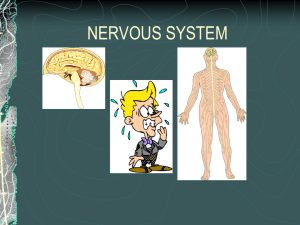
Frontal Lobe - Washington School Counselor Association
... This link is especially important because it will provide you with a list of all treatment agencies and the s This site includes treatment data and admission statistics. This document provides trends in adolescent substance abuse. ...
... This link is especially important because it will provide you with a list of all treatment agencies and the s This site includes treatment data and admission statistics. This document provides trends in adolescent substance abuse. ...
General Psychology - K-Dub
... with information from touch stimuli. The occipital lobe deals with visual information. Auditory information is sent to the temporal lobe. ...
... with information from touch stimuli. The occipital lobe deals with visual information. Auditory information is sent to the temporal lobe. ...
Peripheral Nervous System - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... Example of the speech of an individual with Wernicke’s aphasia. The individual is describing a picture of a child taking a cookie. “Uh, well this is the ... the … of this. This and this and this and this. These things going in there like that. This is … things here. This one here, these two things ...
... Example of the speech of an individual with Wernicke’s aphasia. The individual is describing a picture of a child taking a cookie. “Uh, well this is the ... the … of this. This and this and this and this. These things going in there like that. This is … things here. This one here, these two things ...
The Nervous System
... the nervous system that does not include the vertebrae, brain, and retina. The peripheral nervous system is essentially the “wiring” of the body. ...
... the nervous system that does not include the vertebrae, brain, and retina. The peripheral nervous system is essentially the “wiring” of the body. ...
Print › psych chapter 2 | Quizlet | Quizlet
... A structure in the forebrain through which all sensory information (except smell) must pass to get to the cerebral cortex. ...
... A structure in the forebrain through which all sensory information (except smell) must pass to get to the cerebral cortex. ...
Chapter 2
... 12. Discuss how the pseudoscience called phrenology evolved, and how it ultimately helped advance the idea of cortical localization. 13. Describe the basic sequence of prenatal brain development and the evidence for neurogenesis throughout life. ...
... 12. Discuss how the pseudoscience called phrenology evolved, and how it ultimately helped advance the idea of cortical localization. 13. Describe the basic sequence of prenatal brain development and the evidence for neurogenesis throughout life. ...
Nervous system Nervous system
... – Accept impulses from sensory receptors – Transmit them to the CNS • Interneurons – Convey nerve impulses between various parts of the CNS ...
... – Accept impulses from sensory receptors – Transmit them to the CNS • Interneurons – Convey nerve impulses between various parts of the CNS ...
to-BBB receives Michael J. Fox Foundation funding for
... to-BBB, the Dutch brain drug delivery company, has been awarded funding by The Michael J. Fox Foundation (MJFF) to conduct preclinical research targeting neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease (PD) with its second product in development, 2B3-201. This is to-BBB’s first grant from MJFF. “We strongl ...
... to-BBB, the Dutch brain drug delivery company, has been awarded funding by The Michael J. Fox Foundation (MJFF) to conduct preclinical research targeting neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease (PD) with its second product in development, 2B3-201. This is to-BBB’s first grant from MJFF. “We strongl ...
1-nervous_system
... Holds neurons in place Speeds up transmission Can repair if damaged Keeps messages from being scrambled ...
... Holds neurons in place Speeds up transmission Can repair if damaged Keeps messages from being scrambled ...
Chapter 14
... in pressure --- hydrocephalus In newborn or fetus, the fontanels allow this internal pressure to cause expansion of the skull and damage to the brain tissue ...
... in pressure --- hydrocephalus In newborn or fetus, the fontanels allow this internal pressure to cause expansion of the skull and damage to the brain tissue ...
Cognitive Development - Oakland Schools Moodle
... Paying attention – attention span grows over time. Generally bright babies have a short attention span (in the infancy stage only) ...
... Paying attention – attention span grows over time. Generally bright babies have a short attention span (in the infancy stage only) ...
General PLTW Document - Buncombe County Schools
... and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and col ...
... and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and col ...
Brain Fingerprinting
... legitimate reason, then the test cannot be applied. If a suspect acknowledges being at the scene of the crime, but claims to be a witness and not a perpetrator, then the fact that he knows details about the crime would not be incriminating. There would be no reason to conduct a test, because the res ...
