Brain
... brain disorders. Alterations in brain morphology due to neurological and psychiatric diseases are now being catalogued. ...
... brain disorders. Alterations in brain morphology due to neurological and psychiatric diseases are now being catalogued. ...
The Nervous System
... remember, and reason- and coordinates muscular movement. Your brain is involved in your emotions and everything you sense. The brain makes up only 2% of your total body weight, but uses more than 20% of the oxygen you inhale. The brain has three main divisions: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the ...
... remember, and reason- and coordinates muscular movement. Your brain is involved in your emotions and everything you sense. The brain makes up only 2% of your total body weight, but uses more than 20% of the oxygen you inhale. The brain has three main divisions: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the ...
Neurobiological Ontogenetic Development and Human Language Evolution A Reappraisal and Perspectives
... cortical structures, and the second one is the Radial Unit Hypothesis, which postulates that the embryonic cortical plate forms from vertically oriented cohorts of neurons generated at the same site in the proliferative ventricular zone of the cerebral vesicle. Accordingly, each radial unit consists ...
... cortical structures, and the second one is the Radial Unit Hypothesis, which postulates that the embryonic cortical plate forms from vertically oriented cohorts of neurons generated at the same site in the proliferative ventricular zone of the cerebral vesicle. Accordingly, each radial unit consists ...
Biology of the Mind Powerpoint
... diseases such as schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. From Mapping the Mind, Rita Carter, © 1989 University of California Press ...
... diseases such as schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. From Mapping the Mind, Rita Carter, © 1989 University of California Press ...
Biology of Mind
... diseases such as schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. From Mapping the Mind, Rita Carter, © 1989 University of California Press ...
... diseases such as schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. From Mapping the Mind, Rita Carter, © 1989 University of California Press ...
Chapter 4 Answers to Before You Go On Questions Describe how
... regions do when they are undamaged. Using electroencephalograms (EEGs), scientists can take a broad look at the activity of patients’ brains and compare an injured to an uninjured brain to learn what certain regions of the brain do. 2. What are the main advantages of neuroimaging methods over earlie ...
... regions do when they are undamaged. Using electroencephalograms (EEGs), scientists can take a broad look at the activity of patients’ brains and compare an injured to an uninjured brain to learn what certain regions of the brain do. 2. What are the main advantages of neuroimaging methods over earlie ...
Acute Hemorrhagic Leukoencephalitis
... processes. Causative spectrum is quite wide to be timely worked up when danger for life is present. Clinical evaluation, blood testing, brain computed tomography and lumbar puncture constitute the standard emergency diagnostic sequence. From the physician’s perspective, narrowing the differential di ...
... processes. Causative spectrum is quite wide to be timely worked up when danger for life is present. Clinical evaluation, blood testing, brain computed tomography and lumbar puncture constitute the standard emergency diagnostic sequence. From the physician’s perspective, narrowing the differential di ...
Who am I? - Impact DWI
... Since an adolescent’s brain is still developing, teens who drink heavily are more likely to significantly lower their mental abilities than adults who drink heavily. Research shows that a teen’s brain is more easily damaged than an adult’s brain in the areas that regulate the storage of ...
... Since an adolescent’s brain is still developing, teens who drink heavily are more likely to significantly lower their mental abilities than adults who drink heavily. Research shows that a teen’s brain is more easily damaged than an adult’s brain in the areas that regulate the storage of ...
Trainee Content for Day 1, Segment 4C
... Functions: The orbitofrontal cortex is important in affect regulation and has been nicknamed the senior executive of the social-emotional brain. It contains neurons that process facial and vocal information and is believed to be critical in social adjustment, the control of mood, and the regulation ...
... Functions: The orbitofrontal cortex is important in affect regulation and has been nicknamed the senior executive of the social-emotional brain. It contains neurons that process facial and vocal information and is believed to be critical in social adjustment, the control of mood, and the regulation ...
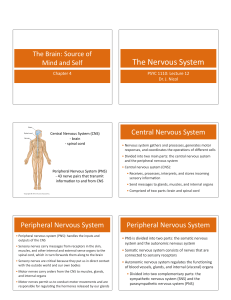
The Nervous System
... systems regulate conditions in the body. d. Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. e. Students know the roles of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in sensation, thought, and response. ...
