Language Processing in the Brain
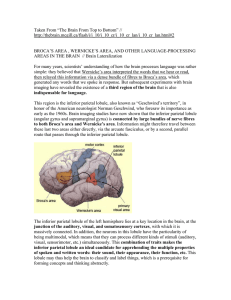
... Major lesions in the left parieto-occipital area can make someone unable to read and/or write while leaving their spoken-language abilities intact. In contrast, lesions in auditory associative areas such as Wernicke’s area will prevent someone both from understanding spoken language and from reading ...
... Major lesions in the left parieto-occipital area can make someone unable to read and/or write while leaving their spoken-language abilities intact. In contrast, lesions in auditory associative areas such as Wernicke’s area will prevent someone both from understanding spoken language and from reading ...
Growth and Development
... As they grow, neurons become arranged by function. Some move into the CEREBRAL CORTEX Others move to subcortical levels, which regulate fundamental activities such as breathing and heart rate (and are below the cerebral cortex). Networks of neurons become more complex over the first few years of lif ...
... As they grow, neurons become arranged by function. Some move into the CEREBRAL CORTEX Others move to subcortical levels, which regulate fundamental activities such as breathing and heart rate (and are below the cerebral cortex). Networks of neurons become more complex over the first few years of lif ...
Test.
... • Basic Assumption: Mind = Brain. • Brain consists of neurons transmitting information by electrical activity. ...
... • Basic Assumption: Mind = Brain. • Brain consists of neurons transmitting information by electrical activity. ...
Chapter 2, continued Basal ganglia Has three principal structures
... Principle 5: The brain is both symmetrical and asymmetrical - language and body control are asymmetrical so that they can be synchronized and unified Principle 6: Brain systems are organized both hierarchically and in parallel - If there were a system that went in a straight line, from one level to ...
... Principle 5: The brain is both symmetrical and asymmetrical - language and body control are asymmetrical so that they can be synchronized and unified Principle 6: Brain systems are organized both hierarchically and in parallel - If there were a system that went in a straight line, from one level to ...
(from quizzes) Bergen 14 Which of the following is true regarding a
... e. All of the above are correct statements. Which of the following is true? a. Effective connectivity refers to a reverse relationship between different brain regions and functional connectivity refers to a causal relationship b. Effective connectivity refers to a causal relationship between differe ...
... e. All of the above are correct statements. Which of the following is true? a. Effective connectivity refers to a reverse relationship between different brain regions and functional connectivity refers to a causal relationship b. Effective connectivity refers to a causal relationship between differe ...
Organization of the Nervous system. Physiology of neurons and glial
... 14,000 genes expressed in the developing/mature brain about 8,000 genes are expressed in all cells and tissues a great deal of “brain specific” genetic information resides in the regulatory DNA sequences that control timing, quantity, variability, and cellular specificity of gene expression indi ...
... 14,000 genes expressed in the developing/mature brain about 8,000 genes are expressed in all cells and tissues a great deal of “brain specific” genetic information resides in the regulatory DNA sequences that control timing, quantity, variability, and cellular specificity of gene expression indi ...
Differential Permeability of the Membrane
... called the presynaptic membrane. The presynaptic membrane is separated from the other neuron by what is called the synaptic cleft. ...
... called the presynaptic membrane. The presynaptic membrane is separated from the other neuron by what is called the synaptic cleft. ...
Physiology Ch 57 p697-709 [4-25
... resulting from capabilities of prefrontal cortex that allow it to plan motor activities c. Broca’s Area – provides neural circuitry for word formation; located in the posterior lateral prefrontal cortex, partly in premotor area; plans motor patterns for expressing individual words or phrases and wor ...
... resulting from capabilities of prefrontal cortex that allow it to plan motor activities c. Broca’s Area – provides neural circuitry for word formation; located in the posterior lateral prefrontal cortex, partly in premotor area; plans motor patterns for expressing individual words or phrases and wor ...
Module 3 - yhernandez
... affects the brain by imitating a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, GABA GABA neurons – GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA GABA ...
... affects the brain by imitating a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, GABA GABA neurons – GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA GABA ...
Midterm 1 - studyfruit
... ■ Nissl stain: German neurologist found that a class of basic dyes would stain the nuclei of neurons and clumps surrounding the nuclei (called nissl bodies). The stain distinguishes neurons and glia from one another and lets histologists (histology = microscopic study of tissue) look at the cytoarch ...
... ■ Nissl stain: German neurologist found that a class of basic dyes would stain the nuclei of neurons and clumps surrounding the nuclei (called nissl bodies). The stain distinguishes neurons and glia from one another and lets histologists (histology = microscopic study of tissue) look at the cytoarch ...
Presentation handouts
... are discarded. Many refer to this as the “use it or lose it” process. Signals are strengthened with experience. As these connections become established through experience, they eventually become exempt from elimination. ...
... are discarded. Many refer to this as the “use it or lose it” process. Signals are strengthened with experience. As these connections become established through experience, they eventually become exempt from elimination. ...
