Topic Presentation: Biopsychology
... Enables reasoning, planning, creating, problem solving Accounts for 2/3 of brain’s total mass ...
... Enables reasoning, planning, creating, problem solving Accounts for 2/3 of brain’s total mass ...
Chapter 2
... The Cerebral Cortex Structure and Functions 1. Each hemisphere is divided up into 4 ...
... The Cerebral Cortex Structure and Functions 1. Each hemisphere is divided up into 4 ...
Chapter 3 Section 2 - 6th
... aggression. If it is damaged, a person can recall old memories but can’t form new ones (50 First Dates) 4. Cerebrum- the part that thinks; it is uniquely human & accounts for 70% of brain weight cerebral cortex-outer layer of the brain, which deals with memory, language, emotions, complex motor func ...
... aggression. If it is damaged, a person can recall old memories but can’t form new ones (50 First Dates) 4. Cerebrum- the part that thinks; it is uniquely human & accounts for 70% of brain weight cerebral cortex-outer layer of the brain, which deals with memory, language, emotions, complex motor func ...
1 Central Nervous System: Brain one of largest organs in body (~3
... largest portion of brain (~60% of brain mass) two hemispheres joined by tracts = corpus callosum heavily convoluted: gyri and sulci each hemisphere: outer gray matter = cerebral cortex (2-4mm) inner white matter = tracts nuclei = islands of gray matter eg. basal nuclei (=basal ganglia) clusters of g ...
... largest portion of brain (~60% of brain mass) two hemispheres joined by tracts = corpus callosum heavily convoluted: gyri and sulci each hemisphere: outer gray matter = cerebral cortex (2-4mm) inner white matter = tracts nuclei = islands of gray matter eg. basal nuclei (=basal ganglia) clusters of g ...
ANATOMY
... the bony structure of the cranium. The brain is further protected by membrane coverings called the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. ...
... the bony structure of the cranium. The brain is further protected by membrane coverings called the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. ...
outline unit III
... 1. controls basic biological functions that keep us alive 2. medulla 1. controls blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing 3. pons 1. controls facial expressions 2. connects the hindbrain with the rest of the brain 4. cerebellum ...
... 1. controls basic biological functions that keep us alive 2. medulla 1. controls blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing 3. pons 1. controls facial expressions 2. connects the hindbrain with the rest of the brain 4. cerebellum ...
Introduction to drugs and the brain
... Drugs Can Change Brain Circuitry Drugs can “hijack” the brain’s natural connections and change them, which can cause a variety of consequences ...
... Drugs Can Change Brain Circuitry Drugs can “hijack” the brain’s natural connections and change them, which can cause a variety of consequences ...
neural migration - proffittscience
... of the brain that are active, with respect to certain actions. Here you can see the two eyes connected to the brain by the optic nerves. The left visual field is giving information to the right side of the primary visual cortex and vice versa. ...
... of the brain that are active, with respect to certain actions. Here you can see the two eyes connected to the brain by the optic nerves. The left visual field is giving information to the right side of the primary visual cortex and vice versa. ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... • Controls endocrine system • Controls autonomic nervous system (body temperature, appetite and thirst regulation) ...
... • Controls endocrine system • Controls autonomic nervous system (body temperature, appetite and thirst regulation) ...
WARM UP 4/20
... each, write down a little note for you to remember where the part is. EX: gyri - ridges pons – bump near bottom of brain ...
... each, write down a little note for you to remember where the part is. EX: gyri - ridges pons – bump near bottom of brain ...
Nervous System
... • brain stem - is located at the base of the brain and controls vital and involuntary processes (for example, breathing, the beating of the heart, and digestion). ...
... • brain stem - is located at the base of the brain and controls vital and involuntary processes (for example, breathing, the beating of the heart, and digestion). ...
The effects of electrical microstimulation on cortical signal propagation
... • In the BMI with somatosensory input, one monkey controlled cursor movements directly by using motor cortical activity while receiving somatosensory instructive signals (ICMS) in S1. • The second monkey also controlled the cursor using motor cortical activity but, since PP ICMS was ineffective, rec ...
... • In the BMI with somatosensory input, one monkey controlled cursor movements directly by using motor cortical activity while receiving somatosensory instructive signals (ICMS) in S1. • The second monkey also controlled the cursor using motor cortical activity but, since PP ICMS was ineffective, rec ...
File
... a bundle of fibers called the _corpus callosum___. 3. Covering the outermost layer of the cerebrum is the _cerebral cortex_. 4. What are the functions of the four lobes? Answer: Frontal- movement, higher thinking, emotional responses. Parietal- attention, language, space perception. Occipital- visio ...
... a bundle of fibers called the _corpus callosum___. 3. Covering the outermost layer of the cerebrum is the _cerebral cortex_. 4. What are the functions of the four lobes? Answer: Frontal- movement, higher thinking, emotional responses. Parietal- attention, language, space perception. Occipital- visio ...
PET (positron emission tomography): measures the different levels
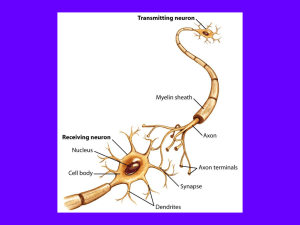
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory ...
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... The thin surface layer of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebrum is called the a. cerebral cortex. b. cerebellum. c. sensory cortex. d. reticular formation. e. corpus callosum. As you are reading this question, the cells in your eyes are firing in response to the light coming from this ...
... The thin surface layer of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebrum is called the a. cerebral cortex. b. cerebellum. c. sensory cortex. d. reticular formation. e. corpus callosum. As you are reading this question, the cells in your eyes are firing in response to the light coming from this ...
Study Questions-Ch2
... The __________ is involved with responses related to fear relatively quickly, allowing people to respond to danger sometimes before even being consciously aware that it exists: ...
... The __________ is involved with responses related to fear relatively quickly, allowing people to respond to danger sometimes before even being consciously aware that it exists: ...
brain research methods 1-10
... A direct brain stimulation technique that involves delivering a magnetic field pulse through the skull, temporarily activating or disrupting the normal activity of neurons in that specific area of the cerebral cortex. The magnetic field used is completely harmless and is transmitted through a small ...
... A direct brain stimulation technique that involves delivering a magnetic field pulse through the skull, temporarily activating or disrupting the normal activity of neurons in that specific area of the cerebral cortex. The magnetic field used is completely harmless and is transmitted through a small ...
Topography of brain
... below the lateral fissure. It is among the most experiences is seizures, hallucinations of frequently injury to the brain during head strange voices, music, people, smells, or ...
... below the lateral fissure. It is among the most experiences is seizures, hallucinations of frequently injury to the brain during head strange voices, music, people, smells, or ...
Brain Development
... • Axons elongate as they grow toward specific targets – Myelination begins prenatally and continues at least into adolescence ...
... • Axons elongate as they grow toward specific targets – Myelination begins prenatally and continues at least into adolescence ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.