Ch. 3 Review - Cobb Learning
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs ______ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size ...
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs ______ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size ...
Anatomia I - univr dsnm
... membrane, the chain of events that leads to the transmission of the signal from synapse to synapse through the axon, Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes; the action potential and muscle contraction. The muscle cell, molecules, enzymes and proteins involved in contraction of the muscle fiber. The musc ...
... membrane, the chain of events that leads to the transmission of the signal from synapse to synapse through the axon, Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes; the action potential and muscle contraction. The muscle cell, molecules, enzymes and proteins involved in contraction of the muscle fiber. The musc ...
organisms - Lyndhurst Schools
... Organisms react to stimuli: Light Temperature Odor Sound Gravity Heat Water Pressure ...
... Organisms react to stimuli: Light Temperature Odor Sound Gravity Heat Water Pressure ...
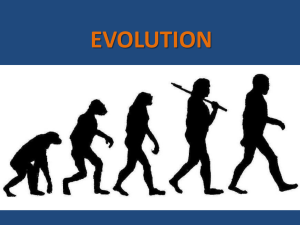
History of Evolution Jelly Bean Review
... passed this on to their offspring. b. Those cheetahs who ran fast were able to get food and survive and reproduce, passing this trait on to offspring. c. Through the survival of the fittest, slow cheetahs died. d. The environment chose fast cheetahs. ...
... passed this on to their offspring. b. Those cheetahs who ran fast were able to get food and survive and reproduce, passing this trait on to offspring. c. Through the survival of the fittest, slow cheetahs died. d. The environment chose fast cheetahs. ...
Image-conscious biology
... The way that we investigate these is primarily using high content screening. High content screening is image-based screening. What a person can do on a microscope, we can now do in small microtitre plates, which enable us to look at hundreds of thousands of images in a very short period of time. We ...
... The way that we investigate these is primarily using high content screening. High content screening is image-based screening. What a person can do on a microscope, we can now do in small microtitre plates, which enable us to look at hundreds of thousands of images in a very short period of time. We ...
Investigation 1 “Living Cells” Big Ideas
... right ventricle, to the lungs, to the left atrium, to the left ventricle, into arteries that flow into capillaries, which are in contact with cells. Blood returns to the heart in veins. 4. How do cells in humans get the nutrients they need? a. The digestive system reduces food to nutrients. Nutrient ...
... right ventricle, to the lungs, to the left atrium, to the left ventricle, into arteries that flow into capillaries, which are in contact with cells. Blood returns to the heart in veins. 4. How do cells in humans get the nutrients they need? a. The digestive system reduces food to nutrients. Nutrient ...
Section 13.1
... • Adaptations include body structures that help an organism feed, move around, and protect itself. ...
... • Adaptations include body structures that help an organism feed, move around, and protect itself. ...
CS 8.1 - 8.4 Assessment Event
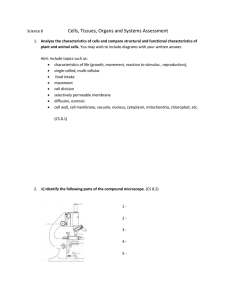
... organ systems in humans and describe two examples of science and technology based careers in Saskatchewan that require an understanding of this knowledge. You may wish to include diagrams with your written answer. Hint: Include topics such as: specialization of cells muscles, nerves, epithelial ...
... organ systems in humans and describe two examples of science and technology based careers in Saskatchewan that require an understanding of this knowledge. You may wish to include diagrams with your written answer. Hint: Include topics such as: specialization of cells muscles, nerves, epithelial ...
Biology Standards Checklist
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
B1.7 Evolution
... Mutations: New forms of genes resulting from changes to existing genes – random – mistakes made when DNA is copied in cell division. Mutations introduce more variety. May have no effect or harmful but if better suited to the environment and more likely to survive and reproduce ...
... Mutations: New forms of genes resulting from changes to existing genes – random – mistakes made when DNA is copied in cell division. Mutations introduce more variety. May have no effect or harmful but if better suited to the environment and more likely to survive and reproduce ...
National 4/5 Biology - Multicelluar Organisms
... - they can carry out all the functions needed for life Many living organisms are composed of only one cell - e.g. an amoeba Most living organisms are made of many millions of cells It would be inefficient if every cell performed exactly the same function ...
