1.1 Cells – structure and function
... 1.2 Specialised cells You, like many other organisms including plants, started life as a single cell – a fertilised egg. This divides and forms an embryo. Cells become specialised to perform different functions. This is called differentiation (becoming different). Some examples of specialised cells ...
... 1.2 Specialised cells You, like many other organisms including plants, started life as a single cell – a fertilised egg. This divides and forms an embryo. Cells become specialised to perform different functions. This is called differentiation (becoming different). Some examples of specialised cells ...
Chapter 19- Bacteria - River Ridge CUSD #210
... 6. Photoautotrophs use sunlight to make food. 7. Chemoautotrophs make food from carbon dioxide but not using the sun they make it by chemical reactions. ...
... 6. Photoautotrophs use sunlight to make food. 7. Chemoautotrophs make food from carbon dioxide but not using the sun they make it by chemical reactions. ...
Asexual reproduction
... The cell cycle in your body Cells don’t live forever, they eventually die. Some cells life spans: Brain cells: 30 – 50 years Red blood cells: 120 days Stomach lining cells: 2 days Skin cells: 20 days You need mitosis and cell division to replace these cells. In your body about 3 billion cel ...
... The cell cycle in your body Cells don’t live forever, they eventually die. Some cells life spans: Brain cells: 30 – 50 years Red blood cells: 120 days Stomach lining cells: 2 days Skin cells: 20 days You need mitosis and cell division to replace these cells. In your body about 3 billion cel ...
B2 Glossary - physicsinfo.co.uk
... A cell produced in early development of an embryo which can become almost any cell Turn into an emulsion, where particles of one liquid are suspended in another liquid Remove the nucleus from a cell An organism’s surroundings, made of factors like air, water, soil and other organisms Protein molecul ...
... A cell produced in early development of an embryo which can become almost any cell Turn into an emulsion, where particles of one liquid are suspended in another liquid Remove the nucleus from a cell An organism’s surroundings, made of factors like air, water, soil and other organisms Protein molecul ...
Evolution by Natural Selection Evolution by Natural Selection
... “Those individuals that possess superior physical, behavioral, or other traits are more likely to survive than those that are not so well-endowed. By surviving, they gain the opportunity to pass on their favorable characteristics to their offspring. As the frequency of these characteristics increase ...
... “Those individuals that possess superior physical, behavioral, or other traits are more likely to survive than those that are not so well-endowed. By surviving, they gain the opportunity to pass on their favorable characteristics to their offspring. As the frequency of these characteristics increase ...
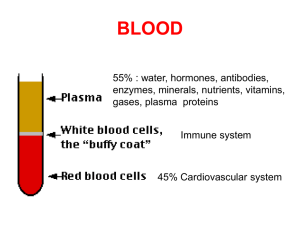
blood
... •large acidophilic granules -appear pink (or red) •nucleus has two lobes connected by a band of nuclear material. (telephone receiver) •granules contain digestive enzymes that are particularly effective against parasitic worms in their larval form. •Phagocyte: antigen - antibody complexes. •These ce ...
... •large acidophilic granules -appear pink (or red) •nucleus has two lobes connected by a band of nuclear material. (telephone receiver) •granules contain digestive enzymes that are particularly effective against parasitic worms in their larval form. •Phagocyte: antigen - antibody complexes. •These ce ...
Notes Pages
... There are trillions (1,000,000,000,000’s) of cells in the human body. All cells were formed in your body from just one cell, the fertilized egg. Cells take on different jobs, (specialize) as they are formed in the egg. Cells that all work together to form a specific function form tissues. There are ...
... There are trillions (1,000,000,000,000’s) of cells in the human body. All cells were formed in your body from just one cell, the fertilized egg. Cells take on different jobs, (specialize) as they are formed in the egg. Cells that all work together to form a specific function form tissues. There are ...
Evolution by Natural Selection
... resist infections, so they were more likely to survive to adulthood. These genes would be more common in the next generation, since more of the cubs with these genes would survive to reproduce. A characteristic which is influenced by genes and passed from parents to offspring is called heritable. Ov ...
... resist infections, so they were more likely to survive to adulthood. These genes would be more common in the next generation, since more of the cubs with these genes would survive to reproduce. A characteristic which is influenced by genes and passed from parents to offspring is called heritable. Ov ...
Evolution by Natural Selection
... resist infections, so they were more likely to survive to adulthood. These genes would be more common in the next generation, since more of the cubs with these genes would survive to reproduce. A characteristic which is influenced by genes and passed from parents to offspring is called heritable. Ov ...
... resist infections, so they were more likely to survive to adulthood. These genes would be more common in the next generation, since more of the cubs with these genes would survive to reproduce. A characteristic which is influenced by genes and passed from parents to offspring is called heritable. Ov ...
Guess This Picture
... Objective • SWBAT arrange in order the organizational levels of the human body from the cell through organ systems. ...
... Objective • SWBAT arrange in order the organizational levels of the human body from the cell through organ systems. ...
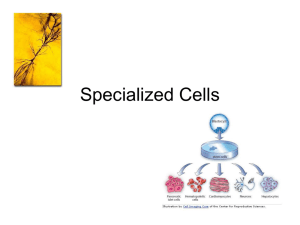
Specialized Cells
... 1. Your body has three main lines of defense against invasion by disease agents. a. First line of defense is made up of your body’s physical and ...
... 1. Your body has three main lines of defense against invasion by disease agents. a. First line of defense is made up of your body’s physical and ...
