Body Cavities and Membranes
... The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level – atoms form molecules O Cellular level – cells and their functional subunits O Tissue level – a group of cells performing a common ...
... The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level – atoms form molecules O Cellular level – cells and their functional subunits O Tissue level – a group of cells performing a common ...
Discovering cells
... What you have learnt A woman becomes ____ when a ____ fertilises her egg. The fertilised egg grows as its cells ____ to make more and more cells. As the number of cells gets bigger and bigger, the cells ____ to become blood cells, muscles cells and other cell types and a ____ is formed. A ____ is a ...
... What you have learnt A woman becomes ____ when a ____ fertilises her egg. The fertilised egg grows as its cells ____ to make more and more cells. As the number of cells gets bigger and bigger, the cells ____ to become blood cells, muscles cells and other cell types and a ____ is formed. A ____ is a ...
File
... Initially, these canals, the pleural (pericardioperitoneal) canals, represent the spaces into which the developing lungs grow. The pleural canals enlarge greatly as the lungs increase in size and ultimately form the pleural cavities. The pleural canals are partially bounded by two paired folds of ti ...
... Initially, these canals, the pleural (pericardioperitoneal) canals, represent the spaces into which the developing lungs grow. The pleural canals enlarge greatly as the lungs increase in size and ultimately form the pleural cavities. The pleural canals are partially bounded by two paired folds of ti ...
The organization of the human body
... • Cellular nutrition consists of all the processes in which cells obtain the matter and energy necessary to perform life functions. To do this, cells take in substances, called nutrients, from the outside. Nutrients are used for energy and to obtain the substances necessary for growth and buildin ...
... • Cellular nutrition consists of all the processes in which cells obtain the matter and energy necessary to perform life functions. To do this, cells take in substances, called nutrients, from the outside. Nutrients are used for energy and to obtain the substances necessary for growth and buildin ...
Jeoparday_Final
... What does this statement mean: “All cells are similar but not exactly the same.” They are made of similar components (organelles) like nucleus and mitochondrion, and they function similarly like they make proteins and produce energy. Different cells are different based on the exact function they hav ...
... What does this statement mean: “All cells are similar but not exactly the same.” They are made of similar components (organelles) like nucleus and mitochondrion, and they function similarly like they make proteins and produce energy. Different cells are different based on the exact function they hav ...
Study Guide
... band of connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone , ligament – a tough band of connective tissue that connects bones or cartilage at a joint or supports an organ, muscle, or other body part. Ossification (also described above) - In the second month of fetal development, much of the skeleton ...
... band of connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone , ligament – a tough band of connective tissue that connects bones or cartilage at a joint or supports an organ, muscle, or other body part. Ossification (also described above) - In the second month of fetal development, much of the skeleton ...
Embryology Review (from Ida) - U
... Wk 8: fetal movement, fetus looks like a baby, critical period for formation of ...
... Wk 8: fetal movement, fetus looks like a baby, critical period for formation of ...
Body Systems Overview
... • Function: Produce subsequent generation (provide egg for female genetic contribution to embryo, pregnancy, lactation) • Structures: Ovaries, Uterus, Fallopian tube; Vagina, Mammary glands • Tissues: Muscle, Connective, Epithelial lining, Glandular • How’s it work? Eggs produced in ovary, fertilize ...
... • Function: Produce subsequent generation (provide egg for female genetic contribution to embryo, pregnancy, lactation) • Structures: Ovaries, Uterus, Fallopian tube; Vagina, Mammary glands • Tissues: Muscle, Connective, Epithelial lining, Glandular • How’s it work? Eggs produced in ovary, fertilize ...
History and basic concepts
... put ic "A hen is only an egg's way of making another egg.,' work on sea urchin eggs showed that after fertilization the egg contains two nuclei, which eventually fuse; one of these nuclei belongs to the egg while the other comes from the sperm. Fertilization therefore results in an egg carrying a nu ...
... put ic "A hen is only an egg's way of making another egg.,' work on sea urchin eggs showed that after fertilization the egg contains two nuclei, which eventually fuse; one of these nuclei belongs to the egg while the other comes from the sperm. Fertilization therefore results in an egg carrying a nu ...
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
... Organ – Two or more tissue types Two or more types of basic tissues organized together to perform a particular function or functions Example: Stomach Inside of stomach lined with epithelial tissue Wall of stomach contains smooth muscle tissue Nervous tissue in stomach controls muscle contraction and ...
