Dissertation 20161009 Text Citations
... Figure 9. Discriminability of East Asian and Caucasian Stimuli based upon neural patterns of activation in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), amygdala (AMG), cuneus (CUN), dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), fusiform gyri / fusiform face area (FFA), posterior superior temporal sulcus (pSTS) an ...
... Figure 9. Discriminability of East Asian and Caucasian Stimuli based upon neural patterns of activation in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), amygdala (AMG), cuneus (CUN), dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), fusiform gyri / fusiform face area (FFA), posterior superior temporal sulcus (pSTS) an ...
Molecular Analysis of Developmental Plasticity in Neocortex
... al., 1991; Wigstrom and Gustafsson, 1985). Since its discovery in the hippocampus, LTP, the sustained increase in synaptic transmission resulting from highfrequency stimulation of excitatory pathways, has been the primary experimental model for studies of the synaptic basis of learning and memory in ...
... al., 1991; Wigstrom and Gustafsson, 1985). Since its discovery in the hippocampus, LTP, the sustained increase in synaptic transmission resulting from highfrequency stimulation of excitatory pathways, has been the primary experimental model for studies of the synaptic basis of learning and memory in ...
ANS: c, p. 42, F, LO=2.1, (1)
... 31. During the action potential, the electrical charge inside the neuron is __________ the electrical charge outside the neuron. a) positive compared to Correct. There are more positively charged ions inside the cell than outside. b) larger than c) negative compared to Incorrect. During resting pote ...
... 31. During the action potential, the electrical charge inside the neuron is __________ the electrical charge outside the neuron. a) positive compared to Correct. There are more positively charged ions inside the cell than outside. b) larger than c) negative compared to Incorrect. During resting pote ...
Mapping Pavlovian Conditioning Effects on the Brain: Blocking
... (CA1), cerebellum, caudate putamen, and solitary nucleus. Contiguity effects may be due to tone-shock pairings common to the toneblocked and -excitor groups rather than their different CER. And 3) excitatory effects: FDG uptake increases limited to the tone-excitor group occurred in a circuit linked ...
... (CA1), cerebellum, caudate putamen, and solitary nucleus. Contiguity effects may be due to tone-shock pairings common to the toneblocked and -excitor groups rather than their different CER. And 3) excitatory effects: FDG uptake increases limited to the tone-excitor group occurred in a circuit linked ...
The Neuropathology of Huntington`s Disease
... The basal ganglia are integrated into a circular interconnected forebrain loop, which forms a cortical/basal ganglia/thalamus/cortical circuit (Nauta and Domesick 1984), (see Fig. 1). The cortex provides a major excitatory glutamatergic input to the caudate nucleus and putamen (Carpenter et al. 1976 ...
... The basal ganglia are integrated into a circular interconnected forebrain loop, which forms a cortical/basal ganglia/thalamus/cortical circuit (Nauta and Domesick 1984), (see Fig. 1). The cortex provides a major excitatory glutamatergic input to the caudate nucleus and putamen (Carpenter et al. 1976 ...
PDF
... responses. Given the need for rapid predator avoidance in animals with vastly different body types, the expression of these responses has been necessarily altered to suit the sensorimotor requirements of each anatomical form. Hale et al. (2002) have demonstrated that the expression of escape behavio ...
... responses. Given the need for rapid predator avoidance in animals with vastly different body types, the expression of these responses has been necessarily altered to suit the sensorimotor requirements of each anatomical form. Hale et al. (2002) have demonstrated that the expression of escape behavio ...
Hemispheric Asymmetry Reduction in Older Adults
... One of the first activation studies of cognitive aging was that of Grady et al. (1994) on visual perception. During face matching, older adults showed weaker activity than younger adults showed in the occipital cortex but stronger activity in more anterior brain ...
... One of the first activation studies of cognitive aging was that of Grady et al. (1994) on visual perception. During face matching, older adults showed weaker activity than younger adults showed in the occipital cortex but stronger activity in more anterior brain ...
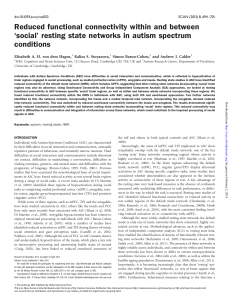
Reduced functional connectivity within and between `social` resting
... network subserves are correlated with the resting functional connectivity of that network (Seeley et al., 2007). In light of these observations, an interesting question is to what extent task-based differences in specific brain regions in ASC are reflected in different connectivity patterns of their ...
... network subserves are correlated with the resting functional connectivity of that network (Seeley et al., 2007). In light of these observations, an interesting question is to what extent task-based differences in specific brain regions in ASC are reflected in different connectivity patterns of their ...
