* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download digestion - GLLM Moodle 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
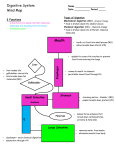
“I Am Smart” Quiz • Where digestion first begins? • What glands secrete hydrochloric acid? • What is the length of the small intestine? • The name of the projections on the villi? • The name of small lymphatic vessels? • What organ produces bile? • What organ secretes bile? • What is the name of the portion of large intestine that contains no villi? What You Need to Know Mouth • Where digestion begins • Name of structure at back of the mouth? Esophagus • Circular and longitudinal bands of muscle • Peristalsis = rhythmic contractions • esophageal sphincter What You Need to Know Stomach • Volume ranges from 50 ml to 6.0 L • Parietal glands secrete HCl • Mucos secreted from mucos neck cells • Chief cells secrete pepsinogen • Little absorption occurs except for alcohol • Chyme is slushy, acidic mixture What You Need to Know Small Intestine • 90% of digestion occurs first two sections • Duodenum, jejunum, ileum • Villi = highly vascularized; contain small projections called microvilli; increase absorptive surface up to 600-fold • Large surface area facilitates speed • Villi contain lymphatics called lacteals • Lacteals transport fatty materials (from the liver) to lymphatic system What You Need to Know Small Intestine • Segmentation contractions • Peristalsis • Bile, produced in the liver and stored and secreted by the gallbladder, helps to increase solubility and digestibility of lipid droplets by emulsifying them • Pancreas secretes bicarbonates (alkali) to help buffer HCl from stomach that remains in the chyme What You Need to Know Large Intestine • Final pathway for digestion • Absorption of water, electrolyes, storage of digestive residue (fecal matter) • Terminal portion of GI tract contains no villi and is known as the colon • Ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal • Bacterial fermintation produces gas (flatus)