... - they can carry out all the functions needed for life Many living organisms are composed of only one cell - e.g. an amoeba Most living organisms are made of many millions of cells It would be inefficient if every cell performed exactly the same function ...
Mutations
... individual’s fitness. A beneficial mutation gives an individual a selective advantage. Most mutations are neutral or harmful. ...
... individual’s fitness. A beneficial mutation gives an individual a selective advantage. Most mutations are neutral or harmful. ...
QS039--Ch21--Mechanisms of Evolution
... a. ____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________ ...
... a. ____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________ ...
study guide for final
... Dominant vs. Recessive traits: dominant appears in every generation Recessive usually skips generations Punnett Squares: need to be able to fill in punnett and determine % & fraction results ** DNA Structure & Mitosis and Meiosis Nucleotides: three parts: sugar, phosphate, base Chargaff’s Rule: A-T, ...
... Dominant vs. Recessive traits: dominant appears in every generation Recessive usually skips generations Punnett Squares: need to be able to fill in punnett and determine % & fraction results ** DNA Structure & Mitosis and Meiosis Nucleotides: three parts: sugar, phosphate, base Chargaff’s Rule: A-T, ...
StudyGuideAdaptationandEvolution
... Favorable mutations are passed down to future generations through reproduction. ...
... Favorable mutations are passed down to future generations through reproduction. ...
StudyGuideBioEvolution
... Favorable mutations are passed down to future generations through reproduction. ...
... Favorable mutations are passed down to future generations through reproduction. ...
Introduction to Cells
... Following the discovery of cells, scientists agreed that both plants and animals are made of cells and are the smallest units of life. This lead to a cornerstone of biology known as “Cell Theory”. ...
... Following the discovery of cells, scientists agreed that both plants and animals are made of cells and are the smallest units of life. This lead to a cornerstone of biology known as “Cell Theory”. ...
Living Systems PowerPoint Notes
... __________________ organisms. Multicellular organisms have _____________ _____________ – (humans have many trillion cells). The cells must remain a part of the organism’s body to _____________. Your body is made up of many _____________ _____________ of cells. You have skin cells, Organisms that are ...
... __________________ organisms. Multicellular organisms have _____________ _____________ – (humans have many trillion cells). The cells must remain a part of the organism’s body to _____________. Your body is made up of many _____________ _____________ of cells. You have skin cells, Organisms that are ...
Physical Anthropology Study Guide for Exam 1 Evolutionary Theory
... Darwin Natural selection Darwin's concept of evolution Wallace Natural selection in action: industrial melanism Chromosomal Genetics Mendel & his Laws Chromosomes DNA Mutation Inheritance Meiosis and Mitosis Genes Alleles Homozygous Heterozygous Dominant Recessive Codominant Punnett Square Phenotype ...
... Darwin Natural selection Darwin's concept of evolution Wallace Natural selection in action: industrial melanism Chromosomal Genetics Mendel & his Laws Chromosomes DNA Mutation Inheritance Meiosis and Mitosis Genes Alleles Homozygous Heterozygous Dominant Recessive Codominant Punnett Square Phenotype ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Living Things
... 8. The chloroplast and the cell wall because they are only found in a plant cell. 9. A. Animal Cell—B. Plant Cell I know this because the plant cell had a cell wall and a chloroplast; Which only plants have and not animals. And diagram B. had large vacuole in its cells, which again a plant has and ...
... 8. The chloroplast and the cell wall because they are only found in a plant cell. 9. A. Animal Cell—B. Plant Cell I know this because the plant cell had a cell wall and a chloroplast; Which only plants have and not animals. And diagram B. had large vacuole in its cells, which again a plant has and ...
BIO109 Survey of Biology - Cape Cod Community College
... • Explain the properties required for life by recognizing the levels of scientific organization • Classify the variety of life forms that have evolved • Assemble lab specimens into taxonomic groups according to comparative data • Utilize the Periodic Table of Elements to demonstrate atomic number an ...
... • Explain the properties required for life by recognizing the levels of scientific organization • Classify the variety of life forms that have evolved • Assemble lab specimens into taxonomic groups according to comparative data • Utilize the Periodic Table of Elements to demonstrate atomic number an ...