lecture 02
... dark areas in figure are primary projection areas. These areas receive input from the sensory systems or project to the spinal motor systems lightly shaded areas receive projections (input) from the primary projection areas and are called secondary projection areas unshaded areas are called highe ...
... dark areas in figure are primary projection areas. These areas receive input from the sensory systems or project to the spinal motor systems lightly shaded areas receive projections (input) from the primary projection areas and are called secondary projection areas unshaded areas are called highe ...
B. ____are thought to provide structural support within the nervous
... A.___the most commonly abused and most potent hallucinogen B. Dimethyl mercury is a ____ that clings to brain neurons C.___the chronic self-administration of a drug in doses high enough to cause addiction D.___most commonly abused drugs E.___prolonged and repeated abuse of a drug may result in this ...
... A.___the most commonly abused and most potent hallucinogen B. Dimethyl mercury is a ____ that clings to brain neurons C.___the chronic self-administration of a drug in doses high enough to cause addiction D.___most commonly abused drugs E.___prolonged and repeated abuse of a drug may result in this ...
General principle of nervous system
... – Signals received by synapses • Located in neural dentrites and cell bodies • Few hundreds to 200,000 synaptic connection ...
... – Signals received by synapses • Located in neural dentrites and cell bodies • Few hundreds to 200,000 synaptic connection ...
Ions in Your Life
... excitation occurs and neurotransmitter stops being produced by the body itself. Neurotransmitters are blocked from going through reuptake transporters by original neuron. Extra excitation occurs and body stops producing neurotransmitter. ...
... excitation occurs and neurotransmitter stops being produced by the body itself. Neurotransmitters are blocked from going through reuptake transporters by original neuron. Extra excitation occurs and body stops producing neurotransmitter. ...
PsychSim 5: PSYCHOLOGY`S TIMELINE
... front of him and the results of his neural activity are graphed. What does the graph tell you about the activity of this neuron while Rizzo performed the action of grasping a wooden block? Does it appear that this neuron is “tuned” to respond to this particular action? ...
... front of him and the results of his neural activity are graphed. What does the graph tell you about the activity of this neuron while Rizzo performed the action of grasping a wooden block? Does it appear that this neuron is “tuned” to respond to this particular action? ...
Nervous System
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
CE7427: Cognitive Neuroscience and Embedded Intelligence
... Things are the way they are because they have evolved that way. Why are stripes useful? For many reasons: • Diseases transmitted by tsetse flies kill over 250,000 people per year. Stripes confuse compound eyes of flies from a distance. Ruxton, G.D. 2002. The possible fitness benefits of striped coat ...
... Things are the way they are because they have evolved that way. Why are stripes useful? For many reasons: • Diseases transmitted by tsetse flies kill over 250,000 people per year. Stripes confuse compound eyes of flies from a distance. Ruxton, G.D. 2002. The possible fitness benefits of striped coat ...
Ch 28 CNS Money [5-11
... - acute neuronal injury (“red neurons”) = acute CNS hypoxia/ischemia - subacute & chronic neuronal injury (“degeneration”) from progressive dz process; seen in ALS - axonal rxn is regen. of the axon; best seen in anterior horn cells of spinal cord when motor axons are damaged - neuronal inclusions o ...
... - acute neuronal injury (“red neurons”) = acute CNS hypoxia/ischemia - subacute & chronic neuronal injury (“degeneration”) from progressive dz process; seen in ALS - axonal rxn is regen. of the axon; best seen in anterior horn cells of spinal cord when motor axons are damaged - neuronal inclusions o ...
Fried et al, 2001 - EMGO Institute for Health and Care Research
... • Increase in chronic stress syndrome • Sizeable prevalence of dementia (about 50% in 90-yearolds) • High levels of frailty, dysfunctionality and multimorbidity • Dying at older ages: with human dignity? • prospects for the 21st century: the era of chronic incompleteness of mind and body? ...
... • Increase in chronic stress syndrome • Sizeable prevalence of dementia (about 50% in 90-yearolds) • High levels of frailty, dysfunctionality and multimorbidity • Dying at older ages: with human dignity? • prospects for the 21st century: the era of chronic incompleteness of mind and body? ...
What drives the plasticity of brain tissues?
... day, exercising but with very little opportunity for learning. Voluntary eXercise ...
... day, exercising but with very little opportunity for learning. Voluntary eXercise ...
Development of the Brain
... • Rats raised in an enriched environment develop a thicker cortex and increased dendritic branching. • Measurable expansion of neurons has also been shown in humans as a function of physical activity. • The thickness of the cerebral cortex declines in old age but much less in those that are physical ...
... • Rats raised in an enriched environment develop a thicker cortex and increased dendritic branching. • Measurable expansion of neurons has also been shown in humans as a function of physical activity. • The thickness of the cerebral cortex declines in old age but much less in those that are physical ...
LESSON 1.2 WORKBOOK How does brain structure impact its function?
... _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ ____________________________ ...
... _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ ____________________________ ...
Nervous System Educator`s Guide
... are cells that form the functional basis of the nervous system. Structurally, they are different in significant ways from any of the body’s other cells. However, at their core there like every other cell in the body, they contain cytoplasm and a nucleus with chromosomes. But what differentiates the ...
