B2 Glossary - physicsinfo.co.uk
... Site on enzyme molecule that has special shape that holds substrate Movement of molecules against concentration gradient using energy A base in DNA that pairs with thymine A stem cell in differentiated tissue that can produce a few kinds of cells Respiration that needs oxygen The muscular tube that ...
... Site on enzyme molecule that has special shape that holds substrate Movement of molecules against concentration gradient using energy A base in DNA that pairs with thymine A stem cell in differentiated tissue that can produce a few kinds of cells Respiration that needs oxygen The muscular tube that ...
The Cell
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
the human body systems
... excretory waste (urea, water) 4. protects against sun’s UV rays 5. produces vitamin D 1. stores and Lymphatic carries WBC’s that fight disease 2. collects excess fluid and returns it to blood (2nd circulatory system-reaches places other one can’t – between cells) ...
... excretory waste (urea, water) 4. protects against sun’s UV rays 5. produces vitamin D 1. stores and Lymphatic carries WBC’s that fight disease 2. collects excess fluid and returns it to blood (2nd circulatory system-reaches places other one can’t – between cells) ...
the human body systems
... excretory waste (urea, water) 4. protects against sun’s UV rays 5. produces vitamin D 1. stores and Lymphatic carries WBC’s that fight disease 2. collects excess fluid and returns it to blood (2nd circulatory system-reaches places other one can’t – between cells) ...
... excretory waste (urea, water) 4. protects against sun’s UV rays 5. produces vitamin D 1. stores and Lymphatic carries WBC’s that fight disease 2. collects excess fluid and returns it to blood (2nd circulatory system-reaches places other one can’t – between cells) ...
Connective Tissue
... Major Cell Types of Connective Tissue Fixed cells continued. Adipose cells/Adipocytes: Found throughout connective tissue Resemble fibroblasts early on, but as they age they become filled with lipid and swell. nucleus gets pushed to the side Adipocytes clustered together form adipose ti ...
... Major Cell Types of Connective Tissue Fixed cells continued. Adipose cells/Adipocytes: Found throughout connective tissue Resemble fibroblasts early on, but as they age they become filled with lipid and swell. nucleus gets pushed to the side Adipocytes clustered together form adipose ti ...
File
... 3. What is a group of cells that are alike and work together? a. a cell team b. a tissue c. a cell family d. a system Read the description. Then, draw a line from the dot next to each description to the matching word. ...
... 3. What is a group of cells that are alike and work together? a. a cell team b. a tissue c. a cell family d. a system Read the description. Then, draw a line from the dot next to each description to the matching word. ...
Clinical pathology
... Haematology Haematology : is the study of the cellular elements of the blood , which can be divided into three categories : 1. The erythrocytes or red blood cells: are responsible for oxygen transport from the lung to all tissues of body . 2. The leukocyte or white blood cells: are responsible in va ...
... Haematology Haematology : is the study of the cellular elements of the blood , which can be divided into three categories : 1. The erythrocytes or red blood cells: are responsible for oxygen transport from the lung to all tissues of body . 2. The leukocyte or white blood cells: are responsible in va ...
Red blood cells - Maria Regina School
... – People who lack Rh factor (negative type), – Have Rh factor are positive (like being O+) – If lack Rh but receive Rh positive blood, body will produce antibodies against blood which can cause blood clots. ...
... – People who lack Rh factor (negative type), – Have Rh factor are positive (like being O+) – If lack Rh but receive Rh positive blood, body will produce antibodies against blood which can cause blood clots. ...
Cell Specialization
... Red blood cells form from undifferentiated cells in the bone marrow throughout your life. Bone marrow is the soft, interior portion of certain bones found in the chest, upper arms, upper legs and hips. The cells located here are undifferentiated, but limited in the type of cell they can become. They ...
... Red blood cells form from undifferentiated cells in the bone marrow throughout your life. Bone marrow is the soft, interior portion of certain bones found in the chest, upper arms, upper legs and hips. The cells located here are undifferentiated, but limited in the type of cell they can become. They ...
Biology HW Chapters 3435
... 76. Because steroid hormones are made of ____________________, they can easily cross cell membranes. 77. The thyroid gland is controlled by the ____________________ and the ____________________. 78. When you drink a lot of water, the organ that prevents your blood from becoming too dilute by removin ...
... 76. Because steroid hormones are made of ____________________, they can easily cross cell membranes. 77. The thyroid gland is controlled by the ____________________ and the ____________________. 78. When you drink a lot of water, the organ that prevents your blood from becoming too dilute by removin ...
lecture notes ch32 Intro Animal Evolution
... cucumbers), but all are bilateral at some point during early development. Bilateria are triploblastic: they have endoderm, ectoderm, and they also have a mesoderm and the tissues that develop from the mesoderm. 11) Bilateral symmetry is an adaptation for an active, mobile lifestyle, while radial sym ...
... cucumbers), but all are bilateral at some point during early development. Bilateria are triploblastic: they have endoderm, ectoderm, and they also have a mesoderm and the tissues that develop from the mesoderm. 11) Bilateral symmetry is an adaptation for an active, mobile lifestyle, while radial sym ...
20 Development of ce..
... INTRODUCTION By the beginning of the 3rd week of development, three germ cell layers become established, Ectoderm, Mesoderm and Endoderm. ...
... INTRODUCTION By the beginning of the 3rd week of development, three germ cell layers become established, Ectoderm, Mesoderm and Endoderm. ...
