Drugs: Antagonists, agonists, and reuptake inhibitors Drugs—why
... help regulate this system by "turning down" dopamine activity. Cocaine and other drugs of abuse can alter dopamine function. Such drugs may have very different actions. The specific action depends on which dopamine receptors the drugs stimulate or block, and how well they mimic dopamine. Dopamine bi ...
... help regulate this system by "turning down" dopamine activity. Cocaine and other drugs of abuse can alter dopamine function. Such drugs may have very different actions. The specific action depends on which dopamine receptors the drugs stimulate or block, and how well they mimic dopamine. Dopamine bi ...
29.5 Brain Function and Chemistry KEY CONCEPT brain.
... New techniques improve our understanding of the brain. • Today, scientists study the brain without surgery. ...
... New techniques improve our understanding of the brain. • Today, scientists study the brain without surgery. ...
Parkinson Meds
... On off effect= long term use of the drug may have an irregulr response to the drug….. Reduce the maintanence dose and substitute another anti parkinson’s drug ...
... On off effect= long term use of the drug may have an irregulr response to the drug….. Reduce the maintanence dose and substitute another anti parkinson’s drug ...
Students list DRUGS
... Synapse is between nerves and neuroeffecter junctions are between a nerve and any other cell types. Neurotransmitters bind to specific receptor site like key and lock. Many drugs and other xenobiotics also fit into various types of receptors and elicit a response – agonists. Those that block the rec ...
... Synapse is between nerves and neuroeffecter junctions are between a nerve and any other cell types. Neurotransmitters bind to specific receptor site like key and lock. Many drugs and other xenobiotics also fit into various types of receptors and elicit a response – agonists. Those that block the rec ...
DOSE *RESPONSE CURVES
... Full Agonists: Compounds that are able to elicit a maximal response following receptor occupation and activation. Partial Agonists: Compounds that can activate receptors but are unable to elicit the maximal response of the receptor system. Inverse agonist: an agent which binds to the same receptor b ...
... Full Agonists: Compounds that are able to elicit a maximal response following receptor occupation and activation. Partial Agonists: Compounds that can activate receptors but are unable to elicit the maximal response of the receptor system. Inverse agonist: an agent which binds to the same receptor b ...
Neuron and Nervous System Review Guide
... Neural Communication Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons Agonist – mimic neurotransmitters Example: Morphine mimics endorphins Antagonist – block neurotransmitters Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, l ...
... Neural Communication Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons Agonist – mimic neurotransmitters Example: Morphine mimics endorphins Antagonist – block neurotransmitters Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, l ...
NEUROTRANSMITTERS AND RECEPTORS AS THE TARGETS FOR ADDICTION TREATMENT: A
... the central nervous system. DA receptors have subtypes they are mainly two families D1 (D1, D5) and D2 (D2, D3, D4) families, which are classified based on the pharmacological action. Activation of D1family receptors increases cyclic adenosine 3, 5,-monophosphate (cAMP) through stimulation of adenyl ...
... the central nervous system. DA receptors have subtypes they are mainly two families D1 (D1, D5) and D2 (D2, D3, D4) families, which are classified based on the pharmacological action. Activation of D1family receptors increases cyclic adenosine 3, 5,-monophosphate (cAMP) through stimulation of adenyl ...
Pharm_essays
... and these channels are activated when the ligand binds at this site. It is on these receptors that the fast neurotransmitters of the body typically act. Eg. of these receptors include the Nicotinic ACh receptor, GABAa receptor and Glutamate gated calcium channel (NMDA, AMPA and kainite types). Thei ...
... and these channels are activated when the ligand binds at this site. It is on these receptors that the fast neurotransmitters of the body typically act. Eg. of these receptors include the Nicotinic ACh receptor, GABAa receptor and Glutamate gated calcium channel (NMDA, AMPA and kainite types). Thei ...
Lesson 7: Advances - Raleigh Charter High School
... useful for treating mild or moderate pain, such as headache or toothache or arthritis. Opioids are the most potent painkillers and are used for severe pain, such as that occurring after major chest or abdominal surgery. Opioids can be injected directly into the spinal cord to block pain without numb ...
... useful for treating mild or moderate pain, such as headache or toothache or arthritis. Opioids are the most potent painkillers and are used for severe pain, such as that occurring after major chest or abdominal surgery. Opioids can be injected directly into the spinal cord to block pain without numb ...
Previous Discussion Section Notes
... a. 3 different pathways blocked—makes this very effective i. Displace norepinephrine, inhibit norepinephrine re-uptake, inhibit degradation by MAO b. Methamphetamine is more lipophilic so that it can effectively cross the blood brain barrier. Depletes norepinephrine catecholamine in vesicles, which ...
... a. 3 different pathways blocked—makes this very effective i. Displace norepinephrine, inhibit norepinephrine re-uptake, inhibit degradation by MAO b. Methamphetamine is more lipophilic so that it can effectively cross the blood brain barrier. Depletes norepinephrine catecholamine in vesicles, which ...
