GASTROINTESTINAL (cont)
... – Sx: abdominal pain, fever – Tx: BR, antibiotics, liquid diet, low fiber diet • When in control managed by dietary changes ...
... – Sx: abdominal pain, fever – Tx: BR, antibiotics, liquid diet, low fiber diet • When in control managed by dietary changes ...
Ch. 25 D
... No circular folds or villi to increase surface area Intestinal crypts (glands sunken into lamina propria) produce mucus only Muscularis externa ...
... No circular folds or villi to increase surface area Intestinal crypts (glands sunken into lamina propria) produce mucus only Muscularis externa ...
large intestine
... • It is derived from two sources 1. Swallowed air [up to 500ml of air may be swallowed during a meal]. 2. Gas produced by bacterial fermentation in the colon. Most gas in the colon is due to result of bacterial activity, but the quantity and the nature of gas produced depend on the type of food eate ...
... • It is derived from two sources 1. Swallowed air [up to 500ml of air may be swallowed during a meal]. 2. Gas produced by bacterial fermentation in the colon. Most gas in the colon is due to result of bacterial activity, but the quantity and the nature of gas produced depend on the type of food eate ...
ENTERO HEALTH PRO - Vetriproline.com
... enterocyte (cells in the small intestine) integrity in the lining of the intestines, which may affect digestion and absorption or allow the passage of pathogens into the body. Slippery Elm Bark — contains a substance called mucilage, which is a polysaccharide that becomes a gel when mixed with water ...
... enterocyte (cells in the small intestine) integrity in the lining of the intestines, which may affect digestion and absorption or allow the passage of pathogens into the body. Slippery Elm Bark — contains a substance called mucilage, which is a polysaccharide that becomes a gel when mixed with water ...
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
... peristalsis (movement of the bowels during digestion) can only occur when the body is relaxed. 6.Disease-promoting diet: The SAD (Standard American Diet) is based on animal products and processed foods, and is typically low in vegetables, legumes, fruits, nuts and seeds, and whole grains. This type ...
... peristalsis (movement of the bowels during digestion) can only occur when the body is relaxed. 6.Disease-promoting diet: The SAD (Standard American Diet) is based on animal products and processed foods, and is typically low in vegetables, legumes, fruits, nuts and seeds, and whole grains. This type ...
Digestion Organs - Hicksville Public Schools
... It's a Gas Scientists estimate that the average adult releases between 12 and 122 cubic inches of intestinal gas each day. Most of that gas is made up of hydrogen and methane produced by the bacteria as they ferment the fiber that was not digested in the stomach or small intestine. Many fruits and ...
... It's a Gas Scientists estimate that the average adult releases between 12 and 122 cubic inches of intestinal gas each day. Most of that gas is made up of hydrogen and methane produced by the bacteria as they ferment the fiber that was not digested in the stomach or small intestine. Many fruits and ...
Gas in the Digestive Tract
... Everyone has gas and eliminates it by burping or passing it through the rectum. However, many people think they have too much gas when they really have normal amounts. Most people produce about 1 to 4 pints a day and pass gas about 14 times a day. Gas is made primarily of odorless vapors— carbon dio ...
... Everyone has gas and eliminates it by burping or passing it through the rectum. However, many people think they have too much gas when they really have normal amounts. Most people produce about 1 to 4 pints a day and pass gas about 14 times a day. Gas is made primarily of odorless vapors— carbon dio ...
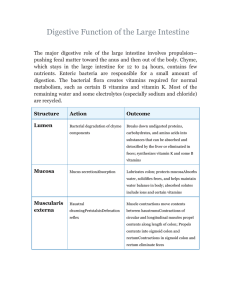
Digestive Function of the Large Intestine
... Digestive Function of the Large Intestine The major digestive role of the large intestine involves propulsion-pushing fecal matter toward the anus and then out of the body. Chyme, which stays in the large intestine for 12 to 24 hours, contains few nutrients. Enteric bacteria are responsible for a sm ...
... Digestive Function of the Large Intestine The major digestive role of the large intestine involves propulsion-pushing fecal matter toward the anus and then out of the body. Chyme, which stays in the large intestine for 12 to 24 hours, contains few nutrients. Enteric bacteria are responsible for a sm ...