Spontaneous and Stimulus-Evoked Intrinsic Optical Signals in
... Spontaneous changes of light reflectance in auditory cortex were observed in the absence of acoustic stimulation in 9/10 cats. In most cases, the spontaneous signals were manifest as irregular variations of reflectance in the no-stimulus condition but were obscured by averaging signals from multiple ...
... Spontaneous changes of light reflectance in auditory cortex were observed in the absence of acoustic stimulation in 9/10 cats. In most cases, the spontaneous signals were manifest as irregular variations of reflectance in the no-stimulus condition but were obscured by averaging signals from multiple ...
Spontaneous and Stimulus-Evoked Intrinsic Optical Signals in
... Spontaneous changes of light reflectance in auditory cortex were observed in the absence of acoustic stimulation in 9/10 cats. In most cases, the spontaneous signals were manifest as irregular variations of reflectance in the no-stimulus condition but were obscured by averaging signals from multiple ...
... Spontaneous changes of light reflectance in auditory cortex were observed in the absence of acoustic stimulation in 9/10 cats. In most cases, the spontaneous signals were manifest as irregular variations of reflectance in the no-stimulus condition but were obscured by averaging signals from multiple ...
download file
... activated by the paired tone and induced primary cortex neurons to become more selective to the paired tone. In the third part of the dissertation I explored induction of experiencedependent plasticity using modulation of attentional mechanisms. It has been previously demonstrated that paying attent ...
... activated by the paired tone and induced primary cortex neurons to become more selective to the paired tone. In the third part of the dissertation I explored induction of experiencedependent plasticity using modulation of attentional mechanisms. It has been previously demonstrated that paying attent ...
Omega–6/Omega–3 Ratio and Brain-Related Functions - Direct-MS
... in fluidizing of the neuronal membrane, while an increase in cholesterol will harden the membrane. The membrane should be at an optimal physiological gel state. Therefore, cholesterol, which is a complex lipid, is involved in many functions in the membrane. It is well established that cholesterol de ...
... in fluidizing of the neuronal membrane, while an increase in cholesterol will harden the membrane. The membrane should be at an optimal physiological gel state. Therefore, cholesterol, which is a complex lipid, is involved in many functions in the membrane. It is well established that cholesterol de ...
Central Nervous System (CNS) The Brain Embryonic Development
... • Forms part of the anterior wall of the fourth ventricle • Fibers of the pons: • Connect higher brain centers and the spinal cord • Relay impulses between the motor cortex and the ...
... • Forms part of the anterior wall of the fourth ventricle • Fibers of the pons: • Connect higher brain centers and the spinal cord • Relay impulses between the motor cortex and the ...
PDF
... and perception using only electrophysiological recordings. Sound stimuli cannot be used to investigate how signals in different parts of the cortex influence behavior because any given sound stimulus could activate thousands or millions of neurons distributed across many cortical areas, thereby maki ...
... and perception using only electrophysiological recordings. Sound stimuli cannot be used to investigate how signals in different parts of the cortex influence behavior because any given sound stimulus could activate thousands or millions of neurons distributed across many cortical areas, thereby maki ...
Mirror neurons in humans: Consisting or confounding
... this fMRI study does not allow us to draw any firm conclusion about ‘mirror’ type of activity, mainly because of methodological problems. First, the analyses were performed by merging data from two different experiments (one considering only execution and one considering both action observation and ex ...
... this fMRI study does not allow us to draw any firm conclusion about ‘mirror’ type of activity, mainly because of methodological problems. First, the analyses were performed by merging data from two different experiments (one considering only execution and one considering both action observation and ex ...
Neurophysiological correlates of hypnotic analgesia
... of a network of cortical and subcortical regions (Tölle, Kaufmann, Siessmeier, Lautenbacher, Berthele, Munz, Zieglgänsberger, Willoch, Schwaiger, Conrad and Bartenstein, 1999; Peyron, Laurent, Garcia and Larrea, 2000; Derbyshire, Jones, Creed, Starz, Meltzer, Townsend, Peterson and Firestone, 2002) ...
... of a network of cortical and subcortical regions (Tölle, Kaufmann, Siessmeier, Lautenbacher, Berthele, Munz, Zieglgänsberger, Willoch, Schwaiger, Conrad and Bartenstein, 1999; Peyron, Laurent, Garcia and Larrea, 2000; Derbyshire, Jones, Creed, Starz, Meltzer, Townsend, Peterson and Firestone, 2002) ...
The Neurology of Music for Post-Traumatic-Stress
... nerve cells, or neurons, which communicate with the rest of the body through the spinal cord and nervous system. Nerve cells from the rest of the body bring information back to the brain, through the spinal cord, where it can be processed and an appropriate response can be computed. There are chemic ...
... nerve cells, or neurons, which communicate with the rest of the body through the spinal cord and nervous system. Nerve cells from the rest of the body bring information back to the brain, through the spinal cord, where it can be processed and an appropriate response can be computed. There are chemic ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.