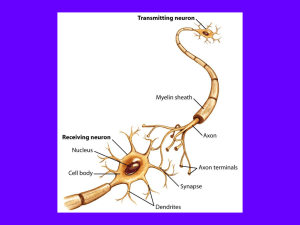
Arithmetic
... Subtraction can have unwanted consequences when the important processing goes on in both conditions. Another approach is known as parametric variation in which variance of each variable is estimated. ...
... Subtraction can have unwanted consequences when the important processing goes on in both conditions. Another approach is known as parametric variation in which variance of each variable is estimated. ...
Adolescents Brain Development
... • Reward centre in overdrive coupled with planning regions that are not fully functional could make an adolescent an entirely different creature to an adult when it comes to seeking pleasure ...
... • Reward centre in overdrive coupled with planning regions that are not fully functional could make an adolescent an entirely different creature to an adult when it comes to seeking pleasure ...
- Philsci
... variable representing time, w is some n-tuple of numerical quantities, including possibly integers, real or complex numbers, taking values in a space of k-tuples, u, of similar objects. I assume you already know what computability on natural numbers means. Computable complex numbers are defined in t ...
... variable representing time, w is some n-tuple of numerical quantities, including possibly integers, real or complex numbers, taking values in a space of k-tuples, u, of similar objects. I assume you already know what computability on natural numbers means. Computable complex numbers are defined in t ...
abstract
... Biology & Neurodegeneration, Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience; Institute for Life Sciences, Center for Neuroscience, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 2Swammerdam ...
... Biology & Neurodegeneration, Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience; Institute for Life Sciences, Center for Neuroscience, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 2Swammerdam ...
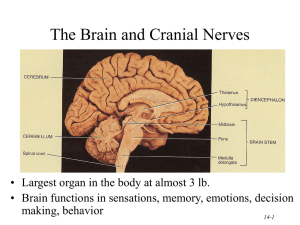
The Brain [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous
... damage causes coma Limbic system • brain structures clustered around brain stem at core of the brain, surrounded by cerebrum; involved in coordinating different brain activities • thalamus: routs activation from reticular formation/sensory impulses to cerebral cortex • hypothalamus: control unit for ...
... damage causes coma Limbic system • brain structures clustered around brain stem at core of the brain, surrounded by cerebrum; involved in coordinating different brain activities • thalamus: routs activation from reticular formation/sensory impulses to cerebral cortex • hypothalamus: control unit for ...
Development of Nervous System
... Specializes in language, math, logic operations, and the processing of serial sequences of information, and visual and auditory details. Specializes in detailed activities required for motor control. ...
... Specializes in language, math, logic operations, and the processing of serial sequences of information, and visual and auditory details. Specializes in detailed activities required for motor control. ...
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior
... • Level Two- In addition to Level One material, Research and find out who or how it was discovered • Level Three: Choose one additional disease/disorder and do Level 0ne/Two work on that disease/disorder • Completed assignment is a word ...
... • Level Two- In addition to Level One material, Research and find out who or how it was discovered • Level Three: Choose one additional disease/disorder and do Level 0ne/Two work on that disease/disorder • Completed assignment is a word ...
Annual Review of Neuroscience
... 2. Investigation of the highest levels of cognitive function using the most sophisticated animal training in neuroscience. Most neurophysiological studies of cognition use relatively basic tasks (“pay attention here.” “hold one thing in mind”) The Miller Lab has taken monkey training to a higher lev ...
... 2. Investigation of the highest levels of cognitive function using the most sophisticated animal training in neuroscience. Most neurophysiological studies of cognition use relatively basic tasks (“pay attention here.” “hold one thing in mind”) The Miller Lab has taken monkey training to a higher lev ...
The Nervous System
... The brain has about 100 billion brain cells. The spinal cord is crucial for everyday function as it transmits commands from the brain to the rest of the body. ...
... The brain has about 100 billion brain cells. The spinal cord is crucial for everyday function as it transmits commands from the brain to the rest of the body. ...
The Nervous System allows communication
... Long term heavy uses- effect varies from person to person: ...
... Long term heavy uses- effect varies from person to person: ...