... legitimate reason, then the test cannot be applied. If a suspect acknowledges being at the scene of the crime, but claims to be a witness and not a perpetrator, then the fact that he knows details about the crime would not be incriminating. There would be no reason to conduct a test, because the res ...
Presentation - Ch 2 Sections Demo-6-7
... • What threshold will result in the fastest learning? • Reinforcement of learning: when output is correct, that path is strengthened (LTP) • Long-Term Potentiation: the post-synaptic neurons become more sensitive to those presynaptic neurons that are exciting it • LTP becomes memory ...
... • What threshold will result in the fastest learning? • Reinforcement of learning: when output is correct, that path is strengthened (LTP) • Long-Term Potentiation: the post-synaptic neurons become more sensitive to those presynaptic neurons that are exciting it • LTP becomes memory ...
Module 4 revised
... a doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and ...
... a doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and ...
Draft Proposal to the Keck Foundation KECK CENTER FOR
... to that of the cellular network. At the macro level, a principal goal is understanding the relationship of signal fluctuations to biological phenomena in brain imaging. We have developed near-ir methods to explore the cerebral cortex non-invasively and in real time. Combining fMRI and near-ir provid ...
... to that of the cellular network. At the macro level, a principal goal is understanding the relationship of signal fluctuations to biological phenomena in brain imaging. We have developed near-ir methods to explore the cerebral cortex non-invasively and in real time. Combining fMRI and near-ir provid ...
Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
... Lesion: tissue destruction, brain lesions are naturally or experimentally caused Electroencephalogram: (EEG) amplified recording of the waves, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. CT computed tomography scan: X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by the computer to compos ...
... Lesion: tissue destruction, brain lesions are naturally or experimentally caused Electroencephalogram: (EEG) amplified recording of the waves, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. CT computed tomography scan: X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by the computer to compos ...
What Our Brains Can Teach Us
... disasters transpiring in the dense communities of our brain cells. We give them names like neurodegeneration, stroke and epilepsy. But just because we can name them doesn’t mean we know how to fix them. For example, we have little idea how to mend the damage from the widespread destruction of a tra ...
... disasters transpiring in the dense communities of our brain cells. We give them names like neurodegeneration, stroke and epilepsy. But just because we can name them doesn’t mean we know how to fix them. For example, we have little idea how to mend the damage from the widespread destruction of a tra ...
Brain Basics
... Brodmann’s parcellation of the brain, published in 1909, has had amazing longevity, as his system is still widely used. In July 2016, a new parcellation, including 180 areas in total, was proposed based on many different types of data. ...
... Brodmann’s parcellation of the brain, published in 1909, has had amazing longevity, as his system is still widely used. In July 2016, a new parcellation, including 180 areas in total, was proposed based on many different types of data. ...
Topic Presentation: Biopsychology
... 1. Specialized support cells for neurons 2. Form the Myelin Sheath a. Multiple Sclerosis is a disease that involves degeneration of the myelin sheath. vi. Plasticity – Ability of the nervous system to adapt or change 1. Learning 2. Effects of experience 3. Repair a. Examples i. After Ashley permanen ...
... 1. Specialized support cells for neurons 2. Form the Myelin Sheath a. Multiple Sclerosis is a disease that involves degeneration of the myelin sheath. vi. Plasticity – Ability of the nervous system to adapt or change 1. Learning 2. Effects of experience 3. Repair a. Examples i. After Ashley permanen ...
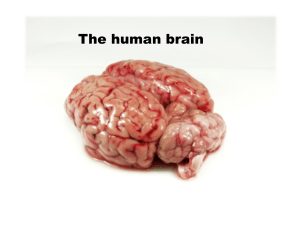
The Brain
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
Neurolinguistics

Neurolinguistics is the study of the neural mechanisms in the human brain that control the comprehension, production, and acquisition of language. As an interdisciplinary field, neurolinguistics draws methodology and theory from fields such as neuroscience, linguistics, cognitive science, neurobiology, communication disorders, neuropsychology, and computer science. Researchers are drawn to the field from a variety of backgrounds, bringing along a variety of experimental techniques as well as widely varying theoretical perspectives. Much work in neurolinguistics is informed by models in psycholinguistics and theoretical linguistics, and is focused on investigating how the brain can implement the processes that theoretical and psycholinguistics propose are necessary in producing and comprehending language. Neurolinguists study the physiological mechanisms by which the brain processes information related to language, and evaluate linguistic and psycholinguistic theories, using aphasiology, brain imaging, electrophysiology, and computer modeling.