Problem Sets - MIT Biology
... dominant phenotypes were used (and these cannot be used in complementation tests), or strains that were not true-breeding were used. Using strains that are not true-breeding is not the proper way to do a complementation test, because then multiple genotypes and phenotypes are produced instead of jus ...
... dominant phenotypes were used (and these cannot be used in complementation tests), or strains that were not true-breeding were used. Using strains that are not true-breeding is not the proper way to do a complementation test, because then multiple genotypes and phenotypes are produced instead of jus ...
Rare inherited disorders of fibrinogen
... (activity and antigen between 0.5 g L)1 and lower limit of normal range for local laboratory). As hypofibrinogenemia is a proportional decrease of functional and immunoreactive fibrinogen, most fibrin-based coagulation tests are variably prolonged, the most sensitive test being thrombin time (usuall ...
... (activity and antigen between 0.5 g L)1 and lower limit of normal range for local laboratory). As hypofibrinogenemia is a proportional decrease of functional and immunoreactive fibrinogen, most fibrin-based coagulation tests are variably prolonged, the most sensitive test being thrombin time (usuall ...
C. neoformans
... N2 nematodes were fed on lawns of C. neoformans and then at different time-points transferred to lawns of non-pathogenic cryptococci. All nematodes that survived transfer were rescued, regained normal non-distended anatomy and no C. neoformans yeast cells could be cultured followed “grinding” of the ...
... N2 nematodes were fed on lawns of C. neoformans and then at different time-points transferred to lawns of non-pathogenic cryptococci. All nematodes that survived transfer were rescued, regained normal non-distended anatomy and no C. neoformans yeast cells could be cultured followed “grinding” of the ...
Baker, B. S., Hoff, G., Kaufman, T. C., Wolfner, M. W., and Hazelrigg, T. (1991). A cytopgenetic analysis of the doublesex locus and its flanking regions. Genetics 127: 125-138.
... affects female sexual differentiation, but only weakly affects male sexual differentiation. T h e interactions of ~ s x " ~ ~with ' * mutations in other genes affecting sexual differentiation are described. These results are discussed in terms of the recent molecular findings that the dsx locus enco ...
... affects female sexual differentiation, but only weakly affects male sexual differentiation. T h e interactions of ~ s x " ~ ~with ' * mutations in other genes affecting sexual differentiation are described. These results are discussed in terms of the recent molecular findings that the dsx locus enco ...
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis katG promoter region contains a
... used as a source of the M. paratuberculosis promoter (Murray et al., 1992). The 218 bp HindIII–BamHI fragment from pANIIIW was cloned into the corresponding restriction sites of pJCluc to form pLPan. In this construct, the PAN promoter is in the correct orientation to promote expression of the lucif ...
... used as a source of the M. paratuberculosis promoter (Murray et al., 1992). The 218 bp HindIII–BamHI fragment from pANIIIW was cloned into the corresponding restriction sites of pJCluc to form pLPan. In this construct, the PAN promoter is in the correct orientation to promote expression of the lucif ...
Finding New Clock Components: Past and Future
... Drosophilia double-time, and hamster tau mutants fall into this category in which mutations caused ≥4-h period changes and null mutations were not available. One could of course argue that this analysis is biased—we have only gone after the extreme mutations, and so these are the ones that we know a ...
... Drosophilia double-time, and hamster tau mutants fall into this category in which mutations caused ≥4-h period changes and null mutations were not available. One could of course argue that this analysis is biased—we have only gone after the extreme mutations, and so these are the ones that we know a ...
Table 2
... pathways, can help prioritize candidate genes for further analysis. However, with rare exceptions, mutations in genes ...
... pathways, can help prioritize candidate genes for further analysis. However, with rare exceptions, mutations in genes ...
