Nucleic Acids - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria. ...
... is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria. ...
Practice MC Questions
... ____ 21. The 'Central Dogma' states that the flow of genetic information is in the direction A. protein, RNA, protein B. RNA, DNA, RNA C. protein, RNA, DNA D. RNA, DNA, protein E. DNA, RNA, protein ____ 22. The function of the polyadenine tail that is added to mRNA in eukaryotic cells is to A. prev ...
... ____ 21. The 'Central Dogma' states that the flow of genetic information is in the direction A. protein, RNA, protein B. RNA, DNA, RNA C. protein, RNA, DNA D. RNA, DNA, protein E. DNA, RNA, protein ____ 22. The function of the polyadenine tail that is added to mRNA in eukaryotic cells is to A. prev ...
ch 3 notes
... The DNA in your bone cells is exactly like the DNA in your skin cells, which is exactly like the DNA in your hair cells, etc….. The DNA Molecule: The Genetic Code DNA: The blueprint of life Chemical template for every aspect of organisms Double helix, ladderlike structure Ladder forms nucleotide Lad ...
... The DNA in your bone cells is exactly like the DNA in your skin cells, which is exactly like the DNA in your hair cells, etc….. The DNA Molecule: The Genetic Code DNA: The blueprint of life Chemical template for every aspect of organisms Double helix, ladderlike structure Ladder forms nucleotide Lad ...
Unit 4 Review KEY File
... D. What is the end result of translation?At the ribosomes a protein is made 17. Using the following mRNA strand, what would the 3 complementary anticodons of tRNA look like and what amino acids would be attached? ...
... D. What is the end result of translation?At the ribosomes a protein is made 17. Using the following mRNA strand, what would the 3 complementary anticodons of tRNA look like and what amino acids would be attached? ...
Biol 505 EXAM 1 (100 points): Due Wed 10/14/09 at the beginning
... drawing,identify (1) origin, (2) polarity (5’ and 3’ ends) of all template strands and newly synthesized strands, (3) leading and lagging strands, (4) Okazaki fragments, and (5) location of primers. 5. What are the major classes of RNA? Where would you expect to find each class of RNA within eukaryo ...
... drawing,identify (1) origin, (2) polarity (5’ and 3’ ends) of all template strands and newly synthesized strands, (3) leading and lagging strands, (4) Okazaki fragments, and (5) location of primers. 5. What are the major classes of RNA? Where would you expect to find each class of RNA within eukaryo ...
Biochemistry ± DNA Chemistry and Analysis DNA o Adenosine
... x A=T melts at lower temps than GŁ& Annealing: H-bond formation allows dsDNA to form complementary single strand o Confirmations of the Double Helix Same base pairing rules apply, but may function differently in gene regulation / expression x Changes in shape of minor / major grooves affect prot ...
... x A=T melts at lower temps than GŁ& Annealing: H-bond formation allows dsDNA to form complementary single strand o Confirmations of the Double Helix Same base pairing rules apply, but may function differently in gene regulation / expression x Changes in shape of minor / major grooves affect prot ...
GE Nova Video Questions
... The following questions are based on the video “Genetic Engineering” available from Phillip & Harris catalogues. Worksheet on Novo Note: This video is 15 minutes in total. The answers to the worksheet are found between 6.55 minutes and 10 minutes approx. ...
... The following questions are based on the video “Genetic Engineering” available from Phillip & Harris catalogues. Worksheet on Novo Note: This video is 15 minutes in total. The answers to the worksheet are found between 6.55 minutes and 10 minutes approx. ...
Introduction to Genetics and Genomics
... and numerous others have shown in both preclinical and clinical studies that BRCA1 is an important determinant of chemotherapy responses in breast cancer. In this review we will outline the current understanding of the role of BRCA1 as a determinant of response to DNA damaging and microtubule damagi ...
... and numerous others have shown in both preclinical and clinical studies that BRCA1 is an important determinant of chemotherapy responses in breast cancer. In this review we will outline the current understanding of the role of BRCA1 as a determinant of response to DNA damaging and microtubule damagi ...
presentation name
... Protein vs. DNA? 1952 Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Blender Experiment • Bacteriophage passed on DNA to next generation, not protein • Radioactive isotopes: 32P in DNA, 35S in Protein • 2nd generation only had 32P present. • Proves DNA as genetic material! ...
... Protein vs. DNA? 1952 Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Blender Experiment • Bacteriophage passed on DNA to next generation, not protein • Radioactive isotopes: 32P in DNA, 35S in Protein • 2nd generation only had 32P present. • Proves DNA as genetic material! ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... a phosphate group, and a nitrogencontaining base. There are four kinds of bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. James Watson and Francis Crick discovered that DNA is shaped like a double helix, or a twisted ladder, in which two strands are wound around each other. The two strands are held ...
... a phosphate group, and a nitrogencontaining base. There are four kinds of bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. James Watson and Francis Crick discovered that DNA is shaped like a double helix, or a twisted ladder, in which two strands are wound around each other. The two strands are held ...