Organ Systems and Homeostasis - Mr. St. Peter's
... function—keeps organisms alive • Tissues: Group of specialized cells that perform the same function—what are the 4 types? ...
... function—keeps organisms alive • Tissues: Group of specialized cells that perform the same function—what are the 4 types? ...
fly2
... After the activity of four different pathways, the D/V patterning of the ectoderm Is controlled by a conserved Ser/Thr receptor that is dependent on the gradient of its ligand dpp and dpp’s interactors ...
... After the activity of four different pathways, the D/V patterning of the ectoderm Is controlled by a conserved Ser/Thr receptor that is dependent on the gradient of its ligand dpp and dpp’s interactors ...
Chap 20 – Organization of Multicellular Organisms
... 4.2 The small size of cells relates to the need to exchange materials across the plasma membrane Cell size must – be large enough to house DNA, proteins, and structures needed to survive and reproduce, but – remain small enough for a SA:volume ratio that will allow for adequate exchange with the e ...
... 4.2 The small size of cells relates to the need to exchange materials across the plasma membrane Cell size must – be large enough to house DNA, proteins, and structures needed to survive and reproduce, but – remain small enough for a SA:volume ratio that will allow for adequate exchange with the e ...
Unit B: Cells and Systems - St. John Paul II Collegiate
... and a poplar tree) Multi-cellular: organisms made up of more than one cell or a system of cells Unicellular: single celled organisms Cells need to be specialized to meet different needs just like band needs to have different instruments to play a variety of songs. Cells in multicellular organisms ar ...
... and a poplar tree) Multi-cellular: organisms made up of more than one cell or a system of cells Unicellular: single celled organisms Cells need to be specialized to meet different needs just like band needs to have different instruments to play a variety of songs. Cells in multicellular organisms ar ...
G7SC_TEST4 rev.docx.docx
... Bacteria and fungi always cause infectious diseases. Bacteria are living organisms, whereas, fungi are not. Both bacteria and fungi rely on living organisms to reproduce and survive. Most bacteria and fungi are harmless and may be beneficial to other living things. ...
... Bacteria and fungi always cause infectious diseases. Bacteria are living organisms, whereas, fungi are not. Both bacteria and fungi rely on living organisms to reproduce and survive. Most bacteria and fungi are harmless and may be beneficial to other living things. ...
Unit 4 Review
... Bacteria are how big? ___________________________________________ Bacteria are unicellular organisms that contain what type of cell? ________________________________ Identify the three types of shapes used to describe bacteria. ...
... Bacteria are how big? ___________________________________________ Bacteria are unicellular organisms that contain what type of cell? ________________________________ Identify the three types of shapes used to describe bacteria. ...
CSP_evolution_7-17
... a. This genetic variation (at least in part) contributes to an individual’sability to survive and reproduce and can change the genetic make-up of the entire population over time. i. Darwin did not know about genetics at the time but with the rediscovery of Mendel’s work in the early 1900’s it made t ...
... a. This genetic variation (at least in part) contributes to an individual’sability to survive and reproduce and can change the genetic make-up of the entire population over time. i. Darwin did not know about genetics at the time but with the rediscovery of Mendel’s work in the early 1900’s it made t ...
Number of individuals in the population
... population is known as the gene pool. This variation is the raw material for evolution This variation is also what allows for natural selection ...
... population is known as the gene pool. This variation is the raw material for evolution This variation is also what allows for natural selection ...
Topic 1 – Measurement and graphing
... Control variables: The size of the body, the launcher, the amount of water. Hypothesis: If the number of fins increases, then the rocket will fly higher. ...
... Control variables: The size of the body, the launcher, the amount of water. Hypothesis: If the number of fins increases, then the rocket will fly higher. ...
Name
... 4. Give an example of how the numbers of organisms found in a specific population depend on a specific abiotic factor found in their environment. What would happen if that abiotic factor was removed from the environment? Rocks in a desert is an example of an abiotic factor you can find in an environ ...
... 4. Give an example of how the numbers of organisms found in a specific population depend on a specific abiotic factor found in their environment. What would happen if that abiotic factor was removed from the environment? Rocks in a desert is an example of an abiotic factor you can find in an environ ...
Cells1 - ClickBiology
... • Identify and describe the structure of plant cells and animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and ...
... • Identify and describe the structure of plant cells and animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and ...
Edexcel AS Level Biology
... • Identify and describe the structure of plant cells and animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and ...
... • Identify and describe the structure of plant cells and animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and ...
An Introduction to Med. Biophysics - Lectures For UG-5
... tissues for cellular metabolism while the air in alveolus is rich in oxygen Because of this concentration gradient, oxygen diffuses into the blood Similarly CO2 diffuses out of the blood into alveolus ...
... tissues for cellular metabolism while the air in alveolus is rich in oxygen Because of this concentration gradient, oxygen diffuses into the blood Similarly CO2 diffuses out of the blood into alveolus ...
BIO101-01 Winter 04 Exam III Study Guide
... population. Traits that vary from individual to individual within a population are called polymorphic (eye color, for example). The variation that we see (the phenotype) is caused by variation at the gene level (the genotype). So, different alleles of the same gene contain polymorphisms (slight vari ...
... population. Traits that vary from individual to individual within a population are called polymorphic (eye color, for example). The variation that we see (the phenotype) is caused by variation at the gene level (the genotype). So, different alleles of the same gene contain polymorphisms (slight vari ...