Forebrain
... • Amygdala is especially important in emotions and drives. • Amygdala has extensive connections with other limbic areas and is also involved in memory, olfaction, and homeostasis. • Amygdala is especially important for attaching emotional significance to various stimuli perceived by the association ...
... • Amygdala is especially important in emotions and drives. • Amygdala has extensive connections with other limbic areas and is also involved in memory, olfaction, and homeostasis. • Amygdala is especially important for attaching emotional significance to various stimuli perceived by the association ...
File
... system (CNS) afflict tens of millions of people worldwide, and often arise due to the failure of CNS tissue due to the loss of functional cells. For many of these conditions, there are no curative treatment options today and effective long-term therapies remain limited. Stem Cell Research Deep B ...
... system (CNS) afflict tens of millions of people worldwide, and often arise due to the failure of CNS tissue due to the loss of functional cells. For many of these conditions, there are no curative treatment options today and effective long-term therapies remain limited. Stem Cell Research Deep B ...
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
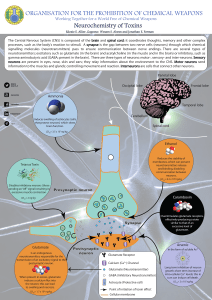
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
Chapter 13 - Las Positas College
... A. Embryonic development and congenital birth defects that involve the brain are anencephaly, spina bifida, and cerebral palsy. (pp. 419–420, Fig. 13.38) B. Postnatal changes in the brain represent many neuronal connections during childhood that are based on early experiences; brain growth stops in ...
... A. Embryonic development and congenital birth defects that involve the brain are anencephaly, spina bifida, and cerebral palsy. (pp. 419–420, Fig. 13.38) B. Postnatal changes in the brain represent many neuronal connections during childhood that are based on early experiences; brain growth stops in ...
The Teenage Brain - Model High School
... Under PET scans and CAT scans, different areas of the brain are used, but we use our whole brain. ...
... Under PET scans and CAT scans, different areas of the brain are used, but we use our whole brain. ...
USC Brain Project Specific Aims
... How does the network respond to a change in the maintained stimulus pattern? Once in equilibrium, one may increase a non-maximal stimulus s2 so that it becomes larger than the previously largest stimulus s1, yet not switch activity to the corresponding element. In neural networks with loops - an int ...
... How does the network respond to a change in the maintained stimulus pattern? Once in equilibrium, one may increase a non-maximal stimulus s2 so that it becomes larger than the previously largest stimulus s1, yet not switch activity to the corresponding element. In neural networks with loops - an int ...
Slide 1
... • Nodes of Ranvier – gap between Schwann cells – serves as points along the neuron for generating a signal – signals jumping from node to node travel hundreds of times faster than signals traveling along the surface of the axon. – allows your brain to communicate with your toes in a few thousandths ...
... • Nodes of Ranvier – gap between Schwann cells – serves as points along the neuron for generating a signal – signals jumping from node to node travel hundreds of times faster than signals traveling along the surface of the axon. – allows your brain to communicate with your toes in a few thousandths ...
Nervous System Notes
... • Nodes of Ranvier – gap between Schwann cells – serves as points along the neuron for generating a signal – signals jumping from node to node travel hundreds of times faster than signals traveling along the surface of the axon. – allows your brain to communicate with your toes in a few thousandths ...
... • Nodes of Ranvier – gap between Schwann cells – serves as points along the neuron for generating a signal – signals jumping from node to node travel hundreds of times faster than signals traveling along the surface of the axon. – allows your brain to communicate with your toes in a few thousandths ...
HBTRC Tour - Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center
... is much larger because the striatum (the brown crescent within the ventricle) has all but melted away. ...
... is much larger because the striatum (the brown crescent within the ventricle) has all but melted away. ...
The Human Brain
... a 42 inch long, 1.2 inch wide, metal rod to be blown right up through his skull and out the top. The rod entered his skull below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
... a 42 inch long, 1.2 inch wide, metal rod to be blown right up through his skull and out the top. The rod entered his skull below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
here
... Your hippocampus is the structure in your brain (sits in the middle of each temporal lobe just under each temple on your skull) that enables you to learn. ...
... Your hippocampus is the structure in your brain (sits in the middle of each temporal lobe just under each temple on your skull) that enables you to learn. ...
studying neurogenesis in cephalopods - UMR BOREA
... is known about the molecular pathways underlying their development. Similarly, the diversity of cephalopod nervous systems indicates a high flexibility and adaptability, which makes them a relevant biological material for evolutionary studies. Nevertheless, neither their development nor the mechanis ...
