Monopoly A monopoly is a firm who is the sole seller of its product
... When output increases, there are two effects on revenue, P×Q. First, there is the output effect. When Q goes up, the second part of P×Q is higher. Second, there is the price effect. When Q goes up, the first part of P×Q is lower, due to the fact that we have a downward sloping demand curve. If the ...
... When output increases, there are two effects on revenue, P×Q. First, there is the output effect. When Q goes up, the second part of P×Q is higher. Second, there is the price effect. When Q goes up, the first part of P×Q is lower, due to the fact that we have a downward sloping demand curve. If the ...
Price Elasticity of Demand
... price elasticity is greater than 1 in absolute value. Relatively Inelastic Demand: Demand is inelastic when the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price, so the price elasticity is less than 1 in absolute ...
... price elasticity is greater than 1 in absolute value. Relatively Inelastic Demand: Demand is inelastic when the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price, so the price elasticity is less than 1 in absolute ...
Document
... Taxes on consumption or production generates the same effects on the market A positive difference is created between the price paid by the consumer and the one paid by the producer This difference is indeed the same, independently on whether the tax is imposed on production or consumption ...
... Taxes on consumption or production generates the same effects on the market A positive difference is created between the price paid by the consumer and the one paid by the producer This difference is indeed the same, independently on whether the tax is imposed on production or consumption ...
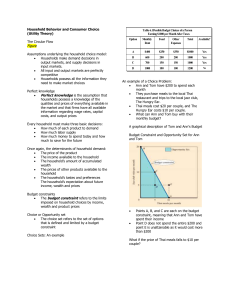
Household Behavior and Consumer Choice (Utility Theory) The
... Points A, B, and C are each on the budget constraint, meaning that Ann and Tom have spent their income Point D does not spend the entire $200 and point E is unattainable as it would cost more than $200 ...
... Points A, B, and C are each on the budget constraint, meaning that Ann and Tom have spent their income Point D does not spend the entire $200 and point E is unattainable as it would cost more than $200 ...
Supply and Shifters of Supply
... government can reduce the Regulation occurs when the supply of some goods by placing an government steps into a market to Production excise tax on them. An excise tax affect the price, quantity, or quality of tax on the production orof saleFuture of a good. Regulation usually raises 6.is aExpectatio ...
... government can reduce the Regulation occurs when the supply of some goods by placing an government steps into a market to Production excise tax on them. An excise tax affect the price, quantity, or quality of tax on the production orof saleFuture of a good. Regulation usually raises 6.is aExpectatio ...
Document
... Besides price, demand depends on buyers’ incomes, tastes, expectations, the prices of substitutes and complements, and number of buyers. If one of these factors changes, the D curve shifts. ...
... Besides price, demand depends on buyers’ incomes, tastes, expectations, the prices of substitutes and complements, and number of buyers. If one of these factors changes, the D curve shifts. ...
ECON 290 Intermediate Microeconomics I
... resort area is -5 in the month of May, while in July the elasticity falls to -1.5. A single vendor supplies the popsicles to the beachgoers. If the marginal cost per popsicle is $0.60, how much should the vendor charge per popsicle in May and June. (2 marks) ...
... resort area is -5 in the month of May, while in July the elasticity falls to -1.5. A single vendor supplies the popsicles to the beachgoers. If the marginal cost per popsicle is $0.60, how much should the vendor charge per popsicle in May and June. (2 marks) ...
Practice_Questions_Midterm_Economics_651
... equal to 0.75. Based on this information, would you advise a firm in this industry to increase its price? If so, what is the percentage loss in total sales this firm should expect to experience? A. Definitely yes. Total revenues would increase, since < 1. Sales would decrease by only .75% for each ...
... equal to 0.75. Based on this information, would you advise a firm in this industry to increase its price? If so, what is the percentage loss in total sales this firm should expect to experience? A. Definitely yes. Total revenues would increase, since < 1. Sales would decrease by only .75% for each ...
The Digital Economist
... a. Given this equation, Economy-class tickets are Price (Elastic/ Inelastic):___________, a (Normal/Inferior)__________________ good, a (Complement/Substitute)___________ for Bus Tickets, and a (Complement/Substitute) _______________ for Hotel Rooms. b. Holding all other variables constant, if marke ...
... a. Given this equation, Economy-class tickets are Price (Elastic/ Inelastic):___________, a (Normal/Inferior)__________________ good, a (Complement/Substitute)___________ for Bus Tickets, and a (Complement/Substitute) _______________ for Hotel Rooms. b. Holding all other variables constant, if marke ...
Answers to Questions in Chapter 9
... (d) Firms providing employees with fringe benefits. Even if marginal productivity theory were not relevant in these cases, the theory would still be accurate in the sense that if firms wanted to maximise profits then they should employ workers to the point where MCL = MRPL. But do any of the above f ...
... (d) Firms providing employees with fringe benefits. Even if marginal productivity theory were not relevant in these cases, the theory would still be accurate in the sense that if firms wanted to maximise profits then they should employ workers to the point where MCL = MRPL. But do any of the above f ...
Slide - MyWeb
... red. From now on all diagrams relating to the behavior of households will be blue or shades of blue and all diagrams relating to the behavior of firms will be red or shades of red. The green color indicates a monetary flow. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall ...
... red. From now on all diagrams relating to the behavior of households will be blue or shades of blue and all diagrams relating to the behavior of firms will be red or shades of red. The green color indicates a monetary flow. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall ...
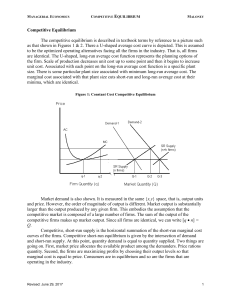
Competitive Equilibrium
... excess profits or losses are received by the firms operating in the industry.1 In terms of the picture described in Figure 1, as the number of firms changes, the short-run supply curve shifts. If the number of firms increases, the supply curve shifts out. If the number of firms contracts, the supply ...
... excess profits or losses are received by the firms operating in the industry.1 In terms of the picture described in Figure 1, as the number of firms changes, the short-run supply curve shifts. If the number of firms increases, the supply curve shifts out. If the number of firms contracts, the supply ...
0506 4C news report by Iris Lau
... service of the pregnant women from the mainland China are greatly reduced. On the other hand, since private hospitals and public hospitals are in competitive demand and they can be replaced by each other. Decrease in quantity demanded for public hospitals service results in increase in demand for pr ...
... service of the pregnant women from the mainland China are greatly reduced. On the other hand, since private hospitals and public hospitals are in competitive demand and they can be replaced by each other. Decrease in quantity demanded for public hospitals service results in increase in demand for pr ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