Ecology
... Energy is the basis of every community. Of course, the origin of all energy is the sun. The soil depends on organic matter for minerals (e.g. decomposing plants or animals) An ecosystem consists of all the organisms in a community and the non-living part of the environment and their interaction. Man ...
... Energy is the basis of every community. Of course, the origin of all energy is the sun. The soil depends on organic matter for minerals (e.g. decomposing plants or animals) An ecosystem consists of all the organisms in a community and the non-living part of the environment and their interaction. Man ...
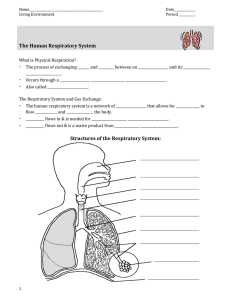
Physical Respiration Notes SI
... The process of exchanging _______ and _________ between an __________________ and its ________________ _____________________. Occurs through a __________________ ____________________ ________________________. Also called ________________________. ...
... The process of exchanging _______ and _________ between an __________________ and its ________________ _____________________. Occurs through a __________________ ____________________ ________________________. Also called ________________________. ...
Greenhouse Effect: natural and enhanced
... Human activities enhance this natural greenhouse effect that in turn promotes climate change ...
... Human activities enhance this natural greenhouse effect that in turn promotes climate change ...
Ch16_EcosystemsStudentNotes[1] - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology
... _______________organisms, and then _______________________________to the nonliving environment. These paths form closed circles, or _______________, called _________________chemical cycles. • In each biogeochemical cycle, a _________________________forms when a substance enters living ______________ ...
... _______________organisms, and then _______________________________to the nonliving environment. These paths form closed circles, or _______________, called _________________chemical cycles. • In each biogeochemical cycle, a _________________________forms when a substance enters living ______________ ...
Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment
... 52.Reproductive technology In vitro-fertilization 53.____________-the process by which organisms have changed overtimesimple,single-celled: complex-single-celled : complex, multicellular 54.Geologic time is based on the ______________ __________. 55.Natural selection overproduction struggle for su ...
... 52.Reproductive technology In vitro-fertilization 53.____________-the process by which organisms have changed overtimesimple,single-celled: complex-single-celled : complex, multicellular 54.Geologic time is based on the ______________ __________. 55.Natural selection overproduction struggle for su ...
GLOSSARY
... **Abiotic Factor: the non-living parts or aspects of an environment which affects organisms in their habitats such as; soil, water, air, temperature, sunlight, elevation, climate. Adaptation: A change or the process of change occurring over long time periods by which a plant or animal becomes better ...
... **Abiotic Factor: the non-living parts or aspects of an environment which affects organisms in their habitats such as; soil, water, air, temperature, sunlight, elevation, climate. Adaptation: A change or the process of change occurring over long time periods by which a plant or animal becomes better ...
Ecology Notes - Rochester Century High School
... 8.Population (interbreeding species) 9.Biological Community (all species in a ...
... 8.Population (interbreeding species) 9.Biological Community (all species in a ...
Ecology 1-
... same geographic location • Community: A group of interacting populations (different species) that occupy the same area at the same time. ...
... same geographic location • Community: A group of interacting populations (different species) that occupy the same area at the same time. ...
Chapter 2: Principles of Ecology
... Population: group of organisms, all of the same species, which interbreed and live in the same area at the same time o ...
... Population: group of organisms, all of the same species, which interbreed and live in the same area at the same time o ...
Principles of Ecology
... Population: group of organisms, all of the same species, which interbreed and live in the same area at the same time o ...
... Population: group of organisms, all of the same species, which interbreed and live in the same area at the same time o ...
ecosystems and biomes
... forms water vapor, a gas, in the atmosphere. • Most water evaporates from oceans and lakes. • Water is also produced through living things; plants release water vapors from their leaves, people release water through waste and water vapor when they exhale. ...
... forms water vapor, a gas, in the atmosphere. • Most water evaporates from oceans and lakes. • Water is also produced through living things; plants release water vapors from their leaves, people release water through waste and water vapor when they exhale. ...
Biomes of the World
... • Temperatures typically fall between 20oC and 25oC for the entire year • As many as 50% of all the world’s animal species may be found here ...
... • Temperatures typically fall between 20oC and 25oC for the entire year • As many as 50% of all the world’s animal species may be found here ...
ecosystems and biomes
... forms water vapor, a gas, in the atmosphere. • Most water evaporates from oceans and lakes. • Water is also produced through living things; plants release water vapors from their leaves, people release water through waste and water vapor when they exhale. ...
... forms water vapor, a gas, in the atmosphere. • Most water evaporates from oceans and lakes. • Water is also produced through living things; plants release water vapors from their leaves, people release water through waste and water vapor when they exhale. ...
The Water Cycle: Lesson Plans and Activities
... What are the water cycle zones? The water cycle occurs everywhere that water is found. These areas can be broken down into three water cycle zones, atmosphere, water surface, and underground. The atmosphere consists of all the water in the thin layer of gas surrounding the earth. Surface water inclu ...
... What are the water cycle zones? The water cycle occurs everywhere that water is found. These areas can be broken down into three water cycle zones, atmosphere, water surface, and underground. The atmosphere consists of all the water in the thin layer of gas surrounding the earth. Surface water inclu ...