... are cells that form the functional basis of the nervous system. Structurally, they are different in significant ways from any of the body’s other cells. However, at their core there like every other cell in the body, they contain cytoplasm and a nucleus with chromosomes. But what differentiates the ...
nerve impulse
... brain or a vessel is obstructed by a clot. Brain tissue supplied with oxygen from that blood source dies, swelling occurs in the brain due to leaking of blood from vessels. Loss of some functions or death may result This is due often to elevated blood pressure or hypertension. ...
... brain or a vessel is obstructed by a clot. Brain tissue supplied with oxygen from that blood source dies, swelling occurs in the brain due to leaking of blood from vessels. Loss of some functions or death may result This is due often to elevated blood pressure or hypertension. ...
[j26]Chapter 8#
... ___ 29. The parietal lobe is the primary area for vision and for the coordination of eye movements. ___ 30. That portion of the cerebrum most implicated in memory encoding and in pain sensation (visceral) and in coordinating the cardiovascular responses to stress, is the temporal lobe. ___ 31. The u ...
... ___ 29. The parietal lobe is the primary area for vision and for the coordination of eye movements. ___ 30. That portion of the cerebrum most implicated in memory encoding and in pain sensation (visceral) and in coordinating the cardiovascular responses to stress, is the temporal lobe. ___ 31. The u ...
[j26]Chapter 8#
... ___ 29. The parietal lobe is the primary area for vision and for the coordination of eye movements. ___ 30. That portion of the cerebrum most implicated in memory encoding and in pain sensation (visceral) and in coordinating the cardiovascular responses to stress, is the temporal lobe. ___ 31. The u ...
... ___ 29. The parietal lobe is the primary area for vision and for the coordination of eye movements. ___ 30. That portion of the cerebrum most implicated in memory encoding and in pain sensation (visceral) and in coordinating the cardiovascular responses to stress, is the temporal lobe. ___ 31. The u ...
Comparative approaches to cortical microcircuits
... operate according to similar principles. These examples confirm the essential value of a comparative approach, based on computation, as beautifully illustrated in the classical comparison of sound localization circuits in the barn owl and jamming-avoidance circuits in the electric fish Eigenmannia [ ...
... operate according to similar principles. These examples confirm the essential value of a comparative approach, based on computation, as beautifully illustrated in the classical comparison of sound localization circuits in the barn owl and jamming-avoidance circuits in the electric fish Eigenmannia [ ...
Dorsolateral Prefrontal Association Cortex
... ◦ Dorsolateral prefrontal association cortex Each composed of several different areas with different functions ...
... ◦ Dorsolateral prefrontal association cortex Each composed of several different areas with different functions ...
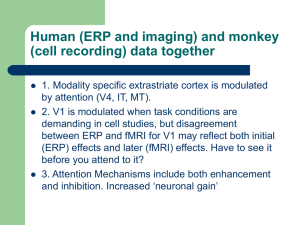
Chapter 7 part two
... between ERP and fMRI for V1 may reflect both initial (ERP) effects and later (fMRI) effects. Have to see it before you attend to it? 3. Attention Mechanisms include both enhancement and inhibition. Increased ‘neuronal gain’ ...
... between ERP and fMRI for V1 may reflect both initial (ERP) effects and later (fMRI) effects. Have to see it before you attend to it? 3. Attention Mechanisms include both enhancement and inhibition. Increased ‘neuronal gain’ ...
Lecture 7 Powerpoint file
... • It is also possible to record from outside the skull altogether! ...
... • It is also possible to record from outside the skull altogether! ...
File
... There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves…… If you can memorize all 31 in 2 minutes, then you get an ec slip….BUT If you don’t get them all, then you have to lose 5 participation points from your grade. ...
... There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves…… If you can memorize all 31 in 2 minutes, then you get an ec slip….BUT If you don’t get them all, then you have to lose 5 participation points from your grade. ...
Slow Virus Infection
... long as 30 years. Once symptoms become evident the patient dies within a year. • TCAs are a group of rare, usually sporadic, rapidly fatal, presenile dementias found worldwide. • They were first defined as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease named after the German neurologists, who each described a few cases. ...
... long as 30 years. Once symptoms become evident the patient dies within a year. • TCAs are a group of rare, usually sporadic, rapidly fatal, presenile dementias found worldwide. • They were first defined as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease named after the German neurologists, who each described a few cases. ...
Brainstem 10
... The brain stem is connected with cerebellum through three pair of cerebellar peduncles. The brain stem is the site of cranial nuclei, the pathway of important ascending & descending tracts & the site of emergence of cranial nerves (from 3rd to 12th). Cranial nerves (with the exception of 4th) eme ...
... The brain stem is connected with cerebellum through three pair of cerebellar peduncles. The brain stem is the site of cranial nuclei, the pathway of important ascending & descending tracts & the site of emergence of cranial nerves (from 3rd to 12th). Cranial nerves (with the exception of 4th) eme ...
The Nervous System - Catherine Huff`s Site
... • Between the adjacent glial cells there are small gaps in meylin sheath called Nodes of Ranvier. • Gaps help to increase speed of impulse along the axons. ...
... • Between the adjacent glial cells there are small gaps in meylin sheath called Nodes of Ranvier. • Gaps help to increase speed of impulse along the axons. ...













![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015149816_1-9d495749ad340ee903e25aea78e4f4ae-300x300.png)
![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010706021_1-9baf14474201fd4015c7c6d48d77223e-300x300.png)