File
... borborygmus – stomach “growling” bulimia – excessive eating followed by purging colic – severe, often fluctuating pain in the abdomen caused by intestinal gas or obstruction in the intestines (often in babies) constipation – decrease in frequency of bowel movements with straining with defecation and ...
... borborygmus – stomach “growling” bulimia – excessive eating followed by purging colic – severe, often fluctuating pain in the abdomen caused by intestinal gas or obstruction in the intestines (often in babies) constipation – decrease in frequency of bowel movements with straining with defecation and ...
Unit I Notes #2 -Key Digestive Processes - Mr. Lesiuk
... - Within each villus (singular) there are blood vessels and a small lymph vessel called a LACTEAL. This lacteal absorbs fluids containing lipoproteins and returns these fatty nutrients back into the circulatory system later on. - Absorption occurs across the walls of each villus by active transport ...
... - Within each villus (singular) there are blood vessels and a small lymph vessel called a LACTEAL. This lacteal absorbs fluids containing lipoproteins and returns these fatty nutrients back into the circulatory system later on. - Absorption occurs across the walls of each villus by active transport ...
CH23_Anatomy_of_the_Large_Intestine
... the final absorption of H2 O Intestinal normal flora manufacture certain vitamins (B complex, K) Formation and expulsion of feces ...
... the final absorption of H2 O Intestinal normal flora manufacture certain vitamins (B complex, K) Formation and expulsion of feces ...
Horse Digestive System Melissa Moser Topic # 3186B Caledonia High School Equine Science
... with a simpler intestinal system Horses & Rabbits have a simple stomach with an extensive intestinal system and an enlarged cecum ...
... with a simpler intestinal system Horses & Rabbits have a simple stomach with an extensive intestinal system and an enlarged cecum ...
Large Intestine
... Mechanical • Haustral churning- the contracting and squeezing of the intestinal contents. • Peristalsis- slower than other parts of GI tract. • Mass peristalsis- strong peristaltic wave that drives the colonic contents into the rectum. – initiated by food in the stomach ...
... Mechanical • Haustral churning- the contracting and squeezing of the intestinal contents. • Peristalsis- slower than other parts of GI tract. • Mass peristalsis- strong peristaltic wave that drives the colonic contents into the rectum. – initiated by food in the stomach ...
Breath Testing at MGI
... treatable components of irritable bowel syndrome is a therapeutic goal for clinicians and patients. SIBO, if found, may offer a different treatment option. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth is also a cause of malabsorption in the elderly and in patients with small intestinal conditions that resu ...
... treatable components of irritable bowel syndrome is a therapeutic goal for clinicians and patients. SIBO, if found, may offer a different treatment option. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth is also a cause of malabsorption in the elderly and in patients with small intestinal conditions that resu ...
Bacterial Overgrowth of the Small Intestine Breath Test
... • Once bacterial overgrowth has been detected, intervention strategies involving diet, digestive support, probiotics and antimicrobials can be used to treat the condition. • Successful eradication of BOSI has been shown to reduce bloating, gas, diarrhea, and abdominal pain in patients more effective ...
... • Once bacterial overgrowth has been detected, intervention strategies involving diet, digestive support, probiotics and antimicrobials can be used to treat the condition. • Successful eradication of BOSI has been shown to reduce bloating, gas, diarrhea, and abdominal pain in patients more effective ...
Gas - Stanford Internal Medicine
... 3. Gas comes from two main sources: swallowed air and normal breakdown of certain foods by harmless bacteria naturally present in the large intestine. 4. Many foods with carbohyd ...
... 3. Gas comes from two main sources: swallowed air and normal breakdown of certain foods by harmless bacteria naturally present in the large intestine. 4. Many foods with carbohyd ...
Lower GI Tract
... cigarettes, chewing gum or tobacco can cause increased salivation and swallowing Eating fast and swallowing large chunks of food or large amounts of beverages Using straws or drinking from a bottle or can Inactivity and lying down after eating ...
... cigarettes, chewing gum or tobacco can cause increased salivation and swallowing Eating fast and swallowing large chunks of food or large amounts of beverages Using straws or drinking from a bottle or can Inactivity and lying down after eating ...
