Fast thinking article 1
... creativity is visual imagery in art2. Research shows that there may be specific parts of the brain where novelty and imagination take place. These are areas of the brain located at greater distance from sensory or motor neurons in a common “neural space”, a kind of distributed space where learning a ...
... creativity is visual imagery in art2. Research shows that there may be specific parts of the brain where novelty and imagination take place. These are areas of the brain located at greater distance from sensory or motor neurons in a common “neural space”, a kind of distributed space where learning a ...
Chapter 2
... CAT/CT (computerized tomography) – soft tissue, structure, x-ray PET (positron emission tomography) – activity, not structure, detects glucose in active circuits fMRI (magnetic resonance imaging) – moving pic. of brain in action ...
... CAT/CT (computerized tomography) – soft tissue, structure, x-ray PET (positron emission tomography) – activity, not structure, detects glucose in active circuits fMRI (magnetic resonance imaging) – moving pic. of brain in action ...
SNS—brain and spinal cord
... Brain—control center of the nervous system surrounded by the skull which provides protection and support. Two hemispheres and four major regions. Left and right hemisphere. Four regions: Cerebrum, diencephalons, brain stem, cerebellum. Pg 1470 fig. Tables Each hemisphere: temporal, front ...
... Brain—control center of the nervous system surrounded by the skull which provides protection and support. Two hemispheres and four major regions. Left and right hemisphere. Four regions: Cerebrum, diencephalons, brain stem, cerebellum. Pg 1470 fig. Tables Each hemisphere: temporal, front ...
BRAIN COMPUTER INTERFACE
... Rhesus monkeys are considered to be better models for human neurophysiology than owl monkeys . ...
... Rhesus monkeys are considered to be better models for human neurophysiology than owl monkeys . ...
Nerve Notes
... B. Dendrites – branched extensions that receive information from other neurons or receptors C. Axon – tube that carries action potential D. Myelin Sheath – insulation along axon, made by Schwan cells 1. Nodes of Ranvier – gaps between Myelin 2. White matter – a. cells with myelin, b. conduction path ...
... B. Dendrites – branched extensions that receive information from other neurons or receptors C. Axon – tube that carries action potential D. Myelin Sheath – insulation along axon, made by Schwan cells 1. Nodes of Ranvier – gaps between Myelin 2. White matter – a. cells with myelin, b. conduction path ...
File
... The human brain is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right, connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum. The hemispheres are strongly, though not entirely, symmetrical. The left brain controls all the muscles on the right-hand side of the body; and the right brain contr ...
... The human brain is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right, connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum. The hemispheres are strongly, though not entirely, symmetrical. The left brain controls all the muscles on the right-hand side of the body; and the right brain contr ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... • Peripheral Nervous System – Somatic Nervous System – Autonomic Nervous System • Sympathetic Nervous System • Parasympathetic Nervous System ...
... • Peripheral Nervous System – Somatic Nervous System – Autonomic Nervous System • Sympathetic Nervous System • Parasympathetic Nervous System ...
Physiological Nature
... * 78% water/fat/proteinslippery * connected to the entire human physiology * in order to understand how the brain works, it is important to understand each of the components, functions, regions, structures, etc. In a review of 37 imaging studies related to intelligence, including their own, Haier a ...
... * 78% water/fat/proteinslippery * connected to the entire human physiology * in order to understand how the brain works, it is important to understand each of the components, functions, regions, structures, etc. In a review of 37 imaging studies related to intelligence, including their own, Haier a ...
Learning and the Brain - Santa Clara County Office of
... parts of speech. It is also involved in purposeful acts such as creativity, judgment, problem solving, and planning. ...
... parts of speech. It is also involved in purposeful acts such as creativity, judgment, problem solving, and planning. ...
Nervous System
... lies deep in the central groove • The cerebrum is further divided into 5 distinct lobes ...
... lies deep in the central groove • The cerebrum is further divided into 5 distinct lobes ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint notes
... = portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
... = portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
6. Brain Lateralization
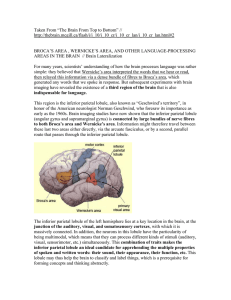
... we will get to know the specialized function of the brain. In reading aloud, the primary visual cortex to left angular gyrus gets active and this transmits the visual code to auditory area where the code gets transformed. After this, the signal goes to Wernicke’s area and it moves through arcuate fa ...
