Introduction to Psychology
... a layer of fatty cells covering the axon of some neurons greatly increases the speed of neural impulses ...
... a layer of fatty cells covering the axon of some neurons greatly increases the speed of neural impulses ...
Document
... Glu - learning and memory GABA - normal brain functioning Endorphins - physical pain, emotion ...
... Glu - learning and memory GABA - normal brain functioning Endorphins - physical pain, emotion ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (8th edition) David Myers
... Aphasia: impairment of language, usually caused by left-hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area or Wernicke’s area. Broca’s area: controls language expression; an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, directs muscle movements involved in speech. Wernicke’s area: controls languag ...
... Aphasia: impairment of language, usually caused by left-hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area or Wernicke’s area. Broca’s area: controls language expression; an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, directs muscle movements involved in speech. Wernicke’s area: controls languag ...
Document
... and thoughts) to provide direct communication and control between the human brain and physical devices by translating different patterns of brain activity into commands in real time. With these commands a mobile robot can be controlled. The intention of the project work is to develop a robot that ca ...
... and thoughts) to provide direct communication and control between the human brain and physical devices by translating different patterns of brain activity into commands in real time. With these commands a mobile robot can be controlled. The intention of the project work is to develop a robot that ca ...
Brain Anatomy - Lone Star College System
... Aphasia: impairment of language, usually caused by left-hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area or Wernicke’s area. Broca’s area: controls language expression; an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, directs muscle movements involved in speech. Wernicke’s area: controls languag ...
... Aphasia: impairment of language, usually caused by left-hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area or Wernicke’s area. Broca’s area: controls language expression; an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, directs muscle movements involved in speech. Wernicke’s area: controls languag ...
abstract
... 5HT in serotonergic neurons. The enzyme activity was determined in two brain regions, cortex and the brainstem, at two time points of 12hr light/12hr dark cycle, namely, mid-light and mid-dark. The results obtained showed that the activity of tryptophan hydroxylase was significantly greater in contr ...
... 5HT in serotonergic neurons. The enzyme activity was determined in two brain regions, cortex and the brainstem, at two time points of 12hr light/12hr dark cycle, namely, mid-light and mid-dark. The results obtained showed that the activity of tryptophan hydroxylase was significantly greater in contr ...
Structure of the Nervous System
... Tract – axons with a common origin and destination. Bundle – axons that run together for awhile. Capsule – axons connecting brain stem with cortex. ...
... Tract – axons with a common origin and destination. Bundle – axons that run together for awhile. Capsule – axons connecting brain stem with cortex. ...
CH3
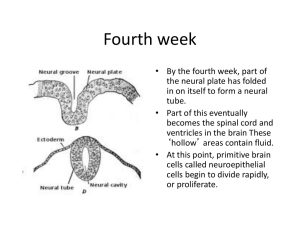
... The nervous system develops from ectoderm (outer layer) which forms a plate (~day 18) The edges of the plate curl and eventually fuse together forming a neural tube By ~day 28, the rostral end of the neural tube has formed the ventricles and the tissue that surrounds ...
... The nervous system develops from ectoderm (outer layer) which forms a plate (~day 18) The edges of the plate curl and eventually fuse together forming a neural tube By ~day 28, the rostral end of the neural tube has formed the ventricles and the tissue that surrounds ...
General PLTW Document
... and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and col ...
... and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and col ...
Ch. 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes
... carried by three neurons • Motor info carried by two neurons ...
... carried by three neurons • Motor info carried by two neurons ...
The Human Brain Cerebrum
... nerves between the two hemispheres • Helps left and right hemispheres talk to each other! (“crosstalk”) • Avidly used by guitar players! ...
... nerves between the two hemispheres • Helps left and right hemispheres talk to each other! (“crosstalk”) • Avidly used by guitar players! ...
Ocular Dominance Columns
... Competition for “trophic factor” secreted by target examples: NGF, BDNF, GDNF; (specific receptors on neurons) ...
... Competition for “trophic factor” secreted by target examples: NGF, BDNF, GDNF; (specific receptors on neurons) ...
Evolutionary Psychology: Understanding Human Nature
... - Motor Cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. - Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in prima ...
... - Motor Cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. - Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in prima ...
Chapter 2 - bobcat
... MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that does not use xrays. The process involves passing a strong magnetic field through the head. The magnetic field used is 30,000 + times that of the earth's magnetic field. It's effect on the body, however, is harmless and temporary. The MRI scanner can detect ...
... MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that does not use xrays. The process involves passing a strong magnetic field through the head. The magnetic field used is 30,000 + times that of the earth's magnetic field. It's effect on the body, however, is harmless and temporary. The MRI scanner can detect ...
Fourth week
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
Transcription and translation of new gene products is critical for
... maintaining long lasting memory. To initiate activity‐dependent transcription, neuronal inputs that arrive at the synapse must be relayed to the nucleus to trigger changes in gene expression. Many of these synaptic contacts are found in distal neuronal projections far from the soma and as such, neur ...
... maintaining long lasting memory. To initiate activity‐dependent transcription, neuronal inputs that arrive at the synapse must be relayed to the nucleus to trigger changes in gene expression. Many of these synaptic contacts are found in distal neuronal projections far from the soma and as such, neur ...
1. Learning Depends on Integration of Brain Structures
... Dendrites are the main way by which neurons get information (learn). Dendrites receive electrical impulses from other neurons and transmit them along a long fiber called an axon. In the synaptic gap, and electrical signal is briefly transmitted into a chemical called a neurotransmitter. – Dopamine a ...
... Dendrites are the main way by which neurons get information (learn). Dendrites receive electrical impulses from other neurons and transmit them along a long fiber called an axon. In the synaptic gap, and electrical signal is briefly transmitted into a chemical called a neurotransmitter. – Dopamine a ...
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior
... • Why can injury to the frontal lobes cause the widest variety of symptoms? • Describe how brain injury can cause personality changes ...
... • Why can injury to the frontal lobes cause the widest variety of symptoms? • Describe how brain injury can cause personality changes ...
1 2 The Advent of Modern Neuroscience
... new type of aphasia that involved an impairment of speech comprehension in a patient who could speak clearly. The brains of people who suffered from Wernicke’s aphasia revealed a lesion in an area now referred to as Wernicke’s area. In patients suffering from Wernicke’s aphasia, speech is fluent, but ...
... new type of aphasia that involved an impairment of speech comprehension in a patient who could speak clearly. The brains of people who suffered from Wernicke’s aphasia revealed a lesion in an area now referred to as Wernicke’s area. In patients suffering from Wernicke’s aphasia, speech is fluent, but ...
Brain and Behavior
... Aggregate field view A reaction against strict materialism (mind not completely biological). ...
... Aggregate field view A reaction against strict materialism (mind not completely biological). ...
Myers AP - Unit 3B
... Figure 3B.14 New technology shows the brain in action This fMRI (functional MRI) scan shows the visual cortex in the occipital lobes activated (color representation of increased bloodflow) as a research participant looks at a photo. When the person stops looking, the region instantly calms down. ...
... Figure 3B.14 New technology shows the brain in action This fMRI (functional MRI) scan shows the visual cortex in the occipital lobes activated (color representation of increased bloodflow) as a research participant looks at a photo. When the person stops looking, the region instantly calms down. ...
6th Study Guide D1w:ans
... 3. The gap or space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another is called a synapse. 4. The part of the brain that allows you to think is the cerebrum. 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that is sensitive to color. 7. Th ...
... 3. The gap or space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another is called a synapse. 4. The part of the brain that allows you to think is the cerebrum. 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that is sensitive to color. 7. Th ...
Sam Wangdescribes some of the physics of our most complex organ
... bit of grey matter in the cerebral cortex is layered like a cake, with connections passing from layer to layer. The layers are arranged such that a hypothetical shuffling of the order of the layers would increase the total amount of wiring used, sometimes considerably. It is not yet known how this w ...
... bit of grey matter in the cerebral cortex is layered like a cake, with connections passing from layer to layer. The layers are arranged such that a hypothetical shuffling of the order of the layers would increase the total amount of wiring used, sometimes considerably. It is not yet known how this w ...
Unit 3 Biology of Behavior The Neuron Dendrites: Tree
... Temporal Lobes: Contain the primary auditory cortex (audition) and areas for the senses of smell (olfaction) and taste (gustatory sense). The LEFT temporal lobe contains Wernicke's Area which control language comprehension and expression. Occipital Lobes: Contains the Primary Visual Cortex. Associat ...
... Temporal Lobes: Contain the primary auditory cortex (audition) and areas for the senses of smell (olfaction) and taste (gustatory sense). The LEFT temporal lobe contains Wernicke's Area which control language comprehension and expression. Occipital Lobes: Contains the Primary Visual Cortex. Associat ...