CE Comprehensive NC Final Review
... 3. What is the difference between a want and a need? 4. What are the three essential economic questions that all societies must answer? 5. Important economic terms - give the definition and an example of each: Economic term Definition ...
... 3. What is the difference between a want and a need? 4. What are the three essential economic questions that all societies must answer? 5. Important economic terms - give the definition and an example of each: Economic term Definition ...
Perfect Competition
... Competition • Since the firm is a price taker and an insignificant part of the total market, the individual firm has no control over the price it can charge, but it can sell as much as it wants at that price. The demand curve, therefore will be “perfectly elastic” (horizontal) at the market price. • ...
... Competition • Since the firm is a price taker and an insignificant part of the total market, the individual firm has no control over the price it can charge, but it can sell as much as it wants at that price. The demand curve, therefore will be “perfectly elastic” (horizontal) at the market price. • ...
Problems 13 Quantity supplied in monopoly market to maximize
... We can see that the Marginal Cost of the firm after subsidy (MC’) is smaller than its initial Marginal Cost (MC). The graphical proof is shown in the following picture: ...
... We can see that the Marginal Cost of the firm after subsidy (MC’) is smaller than its initial Marginal Cost (MC). The graphical proof is shown in the following picture: ...
ECON 6070-001 MA Microeconomics
... Addison Wesley, 1997. Course description: Microeconomics is about what goods get produced and bought, and at what prices. The course teaches the mathematical structure of microeconomic theory. It is designed for first-year MA students. The formulation of the consumer's and the firm's problems is rig ...
... Addison Wesley, 1997. Course description: Microeconomics is about what goods get produced and bought, and at what prices. The course teaches the mathematical structure of microeconomic theory. It is designed for first-year MA students. The formulation of the consumer's and the firm's problems is rig ...
Microeconomic Exam #3 Study Guide (Chapter 14-18)
... Firms can freely enter or exit the market (shape the LR outcome) o Analyzing revenue of the competitive firm Total revenue = P (fixed cost) *Q If the firm is small compared to the world market, it takes the price as given by market conditions Price doesn’t depend on the quantity of output ...
... Firms can freely enter or exit the market (shape the LR outcome) o Analyzing revenue of the competitive firm Total revenue = P (fixed cost) *Q If the firm is small compared to the world market, it takes the price as given by market conditions Price doesn’t depend on the quantity of output ...
Midterm - Wake Forest University
... a) The price elasticity of demand for a Mattoon6.0 must be less than one or inelastic. b) The price elasticity of demand for a Mattoon6.0 must be less than one or elastic. c) The price elasticity of demand for a Mattoon6.0 must be greater than one or inelastic. d) The price elasticity of demand for ...
... a) The price elasticity of demand for a Mattoon6.0 must be less than one or inelastic. b) The price elasticity of demand for a Mattoon6.0 must be less than one or elastic. c) The price elasticity of demand for a Mattoon6.0 must be greater than one or inelastic. d) The price elasticity of demand for ...
elasticity of demand
... week .They also noted down the changes that have taken place in prices of different commodities as well as the changes made in their sale. ...
... week .They also noted down the changes that have taken place in prices of different commodities as well as the changes made in their sale. ...
1. Market Failure and Economic Efficiency
... resources. Economic efficiency occurs when marginal benefit = marginal cost. Marginal benefit: the additional benefit (utility) to a consumer from consuming one more unit of a good or service. Marginal Benefit Curve = Demand Curve ...
... resources. Economic efficiency occurs when marginal benefit = marginal cost. Marginal benefit: the additional benefit (utility) to a consumer from consuming one more unit of a good or service. Marginal Benefit Curve = Demand Curve ...
Market Demand
... *Intensive margin – the change in demand due to each individual consumer already in the market at one price buying more/less as price changes (due to the downward slope of each individual demand curve). ...
... *Intensive margin – the change in demand due to each individual consumer already in the market at one price buying more/less as price changes (due to the downward slope of each individual demand curve). ...
Unit 5: Equilibrium Lesson 5.1: Equilibrium 1 What You Will Learn
... taquerias are willing to make a lot more than they were at prices below. However, the Sharks, hungry as ever, are not all that willing to pay the higher price. So we have a lot more quantity supplied of tacos than we have actually have quantity demanded of tacos. As a result, there is a taco surplus ...
... taquerias are willing to make a lot more than they were at prices below. However, the Sharks, hungry as ever, are not all that willing to pay the higher price. So we have a lot more quantity supplied of tacos than we have actually have quantity demanded of tacos. As a result, there is a taco surplus ...