Nervous System
... oxygen and nourishment, and take away wastes. If brain cells do not get oxygen for 3 to 5 minutes, they begin to die. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds the brain. THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system (CNS). The brain is connected to the spinal cord, which ...
... oxygen and nourishment, and take away wastes. If brain cells do not get oxygen for 3 to 5 minutes, they begin to die. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds the brain. THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system (CNS). The brain is connected to the spinal cord, which ...
14-1
... • Mammillary bodies are relay station for olfactory reflexes; infundibulum suspends the pituitary gland • Major regulator of homeostasis – receives somatic and visceral input, taste, smell & hearing information; monitors osmotic pressure, temperature of blood ...
... • Mammillary bodies are relay station for olfactory reflexes; infundibulum suspends the pituitary gland • Major regulator of homeostasis – receives somatic and visceral input, taste, smell & hearing information; monitors osmotic pressure, temperature of blood ...
Brain Structure - Updated 14
... Goal: gain a hands-on idea of how electrical information is passed along an axon for neural transmission to occur. ...
... Goal: gain a hands-on idea of how electrical information is passed along an axon for neural transmission to occur. ...
Commentary on Clark Being There
... perceptual equipment. At this point the recorded information does become causally active, but only because it is now re-coded elsewhere – namely, inside our skulls. The second difference is that such externally recorded information, when it does become causally engaged with parts of the mind, does s ...
... perceptual equipment. At this point the recorded information does become causally active, but only because it is now re-coded elsewhere – namely, inside our skulls. The second difference is that such externally recorded information, when it does become causally engaged with parts of the mind, does s ...
How Psychologists Study the Brain
... Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal devices inside their body (such as a pacemaker, implanted port or pump). The magnetic force is so strong that it can ...
... Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal devices inside their body (such as a pacemaker, implanted port or pump). The magnetic force is so strong that it can ...
Vertebrate versus invertebrate neural circuits
... show obvious differences in design principles, implying that some brain functions are not equivalent. However, many computational problems need to be solved by all brains. In these cases, insights obtained in one species will be instructive to understand brain functions in other species, even if the ...
... show obvious differences in design principles, implying that some brain functions are not equivalent. However, many computational problems need to be solved by all brains. In these cases, insights obtained in one species will be instructive to understand brain functions in other species, even if the ...
Topic 8
... The brain therefore exists in near neutral buoyancy, which allows the brain to maintain its density without being impaired by its own weight, which could cut blood supply and kill neurons in the lower sections without CSF. 2. Protection: CSF protects the brain tissue from injury when jolted or hit. ...
... The brain therefore exists in near neutral buoyancy, which allows the brain to maintain its density without being impaired by its own weight, which could cut blood supply and kill neurons in the lower sections without CSF. 2. Protection: CSF protects the brain tissue from injury when jolted or hit. ...
Ch 3
... 18. What is the function of the neurotransmitter? Why are neurotransmitters important in psychological functioning? 19. What is plasticity and for what mental function does it play a particularly important role? ...
... 18. What is the function of the neurotransmitter? Why are neurotransmitters important in psychological functioning? 19. What is plasticity and for what mental function does it play a particularly important role? ...
brain1
... nourishment, and take away wastes. If brain cells do not get oxygen for 3 to 5 minutes, they begin to die. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds the brain. ...
... nourishment, and take away wastes. If brain cells do not get oxygen for 3 to 5 minutes, they begin to die. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds the brain. ...
Learning and the Brain - Santa Clara County Office of
... Goal: Let us see how close you come to communicating an accurate image to your partner. Feedback ...
... Goal: Let us see how close you come to communicating an accurate image to your partner. Feedback ...
Ch on Drugs and Prep for Test
... * Contains the primary auditory cortex * Much of it is used for complex visual tasks in conjunction with the primary visual cortex * These include recognizing faces and perceiving motion * Also crucial to memory * In the left hemisphere, aids language skills ...
... * Contains the primary auditory cortex * Much of it is used for complex visual tasks in conjunction with the primary visual cortex * These include recognizing faces and perceiving motion * Also crucial to memory * In the left hemisphere, aids language skills ...



![The Brain [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005074380_1-b4c54e7cf592b472b621b12b4eff42cc-300x300.png)