Damage to the frontal lobes can lead to
... – MRI—shows soft tissue areas of brain using magnetic pulses (good for finding tumors or enlarged/smaller than usual areas) m for magnetic – fMRI—measures second-by-second images of blood flow to show which part of brain is active during certain mental functions f for function – CAT (CT) --x-ray of ...
... – MRI—shows soft tissue areas of brain using magnetic pulses (good for finding tumors or enlarged/smaller than usual areas) m for magnetic – fMRI—measures second-by-second images of blood flow to show which part of brain is active during certain mental functions f for function – CAT (CT) --x-ray of ...
Unit Two: Biological Bases of Behavior
... Action potential: a neural impulse Threshold: minimum intensity needed to fire impulse Neuron firings are all-or-none responses Synapse: gap between neurons (also called a synaptic gap or cleft) • Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that bind to ...
... Action potential: a neural impulse Threshold: minimum intensity needed to fire impulse Neuron firings are all-or-none responses Synapse: gap between neurons (also called a synaptic gap or cleft) • Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that bind to ...
The Brain Summary Notes
... 5. Magnetic Resonance imaging (MRI) It generates detailed pictures of the brains soft tissues by making use of magnetic activity. Makes use of magnetic fields which appear to be less harmful than x-rays. Brain Structure The Brainstem the oldest portion (the central core) in brain is made up of three ...
... 5. Magnetic Resonance imaging (MRI) It generates detailed pictures of the brains soft tissues by making use of magnetic activity. Makes use of magnetic fields which appear to be less harmful than x-rays. Brain Structure The Brainstem the oldest portion (the central core) in brain is made up of three ...
HP Authorized Customer
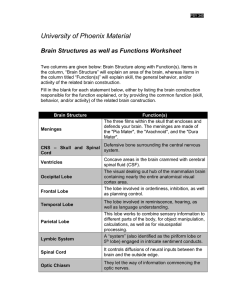
... Brain Structures as well as Functions Worksheet Two columns are given below: Brain Structure along with Function(s). Items in the column, “Brain Structure” will explain an area of the brain, whereas items in the column titled “Function(s)” will explain skill, the general behavior, and/or activity of ...
... Brain Structures as well as Functions Worksheet Two columns are given below: Brain Structure along with Function(s). Items in the column, “Brain Structure” will explain an area of the brain, whereas items in the column titled “Function(s)” will explain skill, the general behavior, and/or activity of ...
Taken from the Body/brain BOOGIE VIDEO by Jeff Haebig
... Body/brain BOOGIE – The Neurobiology of Learning through Movement Jeff Haebig, Ph.D. Experience a rhyming, rhythmical sequence of movements showing how body/brain cells and system work together to learn. We will make dendrites dance, get myelin smiling, synapses singing, and the cerebellum ringing. ...
... Body/brain BOOGIE – The Neurobiology of Learning through Movement Jeff Haebig, Ph.D. Experience a rhyming, rhythmical sequence of movements showing how body/brain cells and system work together to learn. We will make dendrites dance, get myelin smiling, synapses singing, and the cerebellum ringing. ...
Nervous Systems - manorlakesscience
... Somatic – Information from external environments via sense organs, e.g. Eyes Visceral – Information from internal environments, e.g. Heart ...
... Somatic – Information from external environments via sense organs, e.g. Eyes Visceral – Information from internal environments, e.g. Heart ...
Taken from the Body/brain BOOGIE VIDEO by Jeff Haebig
... Body/brain Boogie: Starting with a brief overview helps the more global Right Brain Preferred learners get a reference of what’s ahead. The novel movements, music and playful antics also arouse the Reticular Activation System (RAS) the attentional part of the brain which directs the brain to pay clo ...
... Body/brain Boogie: Starting with a brief overview helps the more global Right Brain Preferred learners get a reference of what’s ahead. The novel movements, music and playful antics also arouse the Reticular Activation System (RAS) the attentional part of the brain which directs the brain to pay clo ...
hendrick
... 86 billion neurons and 85 billion neuroglial cells7000 connections per neocortical neuron in adults. (Young children have many more. A unique number identifying a single neuron in a population of 86 billion can be expressed in 37 bits of information. To identify the two neurons would take 37 + 37 ...
... 86 billion neurons and 85 billion neuroglial cells7000 connections per neocortical neuron in adults. (Young children have many more. A unique number identifying a single neuron in a population of 86 billion can be expressed in 37 bits of information. To identify the two neurons would take 37 + 37 ...
Unit 3- Biological Psychology Study Guide
... Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolutionary perspective and its relationship to biological psychology. Understand and identify the intricate weaving between t ...
... Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolutionary perspective and its relationship to biological psychology. Understand and identify the intricate weaving between t ...
chapter 3 study guide
... The occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) The parietal lobe (primary somatosensory cortex) The temporal lobe (primary auditory cortex) The frontal lobe (primary motor cortex, mirror neurons, prefrontal cortex) ...
... The occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) The parietal lobe (primary somatosensory cortex) The temporal lobe (primary auditory cortex) The frontal lobe (primary motor cortex, mirror neurons, prefrontal cortex) ...
Worksheet - Humble ISD
... There are 3 types of neurons, they are _______________, ______________, & _______________. The ______________ neuron carries impulses from the brain to muscles or glands. The _________________ neuron connects the other two types together. Lastly, the ____________ neuron carries impulses from sense o ...
... There are 3 types of neurons, they are _______________, ______________, & _______________. The ______________ neuron carries impulses from the brain to muscles or glands. The _________________ neuron connects the other two types together. Lastly, the ____________ neuron carries impulses from sense o ...
neural migration - proffittscience
... to a variety of other tests, then it can be determined that the individual is “brain dead” The pathway of the pupil reflex is: ...