Downlaod File
... weather that affected the quantity supplied. This change has affected a lot of other markets as mentioned in this case which are chicken market, fish market, rice market, meet market and feed market “grain”. The findings, that we cannot control the economy; it could rise based on some factors and fa ...
... weather that affected the quantity supplied. This change has affected a lot of other markets as mentioned in this case which are chicken market, fish market, rice market, meet market and feed market “grain”. The findings, that we cannot control the economy; it could rise based on some factors and fa ...
Potential Benefits of Production Information to Cattle Producers
... • Program that supports demand in event of food safety or bioterrorism crisis • Will help producers ...
... • Program that supports demand in event of food safety or bioterrorism crisis • Will help producers ...
Trade
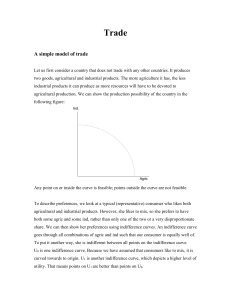
... But using the same reasoning, Y will not be chosen either. We can go further out until we come to Z, where the production possibility frontier and the indifference curve U2 are tangents. Here, there is no feasible point that will be better, so this is the optimal point in a closed economy. One way t ...
... But using the same reasoning, Y will not be chosen either. We can go further out until we come to Z, where the production possibility frontier and the indifference curve U2 are tangents. Here, there is no feasible point that will be better, so this is the optimal point in a closed economy. One way t ...
Econ 111 (04) 2nd MT Winter 2015 A.tst
... 26) Monopolistic competition differs from monopoly because in monopolistic competition A) firms maximize profits. B) firms are free to enter and exit. C) firms set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost to maximize profit. D) All of the above are differences between monopoly and monopolistically c ...
... 26) Monopolistic competition differs from monopoly because in monopolistic competition A) firms maximize profits. B) firms are free to enter and exit. C) firms set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost to maximize profit. D) All of the above are differences between monopoly and monopolistically c ...
File
... Perfectly Inelastic Supply S1 Elasticity of supply = 0 Quantity supplied is the same for any price! ...
... Perfectly Inelastic Supply S1 Elasticity of supply = 0 Quantity supplied is the same for any price! ...
Shifts in the Demand Curve
... changes in price. It does not consider the effects of news reports of any one of the thousands of other factors that change from day to day that could affect the demand for a particular good. • A demand curve is accurate only as long as there are no changes other than price that could affect the con ...
... changes in price. It does not consider the effects of news reports of any one of the thousands of other factors that change from day to day that could affect the demand for a particular good. • A demand curve is accurate only as long as there are no changes other than price that could affect the con ...
4 Demand Systems for Factors of Production
... factor price indices are normalized to be one in 1947, and the factor inputs in that year are in billions of 1947 dollars. Then, in each year, the product of a factor price times a factor quantity equals payments to that factor in billions of current dollars. a. Using these data, and assuming consta ...
... factor price indices are normalized to be one in 1947, and the factor inputs in that year are in billions of 1947 dollars. Then, in each year, the product of a factor price times a factor quantity equals payments to that factor in billions of current dollars. a. Using these data, and assuming consta ...
Ed Dolan, Econ 101, Hayek, and Why We are Losing the War
... Follow this link to view the original graph from which this one was derived ...
... Follow this link to view the original graph from which this one was derived ...
Supply and Demand
... goods will increase and decrease, and the supply of goods will rise and fall. As these things take place, prices adjust to keep markets in balance. We will study how prices and quantities adjust to changes in demand and supply, and see how changes in prices serve as signals to buyers and sellers. 2. ...
... goods will increase and decrease, and the supply of goods will rise and fall. As these things take place, prices adjust to keep markets in balance. We will study how prices and quantities adjust to changes in demand and supply, and see how changes in prices serve as signals to buyers and sellers. 2. ...
Problem Set 5
... c. Deterioration in the quality of the good. d. All of the above are potential impacts of an effective price ceiling. 3. Suppose that the supply of labour is perfectly elastic. Then a labour-saving invention, such as automatic teller machines in the banking industry, results in a a. a decrease in em ...
... c. Deterioration in the quality of the good. d. All of the above are potential impacts of an effective price ceiling. 3. Suppose that the supply of labour is perfectly elastic. Then a labour-saving invention, such as automatic teller machines in the banking industry, results in a a. a decrease in em ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