Monopoly - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • There has to be a total barrier to entry. If not, a new firm will enter and end the monopoly. • There can be no close substitutes for the monopolist’s product. • There is no competitive pressure. A monopolist will charge a higher price and produce a smaller quantity and will not experience a profi ...
... • There has to be a total barrier to entry. If not, a new firm will enter and end the monopoly. • There can be no close substitutes for the monopolist’s product. • There is no competitive pressure. A monopolist will charge a higher price and produce a smaller quantity and will not experience a profi ...
supply
... – Coordination: it functions as a bridge between producers and consumers QUESTION: Why do we need it? ...
... – Coordination: it functions as a bridge between producers and consumers QUESTION: Why do we need it? ...
Supply and Demand - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... economists talk of increasing or decreasing supply, they mean shifts of the supply curve—a change in the quantity supplied at any given price. 8. There are five main factors that shift the supply curve: • A change in input prices • A change in the prices of related goods and services • A change in t ...
... economists talk of increasing or decreasing supply, they mean shifts of the supply curve—a change in the quantity supplied at any given price. 8. There are five main factors that shift the supply curve: • A change in input prices • A change in the prices of related goods and services • A change in t ...
Presentation
... Fall in Demand > Fall in Supply** **According to the Marginalist Principle, it would be rational for consumers to purchase substitution goods (iPad 2) than the iPad. This is due to the fact that the satisfaction gained from consuming an additional iPad < cost paid for that additional iPad. Thus, fal ...
... Fall in Demand > Fall in Supply** **According to the Marginalist Principle, it would be rational for consumers to purchase substitution goods (iPad 2) than the iPad. This is due to the fact that the satisfaction gained from consuming an additional iPad < cost paid for that additional iPad. Thus, fal ...
price - Department of Economics
... Market Supply Demand • The individual firms and consumers in the economy face supply and demand situations • The market supply and demand is the SUM of all individual supply and demand curves • Individual and firms may have different elasticity of demand than the consolidated supply and demand curve ...
... Market Supply Demand • The individual firms and consumers in the economy face supply and demand situations • The market supply and demand is the SUM of all individual supply and demand curves • Individual and firms may have different elasticity of demand than the consolidated supply and demand curve ...
EconomicsToday-Chapter24
... The Long-Run Industry Situation: Exit and Entry Long-Run Industry Supply Curve – A market supply curve showing the relationship between prices and quantities after firms have been allowed time to enter or exit from an industry, depending on whether there have been positive or negative economic pro ...
... The Long-Run Industry Situation: Exit and Entry Long-Run Industry Supply Curve – A market supply curve showing the relationship between prices and quantities after firms have been allowed time to enter or exit from an industry, depending on whether there have been positive or negative economic pro ...
Economics Homework 6 - White Plains Public Schools
... and quantity supplied are equal. (2) The financial and opportunity costs consumers pay when searching for a good or service. (3) A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded. (4) A situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied. 8. Minimum wage is ...
... and quantity supplied are equal. (2) The financial and opportunity costs consumers pay when searching for a good or service. (3) A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded. (4) A situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied. 8. Minimum wage is ...
8) You spent a total of $5 buying songs for your MP3 player
... 27) As an economy produces more of a good, the opportunity costs of producing it increases. This most likely occurs because A) as more of a good is produced the inputs used to produce that good will increase in price. B) consumers would be willing to pay higher prices for the good as more of the go ...
... 27) As an economy produces more of a good, the opportunity costs of producing it increases. This most likely occurs because A) as more of a good is produced the inputs used to produce that good will increase in price. B) consumers would be willing to pay higher prices for the good as more of the go ...
Ch 16 - Cut down version
... Find a general equilibrium by plotting both market-clearing curves on the same graph Horizontal axis shows the price of one good; vertical axis shows the price of the other good Intersection of the two market-clearing curves reveals the general equilibrium prices The two goods markets clear at t ...
... Find a general equilibrium by plotting both market-clearing curves on the same graph Horizontal axis shows the price of one good; vertical axis shows the price of the other good Intersection of the two market-clearing curves reveals the general equilibrium prices The two goods markets clear at t ...
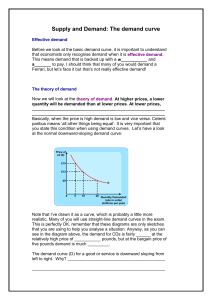
Supply and Demand: The demand curve
... analysis above, we can see that the price itself has the most important role. The rising price has acted as a signal to possible new firms who might want to join this expanding industry. It acted as an incentive, encouraging existing firms to produce more (the movement along the supply curve). You c ...
... analysis above, we can see that the price itself has the most important role. The rising price has acted as a signal to possible new firms who might want to join this expanding industry. It acted as an incentive, encouraging existing firms to produce more (the movement along the supply curve). You c ...
entry
... The output decision for a competitive firm: To maximize profit, produce the output level for which: MR = MC (that is, p = MC) . . . unless p < AVC. In that case, shut-down (produce zero output) for the short-run. If AVC < p < ATC, continue to produce in short-run, but exit in long-run if market cond ...
... The output decision for a competitive firm: To maximize profit, produce the output level for which: MR = MC (that is, p = MC) . . . unless p < AVC. In that case, shut-down (produce zero output) for the short-run. If AVC < p < ATC, continue to produce in short-run, but exit in long-run if market cond ...
Practice Question Set 1 Demand and Revenue Econ 416/516 Sports
... Each of the following 4 questions gives an equation that represents the demand for tickets for a sports team’s games. P represents the ticket price in dollars and Q represents the quantity of tickets demanded per game in thousands. For simplicity, assume that facility capacity is not an issue (i.e. ...
... Each of the following 4 questions gives an equation that represents the demand for tickets for a sports team’s games. P represents the ticket price in dollars and Q represents the quantity of tickets demanded per game in thousands. For simplicity, assume that facility capacity is not an issue (i.e. ...
Call Auction In Pre open session
... Fairer market especially for small, non professional investors because all trades get executed at the same price Simultaneity of trades eliminates possibility of front running customer orders ...
... Fairer market especially for small, non professional investors because all trades get executed at the same price Simultaneity of trades eliminates possibility of front running customer orders ...
File
... economists talk of increasing or decreasing supply, they mean shifts of the supply curve—a change in the quantity supplied at any given price. 8. There are five main factors that shift the supply curve: • A change in input prices • A change in the prices of related goods and services • A change in t ...
... economists talk of increasing or decreasing supply, they mean shifts of the supply curve—a change in the quantity supplied at any given price. 8. There are five main factors that shift the supply curve: • A change in input prices • A change in the prices of related goods and services • A change in t ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