ICS Final Exam Study Guide
... Climate- the average, year-after-year condition of temperature and precipitation in a particular region. Greenhouse effect- the natural situation in which heat is retained by a layer of greenhouse gases. Polar zones- cold area where the sun’s rays strike Earth at a very low angle. Temperate zones- m ...
... Climate- the average, year-after-year condition of temperature and precipitation in a particular region. Greenhouse effect- the natural situation in which heat is retained by a layer of greenhouse gases. Polar zones- cold area where the sun’s rays strike Earth at a very low angle. Temperate zones- m ...
10 Surprising Threats to Biodiversity
... Overhunting animals for fun can affect not only the animals themselves, but also their habitats. Exotic animals such as rhinos are hunted for their purported medicinal benefits. Elephants are hunted for their ivory. Crocodiles are hunted for their skin, which is turned into expensive leather product ...
... Overhunting animals for fun can affect not only the animals themselves, but also their habitats. Exotic animals such as rhinos are hunted for their purported medicinal benefits. Elephants are hunted for their ivory. Crocodiles are hunted for their skin, which is turned into expensive leather product ...
Stream Biotic and Abiotic
... Smaller streams ( 1st order) flow into larger streams (2nd order) and continue on. Two streams of the same order must come together for a stream to move up in order. The size or order of the stream relates directly on the organisms that are in the ecosystem. 1st order streams are home to large ...
... Smaller streams ( 1st order) flow into larger streams (2nd order) and continue on. Two streams of the same order must come together for a stream to move up in order. The size or order of the stream relates directly on the organisms that are in the ecosystem. 1st order streams are home to large ...
Vocabulary Document - Kawameeh Middle School
... Lesson 3: Matter & Energy in Ecosystems 1. Producer: organisms that use an outside energy source, such as the sun, and produce their own food. 2. Consumer: organisms that cannot make their own food. 3. Herbivore: consumers that eat only plants. 4. Carnivores: consumers that eat only animals. 5. Omni ...
... Lesson 3: Matter & Energy in Ecosystems 1. Producer: organisms that use an outside energy source, such as the sun, and produce their own food. 2. Consumer: organisms that cannot make their own food. 3. Herbivore: consumers that eat only plants. 4. Carnivores: consumers that eat only animals. 5. Omni ...
Ecology: Study Guide
... All ecosystems change over time. As they change the type of organisms that live there also changes. Often one community is replaced by another and this is known as succession. Ecosystems are sometimes destroyed by natural catastrophes such as volcanoes, earthquakes, fires, floods. If this leaves beh ...
... All ecosystems change over time. As they change the type of organisms that live there also changes. Often one community is replaced by another and this is known as succession. Ecosystems are sometimes destroyed by natural catastrophes such as volcanoes, earthquakes, fires, floods. If this leaves beh ...
The Forest Ecosystem - Hitchcock Center for the Environment
... environments are connected to, interact with, and are influenced by each other. They study the relationships between Earth and other nearby objects in the solar system and the impact of those relationships ...
... environments are connected to, interact with, and are influenced by each other. They study the relationships between Earth and other nearby objects in the solar system and the impact of those relationships ...
Chapter 2 Living Things and their Environment: Adaptations
... Below are examples of living things in the desert and how they have adapted to their environment. A. Creosote bush – have mainly shallow roots that help them take any rain that may fall. B. Barrel cactus – has thick waxy skin and thick round stem to help it collect and store water. C. Octillo – drop ...
... Below are examples of living things in the desert and how they have adapted to their environment. A. Creosote bush – have mainly shallow roots that help them take any rain that may fall. B. Barrel cactus – has thick waxy skin and thick round stem to help it collect and store water. C. Octillo – drop ...
Ecosystems and Populations
... within an ecosystem all affect one another, acting as either an energy source, or a competitor. The abiotic component is the non-biological part of an ecosystem. This includes the climate, light level and rainfall. Some abiotic factors, such as the soil, can be altered by the presence of organisms. ...
... within an ecosystem all affect one another, acting as either an energy source, or a competitor. The abiotic component is the non-biological part of an ecosystem. This includes the climate, light level and rainfall. Some abiotic factors, such as the soil, can be altered by the presence of organisms. ...
HS Biology Ecosystems and Succession
... within an ecosystem all affect one another, acting as either an energy source, or a competitor. The abiotic component is the non-biological part of an ecosystem. This includes the climate, light level and rainfall. Some abiotic factors, such as the soil, can be altered by the presence of organisms. ...
... within an ecosystem all affect one another, acting as either an energy source, or a competitor. The abiotic component is the non-biological part of an ecosystem. This includes the climate, light level and rainfall. Some abiotic factors, such as the soil, can be altered by the presence of organisms. ...
LEVELS of ORGANIZATION
... -EX: sunlight, water, temperature, soil type, rocks, minerals, wind, pH, salinity -organisms adapt to abiotic factors in their natural environments -A change in these factors could cause an unhealthy environment & possibly result in death ...
... -EX: sunlight, water, temperature, soil type, rocks, minerals, wind, pH, salinity -organisms adapt to abiotic factors in their natural environments -A change in these factors could cause an unhealthy environment & possibly result in death ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.

![Ch16_EcosystemsStudentNotes[1] - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009688549_1-67efd9bcb8e6f5acdcf17bfaf22d0643-300x300.png)