Antipsychotics - 2011
... • Fluvoxamine inhibits olanzapine and clozapine metabolism • Smoking induces Olanzapine metabolism • SSRIs inhibit most antipsychotics and therefore increase serum concentrations • Phenytoin reduces serum concentration of Quetiapine • Others – grapefruit juice, Antibiotics, ...
... • Fluvoxamine inhibits olanzapine and clozapine metabolism • Smoking induces Olanzapine metabolism • SSRIs inhibit most antipsychotics and therefore increase serum concentrations • Phenytoin reduces serum concentration of Quetiapine • Others – grapefruit juice, Antibiotics, ...
Introduction to neuropharmacology
... In the brain the main excitatory (depolarizing) transmitter is glutamate. Glutamate binds to several metabotropic and several ionotropic receptors. The main ionotropic receptor is the AMPA receptor. AMPA is an abbreviation of (±)alpha-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid, obviously ...
... In the brain the main excitatory (depolarizing) transmitter is glutamate. Glutamate binds to several metabotropic and several ionotropic receptors. The main ionotropic receptor is the AMPA receptor. AMPA is an abbreviation of (±)alpha-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid, obviously ...
Neurophysiology leture (3) Prof. Eman Al
... LIVED(lasts about 2-3 hours only) - So … after eating a meal you’ll always feel a bit tired or exhausted as blood is going to the GIT, but this lasts only for a few minutes. However, if you experience this calming effect for few hours it’s most probably due to the increase in serotonin by carbohydra ...
... LIVED(lasts about 2-3 hours only) - So … after eating a meal you’ll always feel a bit tired or exhausted as blood is going to the GIT, but this lasts only for a few minutes. However, if you experience this calming effect for few hours it’s most probably due to the increase in serotonin by carbohydra ...
Untitled
... 2 )Drugs acting on genetic material and immune system Drugs acting on genetic material: Introduction, classification and mechanism of action. a) DNA-intercalating agents-Anticancer and antimalarial agents. Structural formulae of Daunomycin, Adriamycin and Amsacrine. b) DNA- Binding and nicking agent ...
... 2 )Drugs acting on genetic material and immune system Drugs acting on genetic material: Introduction, classification and mechanism of action. a) DNA-intercalating agents-Anticancer and antimalarial agents. Structural formulae of Daunomycin, Adriamycin and Amsacrine. b) DNA- Binding and nicking agent ...
351 Pharmacology 3rd sf
... Receptor/Binding site “A specific protein in either the plasma membrane or interior of a target cell with which a ligand/drug combines” It must be selective in choosing ligands/drugs to bind To avoid constant activation of the receptor by promiscuous binding of many different ligands It must ...
... Receptor/Binding site “A specific protein in either the plasma membrane or interior of a target cell with which a ligand/drug combines” It must be selective in choosing ligands/drugs to bind To avoid constant activation of the receptor by promiscuous binding of many different ligands It must ...
understanding drugs and medicinces what is the
... inactive ingredients, things that give the pill it’s shape, color, size. ...
... inactive ingredients, things that give the pill it’s shape, color, size. ...
Slide ()
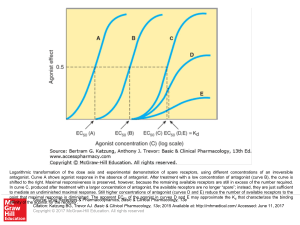
... shifted to the right. Maximal responsiveness is preserved, however, because the remaining available receptors are still in excess of the number required. In curve C, produced after treatment with a larger concentration of antagonist, the available receptors are no longer “spare”; instead, they are j ...
... shifted to the right. Maximal responsiveness is preserved, however, because the remaining available receptors are still in excess of the number required. In curve C, produced after treatment with a larger concentration of antagonist, the available receptors are no longer “spare”; instead, they are j ...
Muscarinic AChR agonist
... Boutons have multiple nerve terminals Simultaneous release Stimulation of contraction via AP Acetylcholine degraded after action ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE ...
... Boutons have multiple nerve terminals Simultaneous release Stimulation of contraction via AP Acetylcholine degraded after action ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE ...
Drugs, the brain and behavior, Objectives:
... Is perhaps the world’s oldest known drug. It has historically been known as a food, and today a drug. It is one of the few drugs that does not act on a specific receptor site in the body. It affects the central nervous system. It is toxic to the liver, heart, brain, gut, pancreas and fetus. Has been ...
... Is perhaps the world’s oldest known drug. It has historically been known as a food, and today a drug. It is one of the few drugs that does not act on a specific receptor site in the body. It affects the central nervous system. It is toxic to the liver, heart, brain, gut, pancreas and fetus. Has been ...
Pharmacodynamics
... A receptor that is embedded in the cell membrane and functions to receive chemical information from the extracellular compartment and to transmit that information to the intracellular compartment. ...
... A receptor that is embedded in the cell membrane and functions to receive chemical information from the extracellular compartment and to transmit that information to the intracellular compartment. ...
(Agonist) of Nuclear Receptor
... A receptor that is embedded in the cell membrane and functions to receive chemical information from the extracellular compartment and to transmit that information to the intracellular compartment. ...
... A receptor that is embedded in the cell membrane and functions to receive chemical information from the extracellular compartment and to transmit that information to the intracellular compartment. ...