slides - DTU CBS
... • Immoral to patent life – why? – living creatures (animals, plants, microorganisms) have been regarded as goods for centuries • Patenting genes is contrary to development – mere allegation, do not confuse patent applications with valid patents ...
... • Immoral to patent life – why? – living creatures (animals, plants, microorganisms) have been regarded as goods for centuries • Patenting genes is contrary to development – mere allegation, do not confuse patent applications with valid patents ...
广西医科大学理论课教案(1)
... 2.To be familiar with the activation energy and free energy change in a reaction system, and why enzymes can increase the rate of reaction catalyzed by enzyme, active site of enzymes, substrate specificity of enzyme as well as enzyme classification 3.To have an appreciation of the chemical equilibri ...
... 2.To be familiar with the activation energy and free energy change in a reaction system, and why enzymes can increase the rate of reaction catalyzed by enzyme, active site of enzymes, substrate specificity of enzyme as well as enzyme classification 3.To have an appreciation of the chemical equilibri ...
CHAPTER 4 ISOLATION, CHARACTERIZATION AND EXPRESSION OF GA20ox
... Among the genes of GA-biosynthesis, GA 20-oxidase is shown to be an important regulator in the pathway. It catalyses several late steps converting GA12 and GA53 in parallel pathways to respective products GA9 and GA12 which then are converted to bioactive forms, GA4 and GA1 by GA 3β-hydroxylase (see ...
... Among the genes of GA-biosynthesis, GA 20-oxidase is shown to be an important regulator in the pathway. It catalyses several late steps converting GA12 and GA53 in parallel pathways to respective products GA9 and GA12 which then are converted to bioactive forms, GA4 and GA1 by GA 3β-hydroxylase (see ...
Annual Plant Reviews Volume 35 : Plant systems Biology
... having a complete description of the molecular components of biological systems and the ways they interact. In the particular case of Arabidopsis, advances in plant systems biology studies lag behind other model organism in terms of the data sets available (e.g. interactomes). However, this lack of ...
... having a complete description of the molecular components of biological systems and the ways they interact. In the particular case of Arabidopsis, advances in plant systems biology studies lag behind other model organism in terms of the data sets available (e.g. interactomes). However, this lack of ...
Identification of proteins that putatively bind the
... based on turgor pressure-induced changes in their shape. Stomatal aperture and density are affected by environmental stimuli such as light quality and quantity, CO2 concentrations, and water availability. The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor MUTE drives the differentiation of trans ...
... based on turgor pressure-induced changes in their shape. Stomatal aperture and density are affected by environmental stimuli such as light quality and quantity, CO2 concentrations, and water availability. The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor MUTE drives the differentiation of trans ...
Cold-Shock Response in Microorganisms
... stable or changing) that microorganisms colonize, it would be anticipated that a variety of mechanisms would be discovered that reflect different evolutionary processes to cope with cold shock. At present, the field is still in its infancy (particularly in comparison to studies on heat shock), altho ...
... stable or changing) that microorganisms colonize, it would be anticipated that a variety of mechanisms would be discovered that reflect different evolutionary processes to cope with cold shock. At present, the field is still in its infancy (particularly in comparison to studies on heat shock), altho ...
Model key paper ppt presentation
... • Involved in melanin pigment synthesis - Characteristic of melanocytes ...
... • Involved in melanin pigment synthesis - Characteristic of melanocytes ...
Classification and substrate head-group specificity of membrane
... are particularly important for cellular signalling [29]. This classification was based on a previous limited phylogenetic analysis of eukaryotic membrane-bound desaturases [25]. For a very diverse protein family, such as the membrane FADs, constructing a high-quality multiple sequence alignment can b ...
... are particularly important for cellular signalling [29]. This classification was based on a previous limited phylogenetic analysis of eukaryotic membrane-bound desaturases [25]. For a very diverse protein family, such as the membrane FADs, constructing a high-quality multiple sequence alignment can b ...
Transcriptomic Footprints Disclose Specificity of Reactive Oxygen
... Because ROS are constantly produced during normal cell metabolism, it is important that their basal levels are tightly controlled. This control is provided by a complex gene network that acts in all subcellular compartments and through elaborate feed-forward/feedback loops between oxidants and antio ...
... Because ROS are constantly produced during normal cell metabolism, it is important that their basal levels are tightly controlled. This control is provided by a complex gene network that acts in all subcellular compartments and through elaborate feed-forward/feedback loops between oxidants and antio ...
GRE BIOCHEMISTRY TEST PRACTICE BOOK
... or weaknesses in the three subfield areas of the GRE Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology Test. The raw subscores are scaled in such a way that they are related to the total scores on the test. On the average, a person who has a comprehensive background in the field can expect to have subscores ...
... or weaknesses in the three subfield areas of the GRE Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology Test. The raw subscores are scaled in such a way that they are related to the total scores on the test. On the average, a person who has a comprehensive background in the field can expect to have subscores ...
