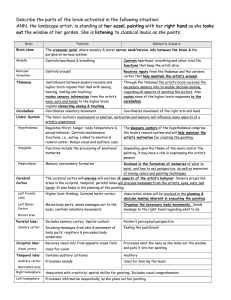
Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation
... Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation: ANN, the landscape artist, is standing at her easel, painting with her right hand as she looks out the window at her garden. She is listening to classical music as she paints. ...
... Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation: ANN, the landscape artist, is standing at her easel, painting with her right hand as she looks out the window at her garden. She is listening to classical music as she paints. ...
answers - Easy Peasy All-in
... What is a synapse and how do nerve impulses pass across a synapse? A synapse is the gap between neurons. Nerve impulses change to a chemical signal when they near the synapse and it triggers an electrical signal when it enters the next neuron. What is a reflex action and how is this a good test of t ...
... What is a synapse and how do nerve impulses pass across a synapse? A synapse is the gap between neurons. Nerve impulses change to a chemical signal when they near the synapse and it triggers an electrical signal when it enters the next neuron. What is a reflex action and how is this a good test of t ...
Organization of Nervous System
... possible to those who learn to use more. It is somewhat a nice thought to think that there is so much untapped brain potential. ...
... possible to those who learn to use more. It is somewhat a nice thought to think that there is so much untapped brain potential. ...
PoNS Fact Sheet - Helius Medical Technologies
... itself. This is part of a new approach being studied for “symptom treatment” for the rising number of patients who have experienced loss of function as a result of neurological disease or trauma. What is the potential impact of the PoNS™? As a result of their disease or injury, many patients are lef ...
... itself. This is part of a new approach being studied for “symptom treatment” for the rising number of patients who have experienced loss of function as a result of neurological disease or trauma. What is the potential impact of the PoNS™? As a result of their disease or injury, many patients are lef ...
Harnessing Plasticity to Reset Dysfunctional Neurons
... (from milliseconds to months), and are incompletely understood. They include changes in synaptic strength, the pruning and growth of neuronal connections, and even the introduction of new neurons within certain existing circuits. The brain can thus develop attributes and abilities far beyond those t ...
... (from milliseconds to months), and are incompletely understood. They include changes in synaptic strength, the pruning and growth of neuronal connections, and even the introduction of new neurons within certain existing circuits. The brain can thus develop attributes and abilities far beyond those t ...
Brain & Behavior
... • Deals largely with involuntary functions • Signals from organs to CNS • Signals from CNS to organs • Sympathetic nerves • Prepare for action ...
... • Deals largely with involuntary functions • Signals from organs to CNS • Signals from CNS to organs • Sympathetic nerves • Prepare for action ...
Chapter 3: The Nervous System
... The nervous system is an electro-chemical communication system that regulates all physiological systems Psychotropic drugs exert effects through the alteration of nervous system activity Understanding drugs means understanding the nervous system ...
... The nervous system is an electro-chemical communication system that regulates all physiological systems Psychotropic drugs exert effects through the alteration of nervous system activity Understanding drugs means understanding the nervous system ...
Ch 3 – Biological Bases of Behavior
... – assembled into a composite image on computer – provide info on location and extent of damage – used for language disorder, damage in stroke, loss of memory ...
... – assembled into a composite image on computer – provide info on location and extent of damage – used for language disorder, damage in stroke, loss of memory ...
COBRE Seminar, 071112 (PDF)
... Taking a Tryp with its Twists and Turns Across the Blood-Brain Barrier Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT; commonly called sleeping sickness) has been claimed to be more deadly than other vector-borne diseases such as malaria because death is inevitable if a patient is untreated. The terminal stages ...
... Taking a Tryp with its Twists and Turns Across the Blood-Brain Barrier Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT; commonly called sleeping sickness) has been claimed to be more deadly than other vector-borne diseases such as malaria because death is inevitable if a patient is untreated. The terminal stages ...
psych mod 4 terms
... 4. Fragile X Syndrome- cause by a defect in the X chromosome. This defect can result in physical changes, such as a relatively large head with protruding ears, as well as mild to profound levels of mental retardation. 5. Theory of Evolution- says that different species arose from common ancestor and ...
... 4. Fragile X Syndrome- cause by a defect in the X chromosome. This defect can result in physical changes, such as a relatively large head with protruding ears, as well as mild to profound levels of mental retardation. 5. Theory of Evolution- says that different species arose from common ancestor and ...
Outline12 CNS - Napa Valley College
... B. Supporting Structures of the CNS 1. Meninges - connective tissue coverings of the CNS dura mater arachnoid pia mater 2. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) - produced by the choroid plexuses of the brain ventricles - CSF circulates through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space around the brain - C ...
... B. Supporting Structures of the CNS 1. Meninges - connective tissue coverings of the CNS dura mater arachnoid pia mater 2. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) - produced by the choroid plexuses of the brain ventricles - CSF circulates through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space around the brain - C ...
AP Psychology - cloudfront.net
... RF also keeps people alert and aroused. Studies on the RF of rats show that they wake up if their RF is stimulated. However if the rat’s RF is destroyed, they slip into a coma and never awaken. ...