Exp 4 Lecture - Seattle Central College
... In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering involves inserting genes coding for new traits into a plasmid. • In this experiment, the pGLO plasmi ...
... In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering involves inserting genes coding for new traits into a plasmid. • In this experiment, the pGLO plasmi ...
Forensic DNA Fingerprinting Kit - Bio-Rad
... 1. How important is enzyme concentration for a DNA digest? 2. How important is DNA concentration (substrate) for a DNA digest? 3. How important is digest time for a DNA digest? 4. How important is digest temperature for a DNA digest? 5. How important is thoroughly mixing the sample prior to a D ...
... 1. How important is enzyme concentration for a DNA digest? 2. How important is DNA concentration (substrate) for a DNA digest? 3. How important is digest time for a DNA digest? 4. How important is digest temperature for a DNA digest? 5. How important is thoroughly mixing the sample prior to a D ...
Lecture Three: Genes and Inheritance
... When a cell needs to make protein, it “unzips” the DNA double helix, and reads the letters. As it reads, special proteins called enzymes manufacture a brand new strand of RNA that matches the code on the DNA. This process is called transcription. (“Transcription” literally means “writing again”, Tha ...
... When a cell needs to make protein, it “unzips” the DNA double helix, and reads the letters. As it reads, special proteins called enzymes manufacture a brand new strand of RNA that matches the code on the DNA. This process is called transcription. (“Transcription” literally means “writing again”, Tha ...
Infection cycle: DNA viruses
... – T ags in SV40 enhance first and then suppresses early; – E ag in BPV is an enhancer for late genes – Mutations in T or Eag/transition lead to tumors ...
... – T ags in SV40 enhance first and then suppresses early; – E ag in BPV is an enhancer for late genes – Mutations in T or Eag/transition lead to tumors ...
Restriction Enzymes, Gel Electrophoresis and Mapping DNA
... • Hybridization kinetics—complexity of regions of DNA, no specifics ...
... • Hybridization kinetics—complexity of regions of DNA, no specifics ...
Fluorescent dye, SYBR Green, is incorporated into PCR reaction
... – 1cM, for example • Probably ~ 1 MB or more in humans • Need very many families to get closer than this in human, or very large populations ...
... – 1cM, for example • Probably ~ 1 MB or more in humans • Need very many families to get closer than this in human, or very large populations ...
File
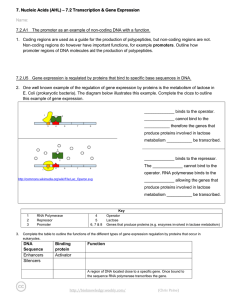
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
DNA WebQuest
... 1. Protein Synthesis is the making of __________________ from instructions coded for in the DNA. 2. There are many types of proteins and a variety of functions which include: hormones (send signals), transportation (move molecules), structural proteins (build form) and ______________ (speed up the r ...
... 1. Protein Synthesis is the making of __________________ from instructions coded for in the DNA. 2. There are many types of proteins and a variety of functions which include: hormones (send signals), transportation (move molecules), structural proteins (build form) and ______________ (speed up the r ...
BioSc 231 Exam 5 2005
... D. cut DNA that has been digested with a restriction endonuclease for use in a cloning experiment. Short Answer (variable points) (2 points) Many new cloning vectors have a DNA sequence called a polylinker (or multicloning site) that contains the recognition sequences for many restriction endonuclea ...
... D. cut DNA that has been digested with a restriction endonuclease for use in a cloning experiment. Short Answer (variable points) (2 points) Many new cloning vectors have a DNA sequence called a polylinker (or multicloning site) that contains the recognition sequences for many restriction endonuclea ...
Label each of the following as homozygous or heterozygous
... 25. From the above pedigree, what type of genetic disorder can you infer that it represents? 26. How many offspring did the P Generation produce? 27. Describe, using a Punnett square, how the F1 generation was determined (determine the genotypes of the parents and do a Punnett square) ...
... 25. From the above pedigree, what type of genetic disorder can you infer that it represents? 26. How many offspring did the P Generation produce? 27. Describe, using a Punnett square, how the F1 generation was determined (determine the genotypes of the parents and do a Punnett square) ...
Hfr cells
... 2. How does the term auxotroph relate to mutant selection? 3. Why is replica plating necessary for the indirect selection of mutants? 4. What is the Ames test? How and why does it result in positive mutant selection? ...
... 2. How does the term auxotroph relate to mutant selection? 3. Why is replica plating necessary for the indirect selection of mutants? 4. What is the Ames test? How and why does it result in positive mutant selection? ...
Genetically modified foods by Tim Harding B.Sc
... plant and animal breeding (long-term) mutagenesis (hit or miss) genetic engineering (short-term) ...
... plant and animal breeding (long-term) mutagenesis (hit or miss) genetic engineering (short-term) ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.