What the Nucellus Can Tell Us
... agl62/agl62 homozygotes, which are embryolethal, do not undergo nucellus degeneration, demonstrating a crucial role of AGL62 in signaling nucellus degeneration (see figure, bottom right). To characterize the regulatory network downstream of the polycomb proteins, the authors conducted a comprehensiv ...
... agl62/agl62 homozygotes, which are embryolethal, do not undergo nucellus degeneration, demonstrating a crucial role of AGL62 in signaling nucellus degeneration (see figure, bottom right). To characterize the regulatory network downstream of the polycomb proteins, the authors conducted a comprehensiv ...
The Cytoskeleton
... GTPase: Molecule switch; Family of enzymes that are activated by GTP binding and inactivated by GTP hydrolysis and phosphate ...
... GTPase: Molecule switch; Family of enzymes that are activated by GTP binding and inactivated by GTP hydrolysis and phosphate ...
Applied and Environmental Microbiologyy
... For flow-chamber experiments, the strains were tagged with the green fluorescent protein (GFP). This was accomplished by the insertion of a miniTn7PA1/04/03-gfp-T0T1 transposon cassette into the chromosomes of target strains using the suicide construct pBK-miniTn7-gfp3 (25). Plasmid pBK-miniTn7-gfp3 ...
... For flow-chamber experiments, the strains were tagged with the green fluorescent protein (GFP). This was accomplished by the insertion of a miniTn7PA1/04/03-gfp-T0T1 transposon cassette into the chromosomes of target strains using the suicide construct pBK-miniTn7-gfp3 (25). Plasmid pBK-miniTn7-gfp3 ...
enzymology
... ‘substrate-product-substrate’ through enzyme catalyzed sequence of reactions are called ‘metabolic pathways’. The sequence of reactions in glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle, pathway of fatty acid catabolism and reactions of nucleotide biosynthesis, etc. are a few examples of ‘metabolic pathway’. ...
... ‘substrate-product-substrate’ through enzyme catalyzed sequence of reactions are called ‘metabolic pathways’. The sequence of reactions in glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle, pathway of fatty acid catabolism and reactions of nucleotide biosynthesis, etc. are a few examples of ‘metabolic pathway’. ...
A phage library and two cosmid libraries were
... Two cosmid libraries were prepared according to different experimental protocols (Materials and Methods). For the construction of both libraries (I and II) Mspl partial digests of the same human placenta DNA were used. The insert of the M13 subclone 1-1 was used to screen both cosmid libraries. A to ...
... Two cosmid libraries were prepared according to different experimental protocols (Materials and Methods). For the construction of both libraries (I and II) Mspl partial digests of the same human placenta DNA were used. The insert of the M13 subclone 1-1 was used to screen both cosmid libraries. A to ...
Original Article Detection of Mycoplasma
... The mycoplasma detection was carried in the pres ence of appropriate controls to eliminate the possibility of false-negative and false-positive results. Internal con trol consisted of PCR-amplified product of A. laidlawii cloned into pGEM-T vector and amplified in E. coli (Uphoff and Drexler, 2002 ...
... The mycoplasma detection was carried in the pres ence of appropriate controls to eliminate the possibility of false-negative and false-positive results. Internal con trol consisted of PCR-amplified product of A. laidlawii cloned into pGEM-T vector and amplified in E. coli (Uphoff and Drexler, 2002 ...
NON-CANONICAL TRANSCRIPTION INITIATION: THE EXPANDING
... how these coenzymes are incorporated into RNA by RNA polymerase (RNAP), and what their biological function(s) might be in these molecules. Of these coenzymes, the main focus is on NAD as it is presently the best studied representative of the 5’ end modifications. This is set into the context of the ...
... how these coenzymes are incorporated into RNA by RNA polymerase (RNAP), and what their biological function(s) might be in these molecules. Of these coenzymes, the main focus is on NAD as it is presently the best studied representative of the 5’ end modifications. This is set into the context of the ...
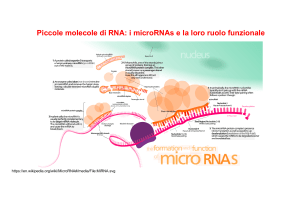
Types of RNA
... recognition that binds to a specific sequence on the messenger RNA chain through hydrogen bonding. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the catalytic component of the ribosomes. Eukaryotic ribosomes contain four different rRNA molecules: 18S, 5.8S, 28S and 5S rRNA. Three of the rRNA molecules are synthesized in ...
... recognition that binds to a specific sequence on the messenger RNA chain through hydrogen bonding. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the catalytic component of the ribosomes. Eukaryotic ribosomes contain four different rRNA molecules: 18S, 5.8S, 28S and 5S rRNA. Three of the rRNA molecules are synthesized in ...
Airgas template
... • An organism’s phenotype refers to its physical traits (e.g., includes hair and eye color in humans). • An organism’s phenotype is the manifestation of that organism’s genotype because genes control all functions of the cell. • Gene: a particular segment of the chromosome. Copyright © 2011 Wolters ...