... to a variety of other tests, then it can be determined that the individual is “brain dead” The pathway of the pupil reflex is: ...
Frontal Lobes
... the body and the halves of the visual field do not work together. Only the left half of the brain has enough verbal ability to express its thoughts out loud. ...
... the body and the halves of the visual field do not work together. Only the left half of the brain has enough verbal ability to express its thoughts out loud. ...
Read our 2014-15 Annual Report - Nuffield Department of Clinical
... Using a new brain imaging technique, our researchers, led by Professor Irene Tracey, discovered that activity in a brain area known as the dorsal posterior insula is directly related to the intensity of pain. As this area connects to many other important brain regions involved in pain experiences, t ...
... Using a new brain imaging technique, our researchers, led by Professor Irene Tracey, discovered that activity in a brain area known as the dorsal posterior insula is directly related to the intensity of pain. As this area connects to many other important brain regions involved in pain experiences, t ...
Nervous System
... Myelinated nerves – have a coat of white fatty material, interrupted along the length of the nerve at regularly spaced intervals -found mostly in the CNS Nonmyelinated nerves – have a thin coat of myelin – found in the autonomic nervous system ...
... Myelinated nerves – have a coat of white fatty material, interrupted along the length of the nerve at regularly spaced intervals -found mostly in the CNS Nonmyelinated nerves – have a thin coat of myelin – found in the autonomic nervous system ...
Brain PowerPoint
... HOW DOES THE BRAIN “LEARN”? Brain Components Hemispheres & Lobes Interior of brain Cortex Relationship to learning ...
... HOW DOES THE BRAIN “LEARN”? Brain Components Hemispheres & Lobes Interior of brain Cortex Relationship to learning ...
Chapter 3 – early studies of the central nervous system
... discoveries; today this is called the Bell-Magendie law. ...
... discoveries; today this is called the Bell-Magendie law. ...
Reading the neural code in behaving animals, ~1000 neurons at a ,me
... A longstanding challenge in neuroscience is to understand how popula3ons of individual neurons and glia contribute to animal behavior and brain disease. Addressing this challenge has been difficult partly due t ...
... A longstanding challenge in neuroscience is to understand how popula3ons of individual neurons and glia contribute to animal behavior and brain disease. Addressing this challenge has been difficult partly due t ...
The Scientific Method - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Review Sheet #1 Chapters 1 and 2 The Scientific Method and Neurobiology Chapter 1: (and the Introduction) Background terms from the book intro: - Famous people: Wilhelm Wundt, Sigmund Freud, John Watson, BF Skinner - Psychology v. Psychiatry - Types of research: Basic, Applied, Clinical - Types of d ...
... Review Sheet #1 Chapters 1 and 2 The Scientific Method and Neurobiology Chapter 1: (and the Introduction) Background terms from the book intro: - Famous people: Wilhelm Wundt, Sigmund Freud, John Watson, BF Skinner - Psychology v. Psychiatry - Types of research: Basic, Applied, Clinical - Types of d ...
Review Sheet 1 scientific method and neurobiology
... Review Sheet #1 The Scientific Method and Neurobiology Chapter 1: (and the Introduction) Background terms from the book intro: - Famous people: Wilhelm Wundt, Sigmund Freud, John Watson, BF Skinner - Psychology v. Psychiatry - Types of research: Basic, Applied, Clinical - Types of descriptive resear ...
... Review Sheet #1 The Scientific Method and Neurobiology Chapter 1: (and the Introduction) Background terms from the book intro: - Famous people: Wilhelm Wundt, Sigmund Freud, John Watson, BF Skinner - Psychology v. Psychiatry - Types of research: Basic, Applied, Clinical - Types of descriptive resear ...
Wallin_Back_to_School_with_the_Thinking_Maps
... • Dendrite: Gathers chemicals in brain fluid. It is continually looking to make connections with other neurons. The dendrite REACHES to other neurons to make connections as it SLURPS up information! BUMP! • Cell Body: Converts chemicals into an electrical charge. They ...
... • Dendrite: Gathers chemicals in brain fluid. It is continually looking to make connections with other neurons. The dendrite REACHES to other neurons to make connections as it SLURPS up information! BUMP! • Cell Body: Converts chemicals into an electrical charge. They ...
Payton
... ‣ spinal cord (vertebral column/spine) ◦ PNS ‣ nerves ‣ peripheral ganglia 2. Meninges • dura(hard) mater: thick, unstretchable, surrounds the brain • arachnoid(think spider) membrane: soft, spongy ◦ sub-arachnoid save filled with Cerebra Spinal Fluid • Pia(religious) mater: follows brain surface, c ...
... ‣ spinal cord (vertebral column/spine) ◦ PNS ‣ nerves ‣ peripheral ganglia 2. Meninges • dura(hard) mater: thick, unstretchable, surrounds the brain • arachnoid(think spider) membrane: soft, spongy ◦ sub-arachnoid save filled with Cerebra Spinal Fluid • Pia(religious) mater: follows brain surface, c ...
Grant Clay
... 1. Cerebral Cortex – Wrinkled outer layer of Cerebrum a. Occipital Lobe – Primary Visual Cortex. Sense of Sight b. Parietal Lobe – Primary Somatosensory cortex. Sense of Touch c. Temporal Lobe – Primary Auditory Cortex. The Sense of Hearing. d. Frontal Lobe – Primary Motor Cortex. Controls movements ...
... 1. Cerebral Cortex – Wrinkled outer layer of Cerebrum a. Occipital Lobe – Primary Visual Cortex. Sense of Sight b. Parietal Lobe – Primary Somatosensory cortex. Sense of Touch c. Temporal Lobe – Primary Auditory Cortex. The Sense of Hearing. d. Frontal Lobe – Primary Motor Cortex. Controls movements ...