... Organ – Two or more tissue types Two or more types of basic tissues organized together to perform a particular function or functions Example: Stomach Inside of stomach lined with epithelial tissue Wall of stomach contains smooth muscle tissue Nervous tissue in stomach controls muscle contraction and ...
Presentation - science
... To build up sugars, nitrates and other nutrients into amino acids which are then built up into proteins. ...
... To build up sugars, nitrates and other nutrients into amino acids which are then built up into proteins. ...
Lymphatic System
... • Produce lymphocytes: type of white blood cell that produce antibodies. • House macrophages: type of white blood cell that eat bacteria and such. • Lymph node swelling is the result of the increased production of wbc and trapping the foreign objects. ...
... • Produce lymphocytes: type of white blood cell that produce antibodies. • House macrophages: type of white blood cell that eat bacteria and such. • Lymph node swelling is the result of the increased production of wbc and trapping the foreign objects. ...
Grade 11 College Biology – Unit 3
... together to perform specific functions. The following chart shows ten of organ systems of the human body. Nervous System – Gathers information from the body and its surroundings AND sends messages between the brain and the body Respiratory System – Takes in oxygen from the air and removes carbon ...
... together to perform specific functions. The following chart shows ten of organ systems of the human body. Nervous System – Gathers information from the body and its surroundings AND sends messages between the brain and the body Respiratory System – Takes in oxygen from the air and removes carbon ...
Respiratory System
... Internal Respiration: exchange of gases between capillaries and body cells Oxygen leaves blood to nourish cells Carbon dioxide is picked up from cells to be breathed out in lung ...
... Internal Respiration: exchange of gases between capillaries and body cells Oxygen leaves blood to nourish cells Carbon dioxide is picked up from cells to be breathed out in lung ...
Intro to Animals Scavenger Hunt
... B. anus In all deuterostome embryos, the blastopore will become the ___________________. (pgs 114-115) A. mouth B. anus ...
... B. anus In all deuterostome embryos, the blastopore will become the ___________________. (pgs 114-115) A. mouth B. anus ...
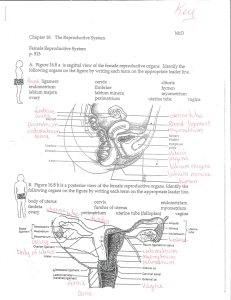
Chapter 16: The Reproductive System p. 513 c Yt(l ligament Iabium
... _ÿ___18. superior rounded region above the entrance of the uterine tubesvct ÿ(\'WX'dt-
...
... _ÿ___18. superior rounded region above the entrance of the uterine tubes
Structural Organisation in Animals
... Connective tissues are most abundant and widely distributed in the body of complex animals. They are named connective tissues because of their special function of linking and supporting other tissues/organs of the body. They range from soft connective tissues to specialised types, which include cart ...
... Connective tissues are most abundant and widely distributed in the body of complex animals. They are named connective tissues because of their special function of linking and supporting other tissues/organs of the body. They range from soft connective tissues to specialised types, which include cart ...
Get cached
... proliferate to form a thin membrane which lines the inner surface of the trophoblastic basal lamina and forms the primitive yolk sac. A new population of cells, the extraembryonic mesoderm, evolves and separates the trophoblast and the yolk sac. Cavities form in this layer which coalesce to form the ...
... proliferate to form a thin membrane which lines the inner surface of the trophoblastic basal lamina and forms the primitive yolk sac. A new population of cells, the extraembryonic mesoderm, evolves and separates the trophoblast and the yolk sac. Cavities form in this layer which coalesce to form the ...
Rat Dissection Guide
... there (such as alcohol, which your liver detoxifies). Waste products from protein metabolism are processed into the less-toxic form of urea, which will be removed in the kidneys. Old red blood cells are broken down, with important things like the iron recycled; the liver is also a major staging site ...
... there (such as alcohol, which your liver detoxifies). Waste products from protein metabolism are processed into the less-toxic form of urea, which will be removed in the kidneys. Old red blood cells are broken down, with important things like the iron recycled; the liver is also a major staging site ...
Tissues and Membranes
... • Most fibrous connective tissue and bone tissue also regenerate well • Skeletal muscle regenerates poorly, if at all • Cardiac muscle and nervous tissue within the brain and spinal cord are only replaced by scar tissue ...
... • Most fibrous connective tissue and bone tissue also regenerate well • Skeletal muscle regenerates poorly, if at all • Cardiac muscle and nervous tissue within the brain and spinal cord are only replaced by scar tissue ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.