... we will get to know the specialized function of the brain. In reading aloud, the primary visual cortex to left angular gyrus gets active and this transmits the visual code to auditory area where the code gets transformed. After this, the signal goes to Wernicke’s area and it moves through arcuate fa ...
Reaction Time Task
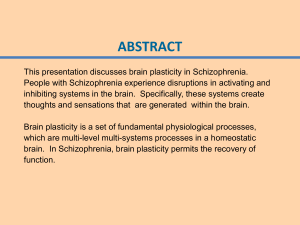
... thoughts and sensations that are generated within the brain. Brain plasticity is a set of fundamental physiological processes, which are multi-level multi-systems processes in a homeostatic brain. In Schizophrenia, brain plasticity permits the recovery of function. ...
... thoughts and sensations that are generated within the brain. Brain plasticity is a set of fundamental physiological processes, which are multi-level multi-systems processes in a homeostatic brain. In Schizophrenia, brain plasticity permits the recovery of function. ...
Chapters 1,2,3 - UCSD Cognitive Science
... the ______ ______and ______ ______, located entirely within the ______ ______ ______. There are two types of interneuron: ______, which form circuits with nearby neurons and are responsible for small pieces of information, and ______, which connect circuits of local interneurons in different brain r ...
... the ______ ______and ______ ______, located entirely within the ______ ______ ______. There are two types of interneuron: ______, which form circuits with nearby neurons and are responsible for small pieces of information, and ______, which connect circuits of local interneurons in different brain r ...
psychology_midterm_review
... Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving (right- (Creative) and left hemispheres-(Logical)) Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli Occipital Lobe- associated with visual processing Te ...
... Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving (right- (Creative) and left hemispheres-(Logical)) Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli Occipital Lobe- associated with visual processing Te ...
The Nervous System - Watchung Hills Regional High School
... Only 3 cm long Controls and regulates numerous visceral organs Allows nerve signals to move from the brain to the ...
... Only 3 cm long Controls and regulates numerous visceral organs Allows nerve signals to move from the brain to the ...
File parts of the brain
... motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
... motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
Connectionism
... • This is repeated until (often) the network solves the problem and yields the desired input-output profile. ...
... • This is repeated until (often) the network solves the problem and yields the desired input-output profile. ...
Chapter 8: Sensation and Perception
... Functions: Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex Transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
... Functions: Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex Transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
The Anatomy of Language Sydney Lamb Rice University, Houston
... Nowadays multiple electrodes can be placed all over the scalp, allowing the recording of the electric activity from many different sites simultaneously Allows the construction of topographic maps of the momentary electric activity on the scalp Also permits study of the time series of these map ...
... Nowadays multiple electrodes can be placed all over the scalp, allowing the recording of the electric activity from many different sites simultaneously Allows the construction of topographic maps of the momentary electric activity on the scalp Also permits study of the time series of these map ...
Language Processing in the Brain
... otherwise be needed to connect regions on opposite sides of the brain. Also, when two symmetrical areas on opposite sides of the brain perform two different functions, the brain’s cognitive capacities are in a sense doubled. Handedness and language are two highly lateralized functions. Though there ...
... otherwise be needed to connect regions on opposite sides of the brain. Also, when two symmetrical areas on opposite sides of the brain perform two different functions, the brain’s cognitive capacities are in a sense doubled. Handedness and language are two highly lateralized functions. Though there ...
Neurolinguistics

Neurolinguistics is the study of the neural mechanisms in the human brain that control the comprehension, production, and acquisition of language. As an interdisciplinary field, neurolinguistics draws methodology and theory from fields such as neuroscience, linguistics, cognitive science, neurobiology, communication disorders, neuropsychology, and computer science. Researchers are drawn to the field from a variety of backgrounds, bringing along a variety of experimental techniques as well as widely varying theoretical perspectives. Much work in neurolinguistics is informed by models in psycholinguistics and theoretical linguistics, and is focused on investigating how the brain can implement the processes that theoretical and psycholinguistics propose are necessary in producing and comprehending language. Neurolinguists study the physiological mechanisms by which the brain processes information related to language, and evaluate linguistic and psycholinguistic theories, using aphasiology, brain imaging, electrophysiology, and computer modeling.