leads to a change in quantity demanded. This is a movement along the same curve. A change in any determinant OTHER THAN PRICE shifts the D curve, and we call this a change in demand. This is not the same as a change in Qd from a change in the price of the good. ...
... A change in a good’s own price leads to a change in quantity demanded. This is a movement along the same curve. A change in any determinant OTHER THAN PRICE shifts the D curve, and we call this a change in demand. This is not the same as a change in Qd from a change in the price of the good. ...
---PROMINENT TOPICS WORTH REVIEWING--
... 3. As we know, scarcity depends on both the available supply of a good or service and the demand for it. Choose a good or service and briefly describe a circumstance in which it would be seen as scarce and one in which it would not be scarce. Make sure that you follow the definition of scarcity in y ...
... 3. As we know, scarcity depends on both the available supply of a good or service and the demand for it. Choose a good or service and briefly describe a circumstance in which it would be seen as scarce and one in which it would not be scarce. Make sure that you follow the definition of scarcity in y ...
2-6 Quantity Supplied / Quantity Demanded
... decrease the demand depending upon whether the related good is a substitute good or a complementary good. *When two products are substitutes the price of one and the demand for the other move in the same direction. *When two products are complements, the price of one good and the demand for the othe ...
... decrease the demand depending upon whether the related good is a substitute good or a complementary good. *When two products are substitutes the price of one and the demand for the other move in the same direction. *When two products are complements, the price of one good and the demand for the othe ...
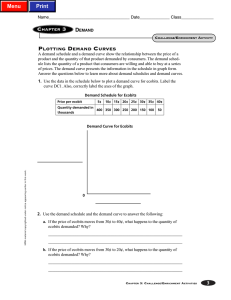
PLOTTING DEMAND CURVES
... b. It increases by 100,000 to 250,000 ecobits, because consumers will buy more ecobits when prices are lower. c. Typical answer: There is an inverse relationship between quantity demanded and price. Quantity demanded will be higher at lower prices, and lower at higher prices. 3. a. Changes in consum ...
... b. It increases by 100,000 to 250,000 ecobits, because consumers will buy more ecobits when prices are lower. c. Typical answer: There is an inverse relationship between quantity demanded and price. Quantity demanded will be higher at lower prices, and lower at higher prices. 3. a. Changes in consum ...
CH 3 QUIZ
... 2. Which of the following is not held constant when constructing a demand curve for digital cameras? a) Price of digital cameras b) Consumer preferences c) Prices of film cameras (a substitute) d) Consumer expectations e) Consumer income 3. When incomes are rising, new car sales increase while used ...
... 2. Which of the following is not held constant when constructing a demand curve for digital cameras? a) Price of digital cameras b) Consumer preferences c) Prices of film cameras (a substitute) d) Consumer expectations e) Consumer income 3. When incomes are rising, new car sales increase while used ...
Market Failure - uwcmaastricht-econ
... marginal benefit falls as quantity consumed increases, the consumer will be willing to buy each extra unit only if the price falls. ...
... marginal benefit falls as quantity consumed increases, the consumer will be willing to buy each extra unit only if the price falls. ...
1 Price Ali Ayşe Arda Ada Market demand $0.00 20 16 4 8 0.50 18
... might be because a. the number of buyers in the market has decreased. b. income has increased and the good is an inferior good. c. the production costs of the sellers have decreased. d. the price of a complementary good has decreased 7. Which of these will not increase the demand for tea? a. The pri ...
... might be because a. the number of buyers in the market has decreased. b. income has increased and the good is an inferior good. c. the production costs of the sellers have decreased. d. the price of a complementary good has decreased 7. Which of these will not increase the demand for tea? a. The pri ...
economic terms
... Capital - factor of production that includes the tools, equipment, and factories used in the production of goods and services. Labor – factor of production that includes people and their efforts, abilities, and skills.] Land – factor of production that includes all natural resources. Capitalism – ec ...
... Capital - factor of production that includes the tools, equipment, and factories used in the production of goods and services. Labor – factor of production that includes people and their efforts, abilities, and skills.] Land – factor of production that includes all natural resources. Capitalism – ec ...
AP Microeconomics
... 3.) Know the Total Revenue (TR) Test – what happens to TR when price changes depends on whether demand is elastic or inelastic. 4.) Who bears the burden of an excise tax? – The party whose supply or demand is more inelastic. Be able to graph this (there will be a problem on this) and use formula to ...
... 3.) Know the Total Revenue (TR) Test – what happens to TR when price changes depends on whether demand is elastic or inelastic. 4.) Who bears the burden of an excise tax? – The party whose supply or demand is more inelastic. Be able to graph this (there will be a problem on this) and use formula to ...
File
... 2. Which of the following explains the relationship between income effect and consumption? a. When the price of goods goes up, people get less for their money, and consumption goes down. b. As incomes rise, consumption of lower-priced goods falls. c. When the price of goods goes up, people buy more, ...
... 2. Which of the following explains the relationship between income effect and consumption? a. When the price of goods goes up, people get less for their money, and consumption goes down. b. As incomes rise, consumption of lower-priced goods falls. c. When the price of goods goes up, people buy more, ...
Microeconomic Concepts Describe how households, businesses
... service increases, the quantity of goods and services offered by suppliers increases and vice versa. Law of Demand – all other factors being equal, as the price of a good or service increases the quantities consumers demand for the good or service will decrease and vice versa. ...
... service increases, the quantity of goods and services offered by suppliers increases and vice versa. Law of Demand – all other factors being equal, as the price of a good or service increases the quantities consumers demand for the good or service will decrease and vice versa. ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