Identity-by-descent filtering of exome sequence data for disease
... the disease gene must be located within an IBD = 2 region, but that affected siblings may also share other IBD = 2 regions by chance. Our method can be used to identify the chromosomal regions that are compatible with the inheritance patterns of a recessive monogenic disorder and can be combined wit ...
... the disease gene must be located within an IBD = 2 region, but that affected siblings may also share other IBD = 2 regions by chance. Our method can be used to identify the chromosomal regions that are compatible with the inheritance patterns of a recessive monogenic disorder and can be combined wit ...
National Toxicology Program Technical Reports Peer Review Panel Meeting October 29, 2013
... several studies referenced in the draft report that indicated negative results with VDC. He also cited Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 51 from the World Health Organization, a report from the Scientific Committee on Occupational Exposure Limits of the European Commission, and a 20 ...
... several studies referenced in the draft report that indicated negative results with VDC. He also cited Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 51 from the World Health Organization, a report from the Scientific Committee on Occupational Exposure Limits of the European Commission, and a 20 ...
genetics - Krishikosh
... in 1900. Educated at the University of Kiev, he began teaching and research at Kiev Agricultural Institute and the University of Leningrad. He came to the United States in 1927, worked with T. H. Morgan and his group at Columbia University and the California Institute of Technology from 1929-1940, w ...
... in 1900. Educated at the University of Kiev, he began teaching and research at Kiev Agricultural Institute and the University of Leningrad. He came to the United States in 1927, worked with T. H. Morgan and his group at Columbia University and the California Institute of Technology from 1929-1940, w ...
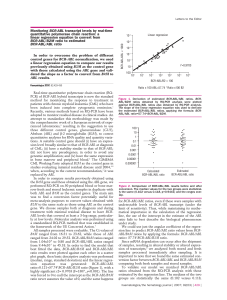
Natural variation in nucleolar dominance reveals
... Navashin noted that in numerous interspecies hybrids, only the chromosomes of one parent display these secondary constrictions (5). Nuclear run-on assays later suggested that transcription of only one parental set of rRNA genes is the molecular explanation for nucleolar dominance (11, 12). Presumabl ...
... Navashin noted that in numerous interspecies hybrids, only the chromosomes of one parent display these secondary constrictions (5). Nuclear run-on assays later suggested that transcription of only one parental set of rRNA genes is the molecular explanation for nucleolar dominance (11, 12). Presumabl ...
The Use of Benlate for Distinguishing Between Haploid and Diploid
... Supporting evidence also comes from the parasexual analyses of the five diploid strains. These diploids were all more sensitive to Benlate than their parental haploid strains, and to the meiotic progeny from the three crosses. The parasexual segregants were provisionally classified as diploid or hap ...
... Supporting evidence also comes from the parasexual analyses of the five diploid strains. These diploids were all more sensitive to Benlate than their parental haploid strains, and to the meiotic progeny from the three crosses. The parasexual segregants were provisionally classified as diploid or hap ...
The Use of Benlate for Distinguishing Between Haploid and Diploid
... Supporting evidence also comes from the parasexual analyses of the five diploid strains. These diploids were all more sensitive to Benlate than their parental haploid strains, and to the meiotic progeny from the three crosses. The parasexual segregants were provisionally classified as diploid or hap ...
... Supporting evidence also comes from the parasexual analyses of the five diploid strains. These diploids were all more sensitive to Benlate than their parental haploid strains, and to the meiotic progeny from the three crosses. The parasexual segregants were provisionally classified as diploid or hap ...
Sideroblastic Anemias Disorder Subdivisions Idiopathic Sideroblastic Anemia
... occur in proximity to iron (Gutteridge et al, 1991). The oxidative metabolic machinery of the mitochondrion makes it an ideal site for the generation of reactive oxygen species. The primary damage that produces iron-laden mitochondria in sideroblastic anemia could produce a feedback loop of escalati ...
