PET (positron emission tomography): measures the different levels
... taken from different angles and combined by computer to create an image that represents a slice through the brain. PET (positron emission tomography): measures the different levels of activity in the brain by detecting where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain is performing a given ta ...
... taken from different angles and combined by computer to create an image that represents a slice through the brain. PET (positron emission tomography): measures the different levels of activity in the brain by detecting where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain is performing a given ta ...
File
... • B. How is our sleep cycle controlled – 1. The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)lies in the hypothalamus and is the body’s main biological clock. – 2. When light hits the retina it sends a signal to the SCN which then relays a message to the pineal glands which in turn secrete melatonin which is a hor ...
... • B. How is our sleep cycle controlled – 1. The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)lies in the hypothalamus and is the body’s main biological clock. – 2. When light hits the retina it sends a signal to the SCN which then relays a message to the pineal glands which in turn secrete melatonin which is a hor ...
The Nervous System
... Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – mental deterioration usually associated with age Epilepsy – sudden episo ...
... Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – mental deterioration usually associated with age Epilepsy – sudden episo ...
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System - dr
... 7. What are the 5 lobes of the brain, what are they named after, what functional regions are found in each? 8. Define the following: a. Sulcus b. Gyrus c. Fissure 9. What major structure separates the left cerebral hemisphere from the right? 10. What major structure separates the cerebrum from the c ...
... 7. What are the 5 lobes of the brain, what are they named after, what functional regions are found in each? 8. Define the following: a. Sulcus b. Gyrus c. Fissure 9. What major structure separates the left cerebral hemisphere from the right? 10. What major structure separates the cerebrum from the c ...
Sp.CBSTH functions
... Control physical behaviors Sleep Fatigue Motivation to perform various activities, walking, eating, urination ...
... Control physical behaviors Sleep Fatigue Motivation to perform various activities, walking, eating, urination ...
CNS=Central Nervous System
... hemisphere? The right hemisphere controls artistic expression, creativity and spatial understanding. 7) What did the study of Phineas Gage teach us about the brain? The brain is not only responsible for language and movement but it is also responsible for determining one’s emotions and personality 8 ...
... hemisphere? The right hemisphere controls artistic expression, creativity and spatial understanding. 7) What did the study of Phineas Gage teach us about the brain? The brain is not only responsible for language and movement but it is also responsible for determining one’s emotions and personality 8 ...
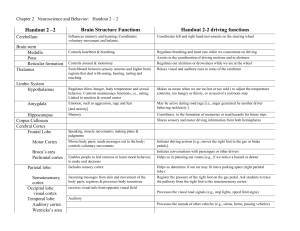
Handout 2 –2 Brain Structure Functions Handout 2-2 driving
... Frontal Lobe Motor Cortex Broca’s area Prefrontal cortex ...
... Frontal Lobe Motor Cortex Broca’s area Prefrontal cortex ...
Review_Day_1
... o The brainstem includes the medulla (heartbeat and breathing), the reticular formation (arousal center), the cerebellum (balance) and the thalamus (the “sensory switchboard”) o The limbic system includes the hippocampus (memory), the hypothalamus (directs the endocrine system/”pleasure center”), an ...
... o The brainstem includes the medulla (heartbeat and breathing), the reticular formation (arousal center), the cerebellum (balance) and the thalamus (the “sensory switchboard”) o The limbic system includes the hippocampus (memory), the hypothalamus (directs the endocrine system/”pleasure center”), an ...
Chapter 5: The First Two Years
... • During the first months and years, major spurts of growth and refinement in axons, dendrites, and synapses occur (connections are being made) • Transient Exuberance is the great increase in the number of dendrites that occurs in an infant’s brain over 1st 2 years of life • Enables neurons to becom ...
... • During the first months and years, major spurts of growth and refinement in axons, dendrites, and synapses occur (connections are being made) • Transient Exuberance is the great increase in the number of dendrites that occurs in an infant’s brain over 1st 2 years of life • Enables neurons to becom ...
Step back and look at the Science
... Cocaine blocks reuptake of neurotransmitter More neurotransmitter remains in synapse to stimulate further ...
... Cocaine blocks reuptake of neurotransmitter More neurotransmitter remains in synapse to stimulate further ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... Sensory Neuron: carry messages from sense receptor cells toward the ...
... Sensory Neuron: carry messages from sense receptor cells toward the ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... • Olfactory mucosa is divided into 4 zones – Each zone contains a variety of different receptors ...
... • Olfactory mucosa is divided into 4 zones – Each zone contains a variety of different receptors ...
The Impact of Ecstasy on the Brain
... • Numerous short-term and long-term side effects occur when taking Ecstasy. • Lacing or substitution in pills make it difficult to predict which effects may occur. • Further studies must be conducted to understand the lasting effects the drugs has on the mind and body. ...
... • Numerous short-term and long-term side effects occur when taking Ecstasy. • Lacing or substitution in pills make it difficult to predict which effects may occur. • Further studies must be conducted to understand the lasting effects the drugs has on the mind and body. ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint notes
... = a neural structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward. ...
... = a neural structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward. ...
Step back and look at the Science
... Cocaine blocks reuptake of neurotransmitter More neurotransmitter remains in synapse to stimulate further ...
... Cocaine blocks reuptake of neurotransmitter More neurotransmitter remains in synapse to stimulate further ...
AGING PRESENTATION
... Ex: 100.000 neuron loss daily resulting in 19.7% loss at the age of 80 [Brody et al.]. With the advancements of neuron counting technology, Terry et al. found out that there is not much age related neural loss in cortex. The small decrease has been explained as the cortical thinning or as the st ...
... Ex: 100.000 neuron loss daily resulting in 19.7% loss at the age of 80 [Brody et al.]. With the advancements of neuron counting technology, Terry et al. found out that there is not much age related neural loss in cortex. The small decrease has been explained as the cortical thinning or as the st ...
brainy tests - WordPress.com
... It is the name given to a large group of motor (body movement) disorders that begin early in life and result from brain injuries that are non-progressive (do not worsen over time). Cerebral Palsy ...
... It is the name given to a large group of motor (body movement) disorders that begin early in life and result from brain injuries that are non-progressive (do not worsen over time). Cerebral Palsy ...
Human Physiology
... maintains homeostasis. Explain how the nervous sends messages and communicates with different parts of the body. Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. ...
... maintains homeostasis. Explain how the nervous sends messages and communicates with different parts of the body. Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. ...
Left hand side, right hand side
... patients has damage to her cerebral cortex. Suggest two processes that are most damaged by this. [2 marks] Suggest how Stuart could find out exactly which parts of the brain are damaged [2 marks] ...
... patients has damage to her cerebral cortex. Suggest two processes that are most damaged by this. [2 marks] Suggest how Stuart could find out exactly which parts of the brain are damaged [2 marks] ...
neural migration - proffittscience
... Self-administration experiments are one of the most common types of animal experimentation, in which mice can choose what type of food to eat. This is useful to determine whether a substance is addictive, and whether it would ...
... Self-administration experiments are one of the most common types of animal experimentation, in which mice can choose what type of food to eat. This is useful to determine whether a substance is addictive, and whether it would ...