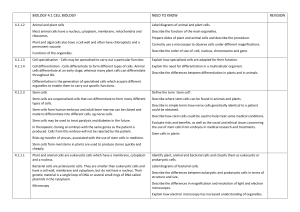
BIOLOGY 4.1 CELL BIOLOGY NEED TO KNOW REVISION
... Calculate the magnification of a light microscope. Carry out calculations using the formula: real size=(image size)/magnification Rearrange the equation to calculate image size or magnification. Convert values for the units: cm, mm, µm and nm. ...
... Calculate the magnification of a light microscope. Carry out calculations using the formula: real size=(image size)/magnification Rearrange the equation to calculate image size or magnification. Convert values for the units: cm, mm, µm and nm. ...
Study Guide with Answers - Mrs. Rasmussen Science Class
... Organelle that helps stuff move around the cell, transportation throughout the cell Found only in plant cells, the stiff outer covering that gives the cell structure and support Found in all cells, the outer covering that controls what goes in and out of the cell, protects Used for storage of food, ...
... Organelle that helps stuff move around the cell, transportation throughout the cell Found only in plant cells, the stiff outer covering that gives the cell structure and support Found in all cells, the outer covering that controls what goes in and out of the cell, protects Used for storage of food, ...
Animalia Overview
... When the “blood” is not contained entirely within vessels (like veins and arteries) Closed circulatory system When the “blood” is contained with in vessels ...
... When the “blood” is not contained entirely within vessels (like veins and arteries) Closed circulatory system When the “blood” is contained with in vessels ...
Levels of Organization
... -In any multi-cellular organism, cells rarely work alone. -Cells that are similar in structure and function are usually joined together to form tissues ...
... -In any multi-cellular organism, cells rarely work alone. -Cells that are similar in structure and function are usually joined together to form tissues ...
Lessons 8-10 Vocabulary Answers
... 14. ventricle-- the lower chambers of each side of the heart (left ventricle, right ventricle) 15. arteries—blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart (with oxygen) 16. veins-- blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart (without oxygen) 17. capillaries—tiny blood vessels that connect th ...
... 14. ventricle-- the lower chambers of each side of the heart (left ventricle, right ventricle) 15. arteries—blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart (with oxygen) 16. veins-- blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart (without oxygen) 17. capillaries—tiny blood vessels that connect th ...
1 Unit 1: The Body as a Whole
... Homeostasis is the maintenance of relatively constant conditions within the body's internal environment. Many physiological parameters, such as blood glucose and body temperature, are precisely regulated by a homeostatic mechanism. Regulation of a physiological event usually occurs via a feedback me ...
... Homeostasis is the maintenance of relatively constant conditions within the body's internal environment. Many physiological parameters, such as blood glucose and body temperature, are precisely regulated by a homeostatic mechanism. Regulation of a physiological event usually occurs via a feedback me ...
Levels of Organization
... body. Blood, fat, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and tendons are all connective tissues. ...
... body. Blood, fat, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and tendons are all connective tissues. ...
Development and Inheritance
... D. The first trimester 1. By the end of the first trimester the fetus is about 3 in long and weighs about ...
... D. The first trimester 1. By the end of the first trimester the fetus is about 3 in long and weighs about ...
January 2005 Biology 1 Exam Papers for 2 diploma
... F. cell division 12. In Mitosis the spindle begins to assemble during _____. A. prophase B. prometaphase C. metaphase D. anaphase E. telophase F. interphase 13. Meristem tissue is found in the __________ of a plant. A. root tips B. shoot tips C. Xylem tissue D. in A and B above E. Phloem tissue F. r ...
... F. cell division 12. In Mitosis the spindle begins to assemble during _____. A. prophase B. prometaphase C. metaphase D. anaphase E. telophase F. interphase 13. Meristem tissue is found in the __________ of a plant. A. root tips B. shoot tips C. Xylem tissue D. in A and B above E. Phloem tissue F. r ...
2.1-3
... • Cell types -- nerve cells and neuroglial (supporting) cells • Nerve cell structure – nucleus & long cell processes conduct nerve signals • dendrite --- signal travels towards the cell body • axon ---- signal travels away from cell body ...
... • Cell types -- nerve cells and neuroglial (supporting) cells • Nerve cell structure – nucleus & long cell processes conduct nerve signals • dendrite --- signal travels towards the cell body • axon ---- signal travels away from cell body ...
Embryonic Cephalocaudal and Lateral Flexion/Folding
... Umbilical cord - embryonic/fetal structure which carries embryonic/fetal blood vessels to and from the fetal component of the placenta. This will be covered in subsequent lectures. ...
... Umbilical cord - embryonic/fetal structure which carries embryonic/fetal blood vessels to and from the fetal component of the placenta. This will be covered in subsequent lectures. ...
Animal Body Plans
... and materials with its surroundings. – As a requirement for maintaining the fluid integrity of the plasma membrane of its cells, an animal’s body must be arranged so that all of its living cells are bathed in an aqueous medium. – Exchange with the environment occurs as dissolved substances diffuse a ...
... and materials with its surroundings. – As a requirement for maintaining the fluid integrity of the plasma membrane of its cells, an animal’s body must be arranged so that all of its living cells are bathed in an aqueous medium. – Exchange with the environment occurs as dissolved substances diffuse a ...
InvertBodyPlans
... and materials with its surroundings. – As a requirement for maintaining the fluid integrity of the plasma membrane of its cells, an animal’s body must be arranged so that all of its living cells are bathed in an aqueous medium. – Exchange with the environment occurs as dissolved substances diffuse a ...
... and materials with its surroundings. – As a requirement for maintaining the fluid integrity of the plasma membrane of its cells, an animal’s body must be arranged so that all of its living cells are bathed in an aqueous medium. – Exchange with the environment occurs as dissolved substances diffuse a ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.