* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
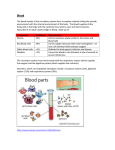
Name:___________________________________ Hour:_____________________________ Zoology Review 1. What is the definition of ecology? The study of the interactions between organisms with one another and their environment 2. All areas of life science build upon something simpler and smaller. Give the order of each level of organization from smallest to largest Cells Tissue Organs Organ Systems Organism Population Community Ecosystem Biosphere 3. What are the five characteristics that all living things share? Made of cells Use energy Respond to surrounding environment Reproduce Grow and develop 4. Give an example of how the numbers of organisms found in a specific population depend on a specific abiotic factor found in their environment. What would happen if that abiotic factor was removed from the environment? Rocks in a desert is an example of an abiotic factor you can find in an environment. If they were removed then the animals like a population of rock dwelling lizards which rely on them for building homes and protecting themselves from the heat would die. If a whole population of lizards dies then the larger predators which rely on those lizards for food would die. 5. Give an example of how the numbers of organisms found in a specific population depend on a specific biotic factor found in their environment. What would happen if that biotic factor was suddenly increased in the environment? If the amount of insects in an environment suddenly increases there is now an increase in food supply for smaller animals. More food would result in more smaller animals. More smaller animal would cause an increase in larger animals, this chain reaction could cause too overpopulation and lose of habitat for other organisms in the environment. 6. Describe ways that human activities can change the number of populations in an ecosystem and then explain what would happen if our actions destroyed one entire population, what effect would that have on other populations found there? Humans can change the number of populations in an ecosystem by actions like pollution-. When we add harmful chemicals to the water, air and land we are slowly destroying the ecosystems which the animals need to survive. If pollution causes a population of fish to die then the birds who depend on those fish for food will either have to move away or die from starvation. The larger animals which eat those birds will then lose their source of food also causing them to either die or have to move away. 7. What do you call the interaction between animals when one animal benefits from their relationship and the other is not affected at all? Commensalism 8. What do you call the nonliving parts of an organism’s environment? Abiotic 9. What do you call an animal that eats other animals to survive? Predation 10. What do you call an animal that lives off of another animal usually harming the animal it is living on? Parasite 11. What do you call the interaction where one organism kills and eats another organism for food? Predator 12. What do you call the living parts of an organism’s environment? Biotic 13. What do you call Behaviors or physical characteristics that allow organisms to live successfully in their environment? Adaptations 14. What do you call a close relationship between two species that benefits at least one of the species? Symbiosis 15. What do you call the interaction where there is a struggle between organisms to survive as they attempt to use the same limited resource? Competition The 11 human body systems are as follows: (Match each system to the correct function) 15. Nervous system* _E_ 16. Respiratory system*__A_ 17. Excretory system _G__ 18. Muscular system __B__ 19. Endocrine system __F_ 20. Immune system _H__ 21. Reproductive system __I_ 22. Circulatory system*_D__ 23. Digestive system*_C__ 24. Skeletal system*_J__ 25. Integumentary system _K_ A. Absorbs oxygen B. Moves bones C. Breaks down food D. Pumps blood E. Sends and receives electrical signals F. Regulates body function G. Gets rid of waste H. Body’s defense against illness I. Produces reproductive cells J. Provides a frame and support K. Protects underlying tissues 26.The purpose of the 11 organ systems is for the human body to maintain Homeostasis . What is homeostasis? The bodies maintenance of a stable internal environment Give an example of how the body performs homeostasis: Body temperature- When we get hot we sweat when we get cold we shiver Blood sugar levels-Too much sugar in the blood, pancreas secretes insulin to lower the amount of sugar Blood pressure-When blood pressure rises, the heart slows down to reduce pressure in the blood vessels 27. Name the 8 organs that make up the digestive system and describe their function. 28.What are the digestive organs that make up the digestive track? **(in order) _Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine 30. Name the five senses the human body has. Sight, Touch, Taste, Smell, Hearing 31. The nervous system is made up of two systems. What are they? Central Nervous System CNS Peripheral Nervous System PNS 32.What two organs make up the CNS? Brain Spinal Cord 33. What is the overall function of the CNS? The control center of the body 34. What organs makes up the PNS? Nerves 35. What is the overall function of the PNS? Carries information 36. What are the three parts of the human brain and what do they control? Cerebrum Controls memory, problem solving, thinking & feeling. It also controls movement Cerebellum Controls coordination and balance Brain Stem Controls automatic functions such as breathing, heart rate and digestion 37. What are the 9 organs (in order) that make up the respiratory system and what are their functions? Nose -- Entry and exit point for air Pharynx--Passage way for both air and food (back of throat) Epiglottis -- Skin flap that covers the trachea when we swallow Larynx-- "Voicebox" - Helps you speak using vocal chords Trachea--"Windpipe" Connects your pharynx to your lungs Bronchial Tubes--Give oxygen to the blood Alveoli- Small round sacs which meet up with your blood vessels found at the end of your bronchial tubes. Lungs -- 2 large organs in the chest that hold oxygen Diaphragm -- Muscles that cause you to breath 38. What is the major muscle of the circulatory system? Heart 39. How many chambers does the human heart have? Four 40. Label the chambers of a human heart. 41. What are the three types of blood vessels and what are their functions? Arteries Carry blood Away from the heart and to the major organs of the body (Have oxygen) Veins Carry blood Towards the heart away from the major organs (No oxygen) Capillaries Smallest blood vessels for gas exchange, they connect the arteries and veins 42. What are the three types of blood cells and what is their function? Red Blood Cells Carry and deliver oxygen and nutrients to all of the cells of the body White Blood Cells Part of the immune system. Fight off bad bacteria and viruses Platelets Clot our blood when we get a cut 43. What are seven reasons why bones are so important? 1. Structure 2. Support 3. Protection 4. Make Red Blood Cells 5. Make White Blood Cells 6. Make Platelets 7. Store Minerals 44. How many bones do we have in our adult bodies? 45. How many bones do we have when we are born? 206 300 46. All of the different cells in our body look completely different. Explain one reason why Nerve cells and Red blood cells look so different. The Nerve Cells have to transport information to one another with chemicals and electricity. The Red Blood Cell works by itself to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the different cells of the body. 47. How do all cells in the body rely on the respiratory system? All cells in the body need oxygen to work and the respiratory system supplies the body's cells with oxygen 48. How do all cells in the body rely on the digestive system? All cells in the body need nutrients to work and the digestive system supplies the body's cell with nutrients 49. How do all cells in the body rely on the skeletal system? All cells in the body need oxygen and nutrients to work and the skeletal system makes the blood which delivers oxygen and nutrients to the body's cells. 50. How do all cells in the body rely on the circulatory system? All cells in the body need oxygen and nutrients to work and the circulatory system delivers blood which brings oxygen and nutrients to the body's cells. 51. How do all cells in the body rely on the nervous system? The nervous system controls all of the organ systems and organs in the body making the delivery of information possible 52. What system is the most important and why? There is no one system that is the most important. They all require each other in order to function properly.