Chapter 2
... How is information transmitted from one place to another in the nervous system? How are things in the environment, such as faces and trees, represented in the brain? Is it possible to read a person’s mind by measuring the activity of the person’s brain? ...
... How is information transmitted from one place to another in the nervous system? How are things in the environment, such as faces and trees, represented in the brain? Is it possible to read a person’s mind by measuring the activity of the person’s brain? ...
The Brain [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous
... mainly of nerve bodies located in a thin layer less than 3mm thick with axons projecting to interior of cortex; cortex deeply grooved making it possible for maximum amount of gray matter to fit in limited space • white matter lies in interior and consists largely of myelin covered nerve fibers; mess ...
... mainly of nerve bodies located in a thin layer less than 3mm thick with axons projecting to interior of cortex; cortex deeply grooved making it possible for maximum amount of gray matter to fit in limited space • white matter lies in interior and consists largely of myelin covered nerve fibers; mess ...
Brain and Cognitive Modeling and Neurocomputation
... to understand how the brain works. • Their view: all there is, is Boolean functions. • Note: Same view as logicians as old as Boole ...
... to understand how the brain works. • Their view: all there is, is Boolean functions. • Note: Same view as logicians as old as Boole ...
The Nervous System
... Definition- the largest most complex part of the brain. This is the site of the most conscious and intelligent activities. Divided into two halves called cerebral hemispheres. The right hemisphere controls the muscular activity of and receives sensory input from the left half of the body. The left h ...
... Definition- the largest most complex part of the brain. This is the site of the most conscious and intelligent activities. Divided into two halves called cerebral hemispheres. The right hemisphere controls the muscular activity of and receives sensory input from the left half of the body. The left h ...
Cerebral cortex (top brain): Heavily wrinkled outer layer (gray matter
... The ‘Reptilian Brain’ and Post Trauma Disorder This illustration shows specific brain functions. We know that Post Trauma Disorder takes place in the oldest part of the brain, or the ‘Reptilian’ brain. The ‘fright and flight’ response takes place here when danger is present. Whenever there is severe ...
... The ‘Reptilian Brain’ and Post Trauma Disorder This illustration shows specific brain functions. We know that Post Trauma Disorder takes place in the oldest part of the brain, or the ‘Reptilian’ brain. The ‘fright and flight’ response takes place here when danger is present. Whenever there is severe ...
Nervous System - Effingham County Schools
... Nervous System Disorders Multiple Sclerosis- Disorder in which the myelin surrounding neurons deteriorate making it hard for signals to travel from one neuron to the next. Symptoms include: loss of motor skills, blindness, numbness, and loss of balance. Caused by white blood cells attacking the ne ...
... Nervous System Disorders Multiple Sclerosis- Disorder in which the myelin surrounding neurons deteriorate making it hard for signals to travel from one neuron to the next. Symptoms include: loss of motor skills, blindness, numbness, and loss of balance. Caused by white blood cells attacking the ne ...
How your Brain Works - Muncy School District
... No matter how many synapses a neuron has, it still has the potential to grow more. Scientific proof that “practice makes perfect”! The brain is constantly changing and reorganizing itself by forming new neural connections. That’s called brain – or neuro – plasticity. This process takes place through ...
... No matter how many synapses a neuron has, it still has the potential to grow more. Scientific proof that “practice makes perfect”! The brain is constantly changing and reorganizing itself by forming new neural connections. That’s called brain – or neuro – plasticity. This process takes place through ...
Neurocognition Cognitive Neuroscience/neuropsychology
... vessels when they are at rest PET - relies on increased delivery of injected radioactive water, which diffuses out of the vessels to reach rest of brain ...
... vessels when they are at rest PET - relies on increased delivery of injected radioactive water, which diffuses out of the vessels to reach rest of brain ...
The body`s information system is built from billions of interconnected
... reading, writing, understanding) and analytical functions (e.g., mathematics) The right hemisphere is specialized for nonverbal activities (e.g., art and musical abilities, perceptual and spatio-manipulative skills, and visual recognition tasks); it also contributes to complex language comprehension ...
... reading, writing, understanding) and analytical functions (e.g., mathematics) The right hemisphere is specialized for nonverbal activities (e.g., art and musical abilities, perceptual and spatio-manipulative skills, and visual recognition tasks); it also contributes to complex language comprehension ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... from the senses to the brain and spinal cord. • Efferent neurons (motor), send information from the central nervous system to the glands and muscles, enabling the body to move. • Interneurons carry information between neurons in the Central Nervous System. ...
... from the senses to the brain and spinal cord. • Efferent neurons (motor), send information from the central nervous system to the glands and muscles, enabling the body to move. • Interneurons carry information between neurons in the Central Nervous System. ...
The Nervous System http://www.gmstigers.com/apps/pages/index
... The spinal cord is the long bundle of nerves that runs down the middle of your back. It serves as the main pathway for messages between the brain and the body. In men the spinal cord is about 45 centimeters long. In women it is about 43 centimeters long. Your backbone protects the spinal cord from d ...