... RF also keeps people alert and aroused. Studies on the RF of rats show that they wake up if their RF is stimulated. However if the rat’s RF is destroyed, they slip into a coma and never awaken. ...
Page 1
... Make a prediction about the answer to each question. Put a star next to the answer that you think is correct for each question. Watch the video about the nervous system. Record the answer for each question on the line before the number as you watch the video. The Nervous System _________1. What are ...
... Make a prediction about the answer to each question. Put a star next to the answer that you think is correct for each question. Watch the video about the nervous system. Record the answer for each question on the line before the number as you watch the video. The Nervous System _________1. What are ...
Nervous System Exam.tst
... A) dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater B) basal nuclei, pineal body, and choroid plexus C) cerebrum, cerebellum, and diencephalon D) thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus E) midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata ...
... A) dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater B) basal nuclei, pineal body, and choroid plexus C) cerebrum, cerebellum, and diencephalon D) thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus E) midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata ...
ALTERATIONS IN NEUROLOGIC FUNCTION
... Attributed to local arteritis and atherosclerosis Signs are usually slowly progressive (stroke in evolution) over several hours Transient ischemic attacks are partial thrombotic strokes or the result of vessel spasm ...
... Attributed to local arteritis and atherosclerosis Signs are usually slowly progressive (stroke in evolution) over several hours Transient ischemic attacks are partial thrombotic strokes or the result of vessel spasm ...
Unit_2_-_Biological_Bases_of_Behavior
... our behavioral differences in terms of our genes, evolutionary psychologists focus on our similarities, as dictated by natural ...
... our behavioral differences in terms of our genes, evolutionary psychologists focus on our similarities, as dictated by natural ...
Unit 3A: Neural Processing and the Endocrine System Introduction
... pressure, blood sugar, and slows digestion. It gets you ready for action. 2. The parasympathetic nervous system kicks in when the “crisis” is over – it calms you down by doing the opposite things. It helps you chill out. The central nervous system 1. Our bodies are amazing, but without the brain, we ...
... pressure, blood sugar, and slows digestion. It gets you ready for action. 2. The parasympathetic nervous system kicks in when the “crisis” is over – it calms you down by doing the opposite things. It helps you chill out. The central nervous system 1. Our bodies are amazing, but without the brain, we ...
The Structures of the Brain
... • Legion in a rat’s hypothalamus causes itself to starv to death (will not eat) • Electroencephalogram (EEG) • Measures surface electrical activity • Filtering out background allows scientist to see response to stimulus. ...
... • Legion in a rat’s hypothalamus causes itself to starv to death (will not eat) • Electroencephalogram (EEG) • Measures surface electrical activity • Filtering out background allows scientist to see response to stimulus. ...
July 18, 2009 CHANGING THE PICTURE IN DEPRESSION: TRANS
... This historical development is coinciding with a relative saturation in other treatment paradigms. For example, the pharmaceutical industry has been struggling lately to find truly novel drugs. The lowhanging fruit, it turns out, is long gone. Moreover, any differences in efficacy between alternativ ...
... This historical development is coinciding with a relative saturation in other treatment paradigms. For example, the pharmaceutical industry has been struggling lately to find truly novel drugs. The lowhanging fruit, it turns out, is long gone. Moreover, any differences in efficacy between alternativ ...
Biology and Psychology - Austin Community College
... guide and help repair the neuron produce myelin nourish & insulate neuron direct growth, remove waste ...
... guide and help repair the neuron produce myelin nourish & insulate neuron direct growth, remove waste ...
Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
... potential arriving at a neuron is additive if the time span between the stimuli is short. This is called temporal summation. • The effect of more than one synaptic potential arriving at a given region of a neuron can also be additive. This is called spatial summation. ...
... potential arriving at a neuron is additive if the time span between the stimuli is short. This is called temporal summation. • The effect of more than one synaptic potential arriving at a given region of a neuron can also be additive. This is called spatial summation. ...
DOC
... Neurotransmitters are brain chemicals that control the action between nerve cells – and therefore they control everything our bodies do. Visitor experience: Users will experience the action as if they are inside the brain of the main character. Users will control the action by making choices at key ...
... Neurotransmitters are brain chemicals that control the action between nerve cells – and therefore they control everything our bodies do. Visitor experience: Users will experience the action as if they are inside the brain of the main character. Users will control the action by making choices at key ...
Chapter 2 Review Notes
... Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. A neuron consists of a cell body and branching fibers: The dendrite fibers receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons, and the axon fibers pass that information along to other neurons. A layer of fatty tissu ...
... Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. A neuron consists of a cell body and branching fibers: The dendrite fibers receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons, and the axon fibers pass that information along to other neurons. A layer of fatty tissu ...
638969476616MyersMod_LG_04
... areas can impair language functioning. The association areas are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions. Rather, they interpret, integrate, and act on information processed by the sensory areas. They are involved in higher mental functions, such as learning, remembering, thinking, and sp ...
... areas can impair language functioning. The association areas are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions. Rather, they interpret, integrate, and act on information processed by the sensory areas. They are involved in higher mental functions, such as learning, remembering, thinking, and sp ...