2013 Anatomy -Training Handout
... receptors – most of the time of our environment is colder than our body temperature The highest concentration of thermoreceptors can be found in the face and ears so your nose and ears always get colder faster than the rest of your body on a chilly winter day ...
... receptors – most of the time of our environment is colder than our body temperature The highest concentration of thermoreceptors can be found in the face and ears so your nose and ears always get colder faster than the rest of your body on a chilly winter day ...
Ren - University of Illinois Archives
... R.-S. Chen, S. Hong, and Y. Li. Neuroscience Program, Beckman Institute, Dept. of Molecular & Integrative Physiology, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL 61801. Studies using cortical and hippocampal brain slices suggest that many young central synapses initially contain only NMDA rece ...
... R.-S. Chen, S. Hong, and Y. Li. Neuroscience Program, Beckman Institute, Dept. of Molecular & Integrative Physiology, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL 61801. Studies using cortical and hippocampal brain slices suggest that many young central synapses initially contain only NMDA rece ...
Structure of the Brain PowerPoint Notes
... – the inside becomes positive & the outside becomes negative NEUROTRANSMITTER – dozens of different chemicals that are made by neurons and then used for communication between neurons during the performance of mental or physical activities • _________________transmitters – ______________ receptor loc ...
... – the inside becomes positive & the outside becomes negative NEUROTRANSMITTER – dozens of different chemicals that are made by neurons and then used for communication between neurons during the performance of mental or physical activities • _________________transmitters – ______________ receptor loc ...
Nervous System - science
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
Nervous System
... In the back of the nose, there is a patch of tissue where hairlike fibers covered in mucus, Molecules enters your nose, stick to the mucus, and bind to the receptors in the hairlike fibers The receptors sends an impulse to your brain, and you perceive the scent. ...
... In the back of the nose, there is a patch of tissue where hairlike fibers covered in mucus, Molecules enters your nose, stick to the mucus, and bind to the receptors in the hairlike fibers The receptors sends an impulse to your brain, and you perceive the scent. ...
210_Lecture6_motor
... Treatments include medications that suppress the immune system or inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
... Treatments include medications that suppress the immune system or inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
Psychopharmacology
... the BFCS neurons take in this substance. • Those neurons are selectively destroyed • Affects learning and memory – i.e., Berger-Sweeney et al. (1994) ...
... the BFCS neurons take in this substance. • Those neurons are selectively destroyed • Affects learning and memory – i.e., Berger-Sweeney et al. (1994) ...
…By the way, where is the fornix???
... Tip to find the amygdala: Look rostral to the hippocampus! ...
... Tip to find the amygdala: Look rostral to the hippocampus! ...
the Unit 2 study guide in RTF format (which you may re
... 5. Describe the function of the primary sensory cortex. What lobe is it in? 6. Where are the parietal lobes located? Learning Objective 6 (pp.99-101): Temporal — Occipital Lobes ...
... 5. Describe the function of the primary sensory cortex. What lobe is it in? 6. Where are the parietal lobes located? Learning Objective 6 (pp.99-101): Temporal — Occipital Lobes ...
learning objectives chapter 2
... 12. Describe the spinal cord and its functions. Define reflex. (see “The Spinal Cord”) 13. Describe the techniques that scientists use to study the brain. (see “The Brain”) 14. Discuss what fMRI research has revealed about behavior and mental processes. (see “Thinking Critically: What Can fMRI Tell ...
... 12. Describe the spinal cord and its functions. Define reflex. (see “The Spinal Cord”) 13. Describe the techniques that scientists use to study the brain. (see “The Brain”) 14. Discuss what fMRI research has revealed about behavior and mental processes. (see “Thinking Critically: What Can fMRI Tell ...
the Unit 2 study guide in PDF format.
... 5. Describe the function of the primary sensory cortex. What lobe is it in? 6. Where are the parietal lobes located? Learning Objective 6 (pp.99-101): Temporal — Occipital Lobes ...
... 5. Describe the function of the primary sensory cortex. What lobe is it in? 6. Where are the parietal lobes located? Learning Objective 6 (pp.99-101): Temporal — Occipital Lobes ...
中樞神經系統
... neurons referred to as sensory pathways. Each side of the brain registers sensations from the opposite side of the body. General sensations of the right side of the body are predominantly experienced by the left somatic sensory area. General sensations of the left side of the body are predomin ...
... neurons referred to as sensory pathways. Each side of the brain registers sensations from the opposite side of the body. General sensations of the right side of the body are predominantly experienced by the left somatic sensory area. General sensations of the left side of the body are predomin ...
BIO 141 Unit 5 Learning Objectives
... a. sulcus (central sulcus, lateral sulcus, and parieto-‐occipital sulcus). ...
... a. sulcus (central sulcus, lateral sulcus, and parieto-‐occipital sulcus). ...