... • An organism’s phenotype refers to its physical traits (e.g., includes hair and eye color in humans). • An organism’s phenotype is the manifestation of that organism’s genotype because genes control all functions of the cell. • Gene: a particular segment of the chromosome. Copyright © 2011 Wolters ...
Genome-wide transcription profiling of aerobic and anaerobic
... <2.5-fold change ratios were significantly altered (q < 0.01). Each data points correspond to b-numbers and plotted in chronological order. Genes displaying >10-fold or <10-fold change are at the outer limits that enable the data to be viewed at a reasonable scale. ...
... <2.5-fold change ratios were significantly altered (q < 0.01). Each data points correspond to b-numbers and plotted in chronological order. Genes displaying >10-fold or <10-fold change are at the outer limits that enable the data to be viewed at a reasonable scale. ...
Transcription | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... "downstream." Unlike DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase does not need a primer to start transcription. The stretch of DNA that is transcribed into RNA is known as the transcription unit. Transcription has three distinct phases: initiation, elongation and termination. During initiation, with the help of ...
... "downstream." Unlike DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase does not need a primer to start transcription. The stretch of DNA that is transcribed into RNA is known as the transcription unit. Transcription has three distinct phases: initiation, elongation and termination. During initiation, with the help of ...
Tilting Plant Metabolism for Improved Metabolite Biosynthesis and
... expression networks at the interface of the two metabolisms [12–15]. Accumulating evidence suggests that many transcriptional factors (TFs) coordinate the transcriptional activation of secondary metabolism genes concurrently with the expression of genes in upstream pathways of primary metabolism [12 ...
... expression networks at the interface of the two metabolisms [12–15]. Accumulating evidence suggests that many transcriptional factors (TFs) coordinate the transcriptional activation of secondary metabolism genes concurrently with the expression of genes in upstream pathways of primary metabolism [12 ...
Assessing Reliability of Protein-Protein Interaction Experiments
... • “ipr” correlates well to common cellular roles, localization, & expression • “ipr” seems to work better than “ig2” ...
... • “ipr” correlates well to common cellular roles, localization, & expression • “ipr” seems to work better than “ig2” ...
Metabolism and Glycolysis
... Glycolysis is an universal metabolic pathway. It occurs, with minor variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient known metabolic pathways. In 1860 Louis Pasteur discovered that microorganisms are resp ...
... Glycolysis is an universal metabolic pathway. It occurs, with minor variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient known metabolic pathways. In 1860 Louis Pasteur discovered that microorganisms are resp ...
Gene regulatory network

A gene regulatory network or genetic regulatory network (GRN) is a collection of regulators thatinteract with each other and with other substances in the cell to govern the gene expression levels of mRNA and proteins.The regulator can be DNA, RNA, protein and their complex. The interaction can be direct or indirect (through their transcribed RNA or translated protein).In general, each mRNA molecule goes on to make a specific protein (or set of proteins). In some cases this protein will be structural, and will accumulate at the cell membrane or within the cell to give it particular structural properties. In other cases the protein will be an enzyme, i.e., a micro-machine that catalyses a certain reaction, such as the breakdown of a food source or toxin. Some proteins though serve only to activate other genes, and these are the transcription factors that are the main players in regulatory networks or cascades. By binding to the promoter region at the start of other genes they turn them on, initiating the production of another protein, and so on. Some transcription factors are inhibitory.In single-celled organisms, regulatory networks respond to the external environment, optimising the cell at a given time for survival in this environment. Thus a yeast cell, finding itself in a sugar solution, will turn on genes to make enzymes that process the sugar to alcohol. This process, which we associate with wine-making, is how the yeast cell makes its living, gaining energy to multiply, which under normal circumstances would enhance its survival prospects.In multicellular animals the same principle has been put in the service of gene cascades that control body-shape. Each time a cell divides, two cells result which, although they contain the same genome in full, can differ in which genes are turned on and making proteins. Sometimes a 'self-sustaining feedback loop' ensures that a cell maintains its identity and passes it on. Less understood is the mechanism of epigenetics by which chromatin modification may provide cellular memory by blocking or allowing transcription. A major feature of multicellular animals is the use of morphogen gradients, which in effect provide a positioning system that tells a cell where in the body it is, and hence what sort of cell to become. A gene that is turned on in one cell may make a product that leaves the cell and diffuses through adjacent cells, entering them and turning on genes only when it is present above a certain threshold level. These cells are thus induced into a new fate, and may even generate other morphogens that signal back to the original cell. Over longer distances morphogens may use the active process of signal transduction. Such signalling controls embryogenesis, the building of a body plan from scratch through a series of sequential steps. They also control and maintain adult bodies through feedback processes, and the loss of such feedback because of a mutation can be responsible for the cell proliferation that is seen in cancer. In parallel with this process of building structure, the gene cascade turns on genes that make structural proteins that give each cell the physical properties it needs.It has been suggested that, because biological molecular interactions are intrinsically stochastic, gene networks are the result of cellular processes and not their cause (i.e. cellular Darwinism). However, recent experimental evidence has favored the attractor view of cell fates.