... systems regulate conditions in the body. d. Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. e. Students know the roles of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in sensation, thought, and response. ...
document
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
T C N B
... review, we describe the principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques, including structural MRI, functional MRI, and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), and how they are implemented in the study of Williams (WS), velocardiofacial (VCFS), and fragile X (FXS) syndromes. From WS we learn that d ...
... review, we describe the principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques, including structural MRI, functional MRI, and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), and how they are implemented in the study of Williams (WS), velocardiofacial (VCFS), and fragile X (FXS) syndromes. From WS we learn that d ...
Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are
... 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? En ...
... 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? En ...
The Nervous System and Senses
... • Both transmit signals to other areas of the body • Nervous system • Very rapid • Uses neurons to relay electrical and chemical signals • Controls all of the body (everything that the body does) ...
... • Both transmit signals to other areas of the body • Nervous system • Very rapid • Uses neurons to relay electrical and chemical signals • Controls all of the body (everything that the body does) ...
The Nervous System
... • Positron emission tomography (PET) -‐ radioacJve glucose-‐like substance injected into blood and accumulates in areas of the brain that are acJve; the radiaJon is read by a scanner and superimposed on ...
... • Positron emission tomography (PET) -‐ radioacJve glucose-‐like substance injected into blood and accumulates in areas of the brain that are acJve; the radiaJon is read by a scanner and superimposed on ...
03&04Psych315Biology&Behavior
... • area of psychology concerned with how variation in behavior and development results from the combo of genetic and environmental factors. • Heritability = an estimate of the proportion of measurable difference/variability on a given trait (e.g. intelligence), in a given population (living in a part ...
... • area of psychology concerned with how variation in behavior and development results from the combo of genetic and environmental factors. • Heritability = an estimate of the proportion of measurable difference/variability on a given trait (e.g. intelligence), in a given population (living in a part ...
File
... The diencephalon gives rise to the thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus The thalamus is the main input center for sensory information, all senses are sorted in the thalamus and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers The hypothalamus contains the body’s thermostat and the central biological clock ...
... The diencephalon gives rise to the thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus The thalamus is the main input center for sensory information, all senses are sorted in the thalamus and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers The hypothalamus contains the body’s thermostat and the central biological clock ...
Neural Networks
... Hoehl, Stefanie, Christine Michel, Vincent M Reid, Eugenio Parise, and Tricia Striano. 2014. “Eye Contact during Live Social Interaction Modulates Infants’ Oscillatory Brain Activity.” Social Neuroscience 00 (00) (February 7 ...
... Hoehl, Stefanie, Christine Michel, Vincent M Reid, Eugenio Parise, and Tricia Striano. 2014. “Eye Contact during Live Social Interaction Modulates Infants’ Oscillatory Brain Activity.” Social Neuroscience 00 (00) (February 7 ...
Focus On Vocabulary Chapter 02
... If you opened a human skull, exposing the brain, you would see a wrinkled organ, shaped somewhat like the meat of an oversized walnut. The human brain has a convoluted (wrinkled) surface, and the cerebral cortex is divided into two halves or hemispheres just like the two lobes of the edible portion ...
... If you opened a human skull, exposing the brain, you would see a wrinkled organ, shaped somewhat like the meat of an oversized walnut. The human brain has a convoluted (wrinkled) surface, and the cerebral cortex is divided into two halves or hemispheres just like the two lobes of the edible portion ...
The Brain - Polk School District
... • In the CNS, the brain helps to control all the body systems and organs. The brain also allows us to think, feel, remember, and imagine. The brain communicates with the rest of the body through the spinal cord and the nerves. Nerves tell the brain what is going on in the body at all times. This sy ...
... • In the CNS, the brain helps to control all the body systems and organs. The brain also allows us to think, feel, remember, and imagine. The brain communicates with the rest of the body through the spinal cord and the nerves. Nerves tell the brain what is going on in the body at all times. This sy ...
What is BLUE BRAIN - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... scientists can crack open the secret of how and why the ...
... scientists can crack open the secret of how and why the ...