... occur in proximity to iron (Gutteridge et al, 1991). The oxidative metabolic machinery of the mitochondrion makes it an ideal site for the generation of reactive oxygen species. The primary damage that produces iron-laden mitochondria in sideroblastic anemia could produce a feedback loop of escalati ...
Evolution of mating types driven by purifying selection
... Sexual cell fusion combines genetic material of two gametes, but why the two reproductive cells have to belong to distinct self-incompatible gamete classes is not known. In a vast majority of sexual eukaryotes, mitochondria are inherited uniparentally from only one of the two mating types, which is ...
... Sexual cell fusion combines genetic material of two gametes, but why the two reproductive cells have to belong to distinct self-incompatible gamete classes is not known. In a vast majority of sexual eukaryotes, mitochondria are inherited uniparentally from only one of the two mating types, which is ...
PDF
... start codon of the abcc6a gene via BAC recombineering (Bussmann and Schulte-Merker, 2011). The mosaic expression of Tg(abcc6a: gal4;uas:gfp) at 7 dpf revealed GFP in the notochord and in cells near the operculum and cleithrum (Fig. 3D; supplementary material Fig. S3). Crossing the stable GAL4 line w ...
... start codon of the abcc6a gene via BAC recombineering (Bussmann and Schulte-Merker, 2011). The mosaic expression of Tg(abcc6a: gal4;uas:gfp) at 7 dpf revealed GFP in the notochord and in cells near the operculum and cleithrum (Fig. 3D; supplementary material Fig. S3). Crossing the stable GAL4 line w ...
New functions of the Drosophila rhomboid gene
... have dominant constitutive extra wing vein phenotypes (Sturtevant et al., 1993), we expected that a more systematic attempt to generate dominant alleles might reveal new functions of rho. Furthermore, such dominant phenotypes could serve as valuable genetic tools for isolating second site suppressor ...
... have dominant constitutive extra wing vein phenotypes (Sturtevant et al., 1993), we expected that a more systematic attempt to generate dominant alleles might reveal new functions of rho. Furthermore, such dominant phenotypes could serve as valuable genetic tools for isolating second site suppressor ...
Monitoring BCR-ABL transcript levels by real-time
... method for monitoring the response to treatment in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who have been induced into complete cytogenetic remission.1 Recently, various methods based on RQ-PCR have been adopted to monitor residual disease in clinical studies. An attempt to standardize this meth ...
... method for monitoring the response to treatment in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who have been induced into complete cytogenetic remission.1 Recently, various methods based on RQ-PCR have been adopted to monitor residual disease in clinical studies. An attempt to standardize this meth ...
Oncogenomics
Oncogenomics is a relatively new sub-field of genomics that applies high throughput technologies to characterize genes associated with cancer. Oncogenomics is synonymous with ""cancer genomics"". Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of mutations to DNA leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers, and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin, and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment.Besides understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms that initiates or drives cancer progression, one of the main goals of oncogenomics is to allow for the development of personalized cancer treatment. Cancer develops due to an accumulation of mutations in DNA. These mutations accumulate randomly, and thus, different DNA mutations and mutation combinations exist between different individuals with the same type of cancer. Thus, identifying and targeting specific mutations which have occurred in an individual patient may lead to increased efficacy of cancer therapy.The completion of the Human Genome Project has greatly facilitated the field of oncogenomics and has increased the abilities of researchers to find cancer causing genes. In addition, the sequencing technologies now available for sequence generation and data analysis have been applied to the study of oncogenomics. With the amount of research conducted on cancer genomes and the accumulation of databases documenting the mutational changes, it has been predicted that the most important cancer-causing mutations, rearrangements, and altered expression levels will be cataloged and well characterized within the next decade.Cancer research may look either on the genomic level at DNA mutations, the epigenetic level at methylation or histone modification changes, the transcription level at altered levels of gene expression, or the protein level at altered levels of protein abundance and function in cancer cells. Oncogenomics focuses on the genomic, epigenomic, and transcript level alterations in cancer.