... is known about the molecular pathways underlying their development. Similarly, the diversity of cephalopod nervous systems indicates a high flexibility and adaptability, which makes them a relevant biological material for evolutionary studies. Nevertheless, neither their development nor the mechanis ...
Hormonal Control
... two systems interact. One example of this interaction is that the production of hormones may be controlled by the nervous system. This is exemplified in hypothalamus and pituitary gland where the distinction between these two systems is blurred. The hypothalamus is a region of the lower brain that r ...
... two systems interact. One example of this interaction is that the production of hormones may be controlled by the nervous system. This is exemplified in hypothalamus and pituitary gland where the distinction between these two systems is blurred. The hypothalamus is a region of the lower brain that r ...
The Nervous System - Marshall Middle
... peripheral nervous system is achieved by dividing it into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. These are opposing actions and check on each other to provide a balance. C. How the System Works: The nervous system uses electro-chemical impulses which travel along the length of the cells. The cell ...
... peripheral nervous system is achieved by dividing it into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. These are opposing actions and check on each other to provide a balance. C. How the System Works: The nervous system uses electro-chemical impulses which travel along the length of the cells. The cell ...
Core concepts - University of Arizona
... There are many fun and easy opportunities to teach about the brain. For example, optical illusions and how our brain plays tricks on us are interesting to everyone. Students, teachers, and adults in general are intrigued to learn about the brain and related research that impacts our everyday life. N ...
... There are many fun and easy opportunities to teach about the brain. For example, optical illusions and how our brain plays tricks on us are interesting to everyone. Students, teachers, and adults in general are intrigued to learn about the brain and related research that impacts our everyday life. N ...
Classes #9-11: Differentiation of the brain vesicles
... class sessions 9-11. The first 46 questions are for review, and can be answered from earlier lectures. Many of these questions are answered in the readings as well. 1. The forebrain probably expanded in evolution initially because of the importance of _________________________________. 2. Give an ex ...
... class sessions 9-11. The first 46 questions are for review, and can be answered from earlier lectures. Many of these questions are answered in the readings as well. 1. The forebrain probably expanded in evolution initially because of the importance of _________________________________. 2. Give an ex ...
Nervous and Muscular System
... appearance of animals and are essential for movement, posture, breathing, circulation, digestion, and many other functions ...
... appearance of animals and are essential for movement, posture, breathing, circulation, digestion, and many other functions ...
Nervous System - science
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
∂ u /∂ t = u(x,t) +∫ w(x,y)f(u(y,t)) + I(x) + L(x)
... pioneered the use of multielectrode recordings in the honeybee brain during odor stimulation. This technique provides high temporal resolution of the activity of many neurons simultaneously. Using this technique in coordination with behavioral and mathematical modeling st ...
... pioneered the use of multielectrode recordings in the honeybee brain during odor stimulation. This technique provides high temporal resolution of the activity of many neurons simultaneously. Using this technique in coordination with behavioral and mathematical modeling st ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... • The sympathetic nervous system gears up the body for stressful or emergency situations while the parasympathetic nervous system adjusts body functioning so that energy is conserved during nonstressful ...
... • The sympathetic nervous system gears up the body for stressful or emergency situations while the parasympathetic nervous system adjusts body functioning so that energy is conserved during nonstressful ...
http://catnet.adventist.ca/files/articles/pdf/oj_ID194.pdf
... I don’t know what your attitude toward dandelions is, but mine was generally one of tolerance, provided there were not too many. That is because as a child I enjoyed the wild green mix my grandmother picked and cooked in the spring, and tender dandelion leaves were one of her favorite ingredients. A ...
... I don’t know what your attitude toward dandelions is, but mine was generally one of tolerance, provided there were not too many. That is because as a child I enjoyed the wild green mix my grandmother picked and cooked in the spring, and tender dandelion leaves were one of her favorite ingredients. A ...
Brain`s Building Blocks
... ◦ primate and human brain researchers conclude that adult monkey and human brains are capable of growing relatively limited numbers of neurons throughout adulthood Some new neurons play important role in continuing to learn and remember new things (hippocampus) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F ...
... ◦ primate and human brain researchers conclude that adult monkey and human brains are capable of growing relatively limited numbers of neurons throughout adulthood Some new neurons play important role in continuing to learn and remember new things (hippocampus) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F ...
Slide 1
... Cajal turned all his efforts to improving the silver nitrate technique. As Golgi had developed it, the staining involved including soaking the tissue in various substances. Cajal added several levels of preparation and made other refinements as the debate over the true structure of the central nervo ...
... Cajal turned all his efforts to improving the silver nitrate technique. As Golgi had developed it, the staining involved including soaking the tissue in various substances. Cajal added several levels of preparation and made other refinements as the debate over the true structure of the central nervo ...