Instructor`s Resource Manual for Berk / Development
... development, the brain grows faster than any other organ of the body. As neurons form an elaborate communication system in the brain, stimulation becomes necessary for their survival. The cerebral cortex is the largest, most complex brain structure—accounting for 85 percent of the brain’s weight, co ...
... development, the brain grows faster than any other organ of the body. As neurons form an elaborate communication system in the brain, stimulation becomes necessary for their survival. The cerebral cortex is the largest, most complex brain structure—accounting for 85 percent of the brain’s weight, co ...
The Nervous System
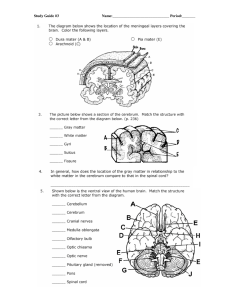
... • Largest section, made of many folded regions called fissures (why?) • Longitudinal central fissure runs through the middle, dividing the brain into hemispheres • Right and left connected by corpus callosum • Controls voluntary actions • Further divided into four lobes ...
... • Largest section, made of many folded regions called fissures (why?) • Longitudinal central fissure runs through the middle, dividing the brain into hemispheres • Right and left connected by corpus callosum • Controls voluntary actions • Further divided into four lobes ...
Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do
... What study methods will you use to remember this information? What functions is the Central Nervous System responsible for? What functions is the Peripheral Nervous System responsible for? What are two reasons that you need to know this information for a psychology class? What functions is t ...
... What study methods will you use to remember this information? What functions is the Central Nervous System responsible for? What functions is the Peripheral Nervous System responsible for? What are two reasons that you need to know this information for a psychology class? What functions is t ...
Chapter 12
... • 1.6 kg in males/1.45 kg in females (size is not representative of intelligence, only overall average body size) • Complexity dictates processing power ...
... • 1.6 kg in males/1.45 kg in females (size is not representative of intelligence, only overall average body size) • Complexity dictates processing power ...
the brain: anatomical regions
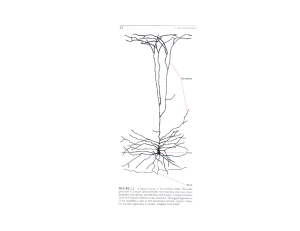
... Cerebrum is made of grey matter Grey matter is made of cell bodies, dendrites, neuroglia, and unmyelinated axons. ...
... Cerebrum is made of grey matter Grey matter is made of cell bodies, dendrites, neuroglia, and unmyelinated axons. ...
Unit 01 Biology and the Brain_Part 2
... • Making plans, judgment, speaking • Contains Motor Cortex: sends signals to our body controlling muscle movements. • Contains Broca’s Area: responsible for controlling muscles that produce speech. • Damage to Broca’s Area is called Broca’s Aphasia: unable to make movements to talk. ...
... • Making plans, judgment, speaking • Contains Motor Cortex: sends signals to our body controlling muscle movements. • Contains Broca’s Area: responsible for controlling muscles that produce speech. • Damage to Broca’s Area is called Broca’s Aphasia: unable to make movements to talk. ...
Physically-fit children are officially brainier than their punier peers
... Previous research has linked physical fitness in children to larger brain volumes of “grey matter” — the cell bodies of neurons. US lead researcher Dr Laura Chaddock-Heyman, from the University of Illinois, said: “This study extends our previous work and suggests that white-matter structure may be o ...
... Previous research has linked physical fitness in children to larger brain volumes of “grey matter” — the cell bodies of neurons. US lead researcher Dr Laura Chaddock-Heyman, from the University of Illinois, said: “This study extends our previous work and suggests that white-matter structure may be o ...
Nervous system slides
... Average weight 1.4 kg Over 1 billion neurons Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF) with a half life of about 3.5 hours ...
... Average weight 1.4 kg Over 1 billion neurons Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF) with a half life of about 3.5 hours ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
... brain. Includes the brain areas that are responsible for the most complex mental activities, including learning, remembering, thinking, and consciousness. LOBES OF THE BRAIN Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes. Each is dedicated to specific purposes. Frontal lobe: contains areas that ...
... brain. Includes the brain areas that are responsible for the most complex mental activities, including learning, remembering, thinking, and consciousness. LOBES OF THE BRAIN Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes. Each is dedicated to specific purposes. Frontal lobe: contains areas that ...
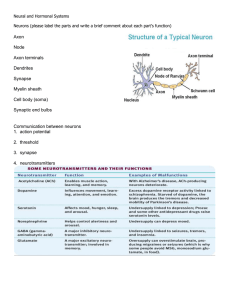
Neural and Hormonal Systems Neurons (please label the parts and
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
Myers` Psychology for AP
... 2. Describe the components of the brainstem, and summarize the functions of the brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum. LO #2 brainstem – medulla – reticular – thalamus – cerebellum – limbic system – amygdala – hypothalamus – The Cerebral Cortex 3. Describe the structure of the cerebral cortex, and exp ...
... 2. Describe the components of the brainstem, and summarize the functions of the brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum. LO #2 brainstem – medulla – reticular – thalamus – cerebellum – limbic system – amygdala – hypothalamus – The Cerebral Cortex 3. Describe the structure of the cerebral cortex, and exp ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... AS A RESULT OF INJURY TO HER BRAIN, BRIAN NO LONGER CAN UNDERSTAND WHAT PEOPLE SAY TO HER, ALTHOUGH SHE HEARS THEM. THE REGION OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX MOST LIKELY INJURED IS HER Temporal Lobe ...
... AS A RESULT OF INJURY TO HER BRAIN, BRIAN NO LONGER CAN UNDERSTAND WHAT PEOPLE SAY TO HER, ALTHOUGH SHE HEARS THEM. THE REGION OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX MOST LIKELY INJURED IS HER Temporal Lobe ...
05-Study Guide
... #3-Discuss and describe the neurons and neurotransmitters in the central nervous system, along with transient exuberance and pruning of these. ...
... #3-Discuss and describe the neurons and neurotransmitters in the central nervous system, along with transient exuberance and pruning of these. ...
Document
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.