AP Micro Syllabus
... Additional assignments may/will include, but are not limited to, web-based assignments, special projects, research projects, oral and multi-media presentations, simulations, round-table discussions, and group work. Anticipated Homework/Study Load: It is anticipated that students in AP Microeconomi ...
... Additional assignments may/will include, but are not limited to, web-based assignments, special projects, research projects, oral and multi-media presentations, simulations, round-table discussions, and group work. Anticipated Homework/Study Load: It is anticipated that students in AP Microeconomi ...
Pure Monopoly - Cloudfront.net
... Monopoly Demand Table 10.1 Revenue and Cost Data of a Pure Monopolist Revenue Data ...
... Monopoly Demand Table 10.1 Revenue and Cost Data of a Pure Monopolist Revenue Data ...
Anderson, PUBLIC FINANCE Chapter 12 End-of
... 1. Suppose that the demand for a good is given by the inverse demand function: p =0-3q. a. Plot the demand curve on a graph. b. Compute the price at which 2 units of the good will be demanded. c. Suppose that a unit tax of 1 is introduced. Plot the new demand curve. d. What is the price at which 2 u ...
... 1. Suppose that the demand for a good is given by the inverse demand function: p =0-3q. a. Plot the demand curve on a graph. b. Compute the price at which 2 units of the good will be demanded. c. Suppose that a unit tax of 1 is introduced. Plot the new demand curve. d. What is the price at which 2 u ...
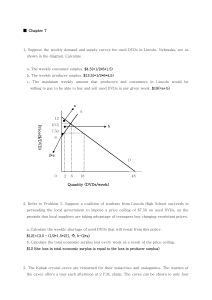
Chapter 7 Practice Questions
... causes an increase in competition so that the firms cannot raise their prices (because then consumers would opt to buy the goods from other firms who offer it for lower prices), if they want to stay in business. Therefore, in the long term, all firms would be breaking even. b) To what extent is the ...
... causes an increase in competition so that the firms cannot raise their prices (because then consumers would opt to buy the goods from other firms who offer it for lower prices), if they want to stay in business. Therefore, in the long term, all firms would be breaking even. b) To what extent is the ...
Perfect Competition
... of the entire market or industry. Firms produce ‘homogeneous’ products. Relative ease of firm entry in to or exit out of the market. Information about prices and production costs widely available. Firms have no control over prices and are price ‘takers’. In long run, product price = minimum average ...
... of the entire market or industry. Firms produce ‘homogeneous’ products. Relative ease of firm entry in to or exit out of the market. Information about prices and production costs widely available. Firms have no control over prices and are price ‘takers’. In long run, product price = minimum average ...
What is the relationship between economic and accounting profit
... 3. Economic profits may result from: a. innovation b. risk taking c. exploiting market inefficiencies d. all the above e. a and b 4. The demand for personal computers has been estimated to be Q = 500,000 – 700P + 200I - 500S. Assume that per capita income I is $13,000 and the average price of softwa ...
... 3. Economic profits may result from: a. innovation b. risk taking c. exploiting market inefficiencies d. all the above e. a and b 4. The demand for personal computers has been estimated to be Q = 500,000 – 700P + 200I - 500S. Assume that per capita income I is $13,000 and the average price of softwa ...
three rules and four models spring 2013 answers
... one firm tries to charge a higher price all customers would buy from someone else. If one firm decides to sell nothing it has no effect on the market supply because there each firm produces an insignificant amount of the total Why does P = MR? Because the demand curve s perfectly price elastic. Sinc ...
... one firm tries to charge a higher price all customers would buy from someone else. If one firm decides to sell nothing it has no effect on the market supply because there each firm produces an insignificant amount of the total Why does P = MR? Because the demand curve s perfectly price elastic. Sinc ...
Monopoly - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • The intersection of the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves establishes the profit-maximizing rate of output. • The demand curve tells us the highest price consumers are willing to pay for that specific quantity of output. • Only one price is compatible with the profit-maximizing rate of out ...
... • The intersection of the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves establishes the profit-maximizing rate of output. • The demand curve tells us the highest price consumers are willing to pay for that specific quantity of output. • Only one price is compatible with the profit-maximizing rate of out ...