File
... Diarrhea- frequent or unusually liquid bowel movements Dumping syndrome- a group of symptoms that occurs with rapid passage of large amounts of food from the stomach into the small intestine. Symptoms include dizziness, sweating, decreased BP, and diarrhea Dysgeusia- abnormalities in or reduced abil ...
... Diarrhea- frequent or unusually liquid bowel movements Dumping syndrome- a group of symptoms that occurs with rapid passage of large amounts of food from the stomach into the small intestine. Symptoms include dizziness, sweating, decreased BP, and diarrhea Dysgeusia- abnormalities in or reduced abil ...
digestion - GLLM Moodle 2
... What You Need to Know Large Intestine • Final pathway for digestion • Absorption of water, electrolyes, storage of digestive residue (fecal matter) • Terminal portion of GI tract contains no villi and is known as the colon • Ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal • ...
... What You Need to Know Large Intestine • Final pathway for digestion • Absorption of water, electrolyes, storage of digestive residue (fecal matter) • Terminal portion of GI tract contains no villi and is known as the colon • Ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal • ...
Digestion: 8 interesting things you should know - Dis-Chem
... Many people refer to the large intestine and the colon as one in the same, however, the colon is just one part of the large intestine. It has many separate parts, starting with the caecum, appendix, colon, rectum and ends with the anus. Flatulence Is More Than Air ...
... Many people refer to the large intestine and the colon as one in the same, however, the colon is just one part of the large intestine. It has many separate parts, starting with the caecum, appendix, colon, rectum and ends with the anus. Flatulence Is More Than Air ...
File - Jillian M. O`Neil
... Diarrhea- frequent or unusually liquid bowel movements Dumping syndrome- a group of symptoms that occurs with rapid passage of large amounts of food from the stomach into the small intestine. Symptoms include dizziness, sweating, decreased BP, and diarrhea Dysgeusia- abnormalities in or reduced abil ...
... Diarrhea- frequent or unusually liquid bowel movements Dumping syndrome- a group of symptoms that occurs with rapid passage of large amounts of food from the stomach into the small intestine. Symptoms include dizziness, sweating, decreased BP, and diarrhea Dysgeusia- abnormalities in or reduced abil ...
chronic_diarrhea_in_cats
... (known as "lymphangiectasia"); condition in which a high number of bacteria are found in the upper small intestine (known as "small intestinal bacterial overgrowth"); diarrhea and other signs caused by absence of a long section of small intestine, usually because of surgical removal (condition known ...
... (known as "lymphangiectasia"); condition in which a high number of bacteria are found in the upper small intestine (known as "small intestinal bacterial overgrowth"); diarrhea and other signs caused by absence of a long section of small intestine, usually because of surgical removal (condition known ...
Flatulence

Flatulence is defined in the medical literature as ""flatus expelled through the anus"" or the ""quality or state of being flatulent"", which is defined in turn as ""marked by or affected with gases generated in the intestine or stomach; likely to cause digestive flatulence"". The root of these words is from the Latin flatus – ""a blowing, a breaking wind"". Flatus is also the medical word for gas generated in the stomach or bowels. These standard definitions do not reflect the fact that a proportion of intestinal gas may be composed of swallowed environmental air, and hence flatus is not totally generated in the stomach or bowels. The scientific study of this area of medicine is termed flatology.It is normal for humans to pass flatus through the rectum, although the volume and frequency may vary greatly between individuals. It is also normal for intestinal gas passed through the rectum to have a characteristic feculent smell, although this too may vary in concentration. Flatus is brought to the rectum by specialised contractions of the muscles in the intestines and colon. The noises commonly associated with flatulence (""Blowing a raspberry"") are caused by the vibration of anal sphincters, and occasionally by the closed buttocks. Both the noise and smell associated with flatus leaving the anus can be sources of embarrassment or comedy in many cultures.There are five general symptoms related to intestinal gas: pain, bloating and abdominal distension, excessive flatus volume, excessive flatus smell and gas incontinence. Furthermore, eructation (""an act or instance of belching"", colloquially known as ""burping"") is sometimes included under the topic of flatulence.