Nervous System Graphics - Beacon Learning Center
... your feet that hurt and that it hurts where your shoes are touching it. Your brain reasons that since your feet hurt where your shoes are touching them, your shoes are hurting your feet. 8. Does our brain control the blood that is flowing to the brain? Yes – our brain controls EVERYTHING 9. Why must ...
... your feet that hurt and that it hurts where your shoes are touching it. Your brain reasons that since your feet hurt where your shoes are touching them, your shoes are hurting your feet. 8. Does our brain control the blood that is flowing to the brain? Yes – our brain controls EVERYTHING 9. Why must ...
Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience)
... 3. Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. 4. Describe how nerve cells communicate. 5. Explain how neurotransmitters affect behavior, and outline the effects of acetylcholine and the endorphins. 6. Explain how drugs other chemicals affect neurotransmission, and de ...
... 3. Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. 4. Describe how nerve cells communicate. 5. Explain how neurotransmitters affect behavior, and outline the effects of acetylcholine and the endorphins. 6. Explain how drugs other chemicals affect neurotransmission, and de ...
IV. PSYCHOBIOLOGY
... Integrates, interprets, acts on information. (i.e. important to communication). Areas and their associated behaviors have been identified based on what happens when those areas are damaged. ...
... Integrates, interprets, acts on information. (i.e. important to communication). Areas and their associated behaviors have been identified based on what happens when those areas are damaged. ...
Concepts of Neurobiology
... CNS: neurons, composed of: Cell body, contains nucleus Axon, transmits message to next cell Dendrites, receives messages from cells Three classes of neurons in CNS Afferent (sensory) Efferent (motor) Interneurons in CNS ...
... CNS: neurons, composed of: Cell body, contains nucleus Axon, transmits message to next cell Dendrites, receives messages from cells Three classes of neurons in CNS Afferent (sensory) Efferent (motor) Interneurons in CNS ...
I. How Do Scientists Study the Nervous System?
... The strong popular bias about hemispheric differences (“right brain” vs. “left brain”) is overstated. Research shows that the two hemispheres are more similar than different and that any differences are usually relative. For most right-handed people, Wernicke’s and Broca’s areas related to speech an ...
... The strong popular bias about hemispheric differences (“right brain” vs. “left brain”) is overstated. Research shows that the two hemispheres are more similar than different and that any differences are usually relative. For most right-handed people, Wernicke’s and Broca’s areas related to speech an ...
Chapter 11
... Functions of Cerebrum • 3 basic functions: 1. Motor area – sends impulses to muscles 2. Sensory area – interpret impulses from sensory ...
... Functions of Cerebrum • 3 basic functions: 1. Motor area – sends impulses to muscles 2. Sensory area – interpret impulses from sensory ...
Neurological Diseases ppt
... Seizure disorder of the brain, characterized by recurring and excessive discharge from neurons Seizures believed to be a result of spontaneous uncontrolled electrical activity of neurons Cause – Uncertain Diagnosed with EEG (electroencephalogram) ...
... Seizure disorder of the brain, characterized by recurring and excessive discharge from neurons Seizures believed to be a result of spontaneous uncontrolled electrical activity of neurons Cause – Uncertain Diagnosed with EEG (electroencephalogram) ...
IV. Conduction Across Synapses
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
The Nervous System - Watchung Hills Regional High School
... Damage to brain begins 10 to 20 years before any problems are ...
... Damage to brain begins 10 to 20 years before any problems are ...
Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
... • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excitatory potentials may be needed before a postsynaptic ...
... • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excitatory potentials may be needed before a postsynaptic ...
Module 4 revised
... isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them ...
... isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them ...
Clinical Day
... • Progressive neurodegenerative disease that attacks nerve cells in brain and spinal cord • As neurons die, body functions lost ...
... • Progressive neurodegenerative disease that attacks nerve cells in brain and spinal cord • As neurons die, body functions lost ...
Brain Anatomy
... Must be wary of using pictures of brain “hot spots” that locate complex functions in precise brain areas Parietal Lobes: enable mathematical & spatial reasoning Temporal Lobes: facial recognition ...
... Must be wary of using pictures of brain “hot spots” that locate complex functions in precise brain areas Parietal Lobes: enable mathematical & spatial reasoning Temporal Lobes: facial recognition ...
Overview
... the human is the most highly organized system of the body. The overall function of the nervous system is control and coordination of the human body. ...
... the human is the most highly organized system of the body. The overall function of the nervous system is control and coordination of the human body. ...
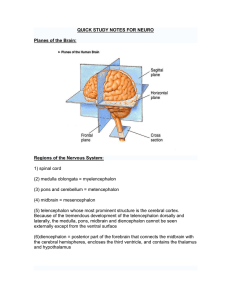
quick study notes for neuro
... - grey matter is so-called because in section it has a grey colour due to all the grey nuclei in the cells that make it up. In fact, in the living body, grey matter is pink. - neurons in the grey matter consist of neuronal cell bodies and their dendrites, the short protrusions that communicate with ...
... - grey matter is so-called because in section it has a grey colour due to all the grey nuclei in the cells that make it up. In fact, in the living body, grey matter is pink. - neurons in the grey matter consist of neuronal cell bodies and their dendrites, the short protrusions that communicate with ...
nervous_system_-_cns_and_pns_part_2_-_2015
... convoluted outer layer of gray matter covering both hemispheres. ...
... convoluted outer layer of gray matter covering both hemispheres. ...
Ch. 13 Central Nervous System
... Dopamine inhibits the excitatory effects of acetylcholine. In Parkinson disease, these neurons degenerate, so you don’t have the dopamine. The cerebral nuclei produce excess signals that affect the voluntary muscles. Overstimulation of the postural muscles of the neck, trunk, and upper limbs produce ...
... Dopamine inhibits the excitatory effects of acetylcholine. In Parkinson disease, these neurons degenerate, so you don’t have the dopamine. The cerebral nuclei produce excess signals that affect the voluntary muscles. Overstimulation of the postural muscles of the neck, trunk, and upper limbs produce ...
The Nervous System
... with fluid called the aqueous humor. At the back of this chamber is the iris, the color part of the eye with an opening called the pupil. ...
... with fluid called the aqueous humor. At the back of this chamber is the iris, the color part of the eye with an opening called the pupil. ...
Study Shows Practice May Have Potential to Change Brain`s
... Brain research is beginning to produce concrete evidence for something that Buddhist practitioners of meditation have maintained for centuries: Mental discipline and meditative practice can change the workings of the brain and allow people to achieve different levels of awareness. Those transformed ...
... Brain research is beginning to produce concrete evidence for something that Buddhist practitioners of meditation have maintained for centuries: Mental discipline and meditative practice can change the workings of the brain and allow people to achieve different levels of awareness. Those transformed ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Language – Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas – loss of language – aphasia ...
... Language – Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas – loss of language – aphasia ...
GEOTRAN - Life Solutions Institute
... In the human brain, there are more than several hundred million neurons. In these neurons ion currents flow. The ion currents produce the magnetic field. This magnetic field emerges out of the head through the brain, the scalp and the head. ...
... In the human brain, there are more than several hundred million neurons. In these neurons ion currents flow. The ion currents produce the magnetic field. This magnetic field emerges out of the head through the brain, the scalp and the head. ...