Three Rules and Four Models Fall 2012 Answers
... one firm tries to charge a higher price all customers would buy from someone else. If one firm decides to sell nothing it has no effect on the market supply because there each firm produces an insignificant amount of the total Why does P = MR? Because the demand curve s perfectly price elastic. Sinc ...
... one firm tries to charge a higher price all customers would buy from someone else. If one firm decides to sell nothing it has no effect on the market supply because there each firm produces an insignificant amount of the total Why does P = MR? Because the demand curve s perfectly price elastic. Sinc ...
Chapter 14
... – A large number of firms in the market. – That each firm produces and sells a differentiated product with other firm’s products being close substitutes. – Low barriers to entry into the industry. – Firm has some price control but it is limited by the number of available substitutes. ...
... – A large number of firms in the market. – That each firm produces and sells a differentiated product with other firm’s products being close substitutes. – Low barriers to entry into the industry. – Firm has some price control but it is limited by the number of available substitutes. ...
ch 15 monopoly
... discrimination, and why is each important? MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 16) Which of the following statements correctly describes short run profit in 16) ______ perfectly competitive and monopoly markets? A) Short-run profit i ...
... discrimination, and why is each important? MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 16) Which of the following statements correctly describes short run profit in 16) ______ perfectly competitive and monopoly markets? A) Short-run profit i ...
Practice Final Exam
... c. there are many existing sellers, but it is difficult for new sellers to enter the market d. one dominant seller must negotiate with one dominant buyer e. there are many sellers, and they produce a standardized product 3. In perfect competition, no individual producer can significantly affect the ...
... c. there are many existing sellers, but it is difficult for new sellers to enter the market d. one dominant seller must negotiate with one dominant buyer e. there are many sellers, and they produce a standardized product 3. In perfect competition, no individual producer can significantly affect the ...
Problems 7
... afford to cut each family's annual taxes? 5 dollars d. If the government abandoned its oil subsidy and implemented the tax cut, by how much would each family be better off? 0.5 dollar e. How does the resulting total gain for the 1 million families compare with your calculation of the lost surplus in ...
... afford to cut each family's annual taxes? 5 dollars d. If the government abandoned its oil subsidy and implemented the tax cut, by how much would each family be better off? 0.5 dollar e. How does the resulting total gain for the 1 million families compare with your calculation of the lost surplus in ...
Price Optimization and Competition for Multi-Products under the Nested Logit Model with Product-Differentiated Price Coefficients
... coefficients and general nest-heterogenous degrees and show that the adjusted markup, which is defined as price minus cost minus the reciprocal of the price coefficient, is constant across all the products in each nest at optimal prices. When optimizing multiple nests of products, the adjusted neste ...
... coefficients and general nest-heterogenous degrees and show that the adjusted markup, which is defined as price minus cost minus the reciprocal of the price coefficient, is constant across all the products in each nest at optimal prices. When optimizing multiple nests of products, the adjusted neste ...
Week 9 Slides:
... – U sets pU equal to pM minus D’s MC (zero in this case). • Idea: U chooses upstream and downstream price. – Internalise externality. – Just make sure D gets positive profits. • So there are contractual solutions to double marginalisation – But many supply chains still suffer. – For example, we assu ...
... – U sets pU equal to pM minus D’s MC (zero in this case). • Idea: U chooses upstream and downstream price. – Internalise externality. – Just make sure D gets positive profits. • So there are contractual solutions to double marginalisation – But many supply chains still suffer. – For example, we assu ...
Chapter24 - QC Economics
... The Long-Run Industry Situation: Exit and Entry Long-Run Industry Supply Curve – A market supply curve showing the relationship between prices and quantities after firms have been allowed time to enter or exit from an industry, depending on whether there have been positive or negative economic pro ...
... The Long-Run Industry Situation: Exit and Entry Long-Run Industry Supply Curve – A market supply curve showing the relationship between prices and quantities after firms have been allowed time to enter or exit from an industry, depending on whether there have been positive or negative economic pro ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