... The spinal cord is the long bundle of nerves that runs down the middle of your back. It serves as the main pathway for messages between the brain and the body. In men the spinal cord is about 45 centimeters long. In women it is about 43 centimeters long. Your backbone protects the spinal cord from d ...
Thrills That Kill
... Even though science continues to give us ever increasing insights into what memory is, much of it remains a mystery. Researchers consider memory a process, and when you remember you are actually reconstructing the event from bits of information stored in various parts of the brain. But the mystery i ...
... Even though science continues to give us ever increasing insights into what memory is, much of it remains a mystery. Researchers consider memory a process, and when you remember you are actually reconstructing the event from bits of information stored in various parts of the brain. But the mystery i ...
The Nervous System
... There are three types of neurons: sensory respond to touch, sound, light and numerous other stimuli affecting cells of the sensory organs that then send signals to the spinal cord and brain. Motor Neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord and cause muscle contractions and affect ...
... There are three types of neurons: sensory respond to touch, sound, light and numerous other stimuli affecting cells of the sensory organs that then send signals to the spinal cord and brain. Motor Neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord and cause muscle contractions and affect ...
Chapter1
... The brain is an anticipating memory system. It learns to represent the world, or more specifically, expectations of the world, which can be used to generate goal directed behavior. ...
... The brain is an anticipating memory system. It learns to represent the world, or more specifically, expectations of the world, which can be used to generate goal directed behavior. ...
Page 1
... Name_____________________________________________Date____________Hour____Table____ Make a prediction about the answer to each question. Put a star next to the answer that you think is correct for each question. Watch the video about the nervous system. Record the answer for each question on the line ...
... Name_____________________________________________Date____________Hour____Table____ Make a prediction about the answer to each question. Put a star next to the answer that you think is correct for each question. Watch the video about the nervous system. Record the answer for each question on the line ...
Chapter 2 Vocabulary
... 43. Located on the sides of the brain, the __________________ __________________ contain the auditory areas, which receive information from the ears. (p. 65) Memory aid: The __________________ __________________ are located near the temples. 44. Located at the back of the frontal lobe, the _________ ...
... 43. Located on the sides of the brain, the __________________ __________________ contain the auditory areas, which receive information from the ears. (p. 65) Memory aid: The __________________ __________________ are located near the temples. 44. Located at the back of the frontal lobe, the _________ ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... 2. sound waves are processed by the ears and turned into neural impulses that temporal lobes interpret d. Brain Plasticity i. Parts of the brain can adapt to perform other functions ii. Because dendrites grow throughout our lives iii. Younger brains are more plastic 5. Endocrine System a. Adrenal Gl ...
... 2. sound waves are processed by the ears and turned into neural impulses that temporal lobes interpret d. Brain Plasticity i. Parts of the brain can adapt to perform other functions ii. Because dendrites grow throughout our lives iii. Younger brains are more plastic 5. Endocrine System a. Adrenal Gl ...
node of action heroin
... clinics on a regular basis over the past 3 years. He has had drug dependency and addiction issues for around 5-6 years which has seriously jeopardized his health. Pete abuses heroin on a regular basis, mainly injecting the substance. However, he has failed to fully comply with any of his doctor’s or ...
... clinics on a regular basis over the past 3 years. He has had drug dependency and addiction issues for around 5-6 years which has seriously jeopardized his health. Pete abuses heroin on a regular basis, mainly injecting the substance. However, he has failed to fully comply with any of his doctor’s or ...
Connectionism
... • This is repeated until (often) the network solves the problem and yields the desired input-output profile. ...
... • This is repeated until (often) the network solves the problem and yields the desired input-output profile. ...
Intro-The neuron
... - Transmission within and between neurons • Weds and Thurs: gross anatomy of the brain ...
... - Transmission within and between neurons • Weds and Thurs: gross anatomy of the brain ...
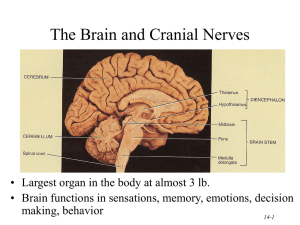
14-1
... Blood Supply to Brain • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanent injury • at that time, lysosome release enzymes ...
... Blood Supply to Brain • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanent injury • at that time, lysosome release enzymes ...
Word version - World Book Encyclopedia
... 7. The part of the brain that coordinates muscular movements with sensory information and helps maintain your body’s sense of balance is the: a. cerebrum b. cerebellum c. thalamus 8. The brain controls actions that you choose to do. Give two examples of voluntary actions. 1. _______________________ ...
... 7. The part of the brain that coordinates muscular movements with sensory information and helps maintain your body’s sense of balance is the: a. cerebrum b. cerebellum c. thalamus 8. The brain controls actions that you choose to do. Give two examples of voluntary actions. 1. _______________________ ...

![The Brain [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005074380_1-b4c54e7cf592b472b621b12b4eff42cc-300x300.png)