Biology 0200
... • a Repressor for the operon is coded for by the trpR gene, found elsewhere in the genome. • tryptophan itself serves as a co-repressor for the operon • The five gene products of the operon (the proteins coded for by tryp E, tryp D, etc...) are enzymes in a pathway that converts chorismic acid to tr ...
... • a Repressor for the operon is coded for by the trpR gene, found elsewhere in the genome. • tryptophan itself serves as a co-repressor for the operon • The five gene products of the operon (the proteins coded for by tryp E, tryp D, etc...) are enzymes in a pathway that converts chorismic acid to tr ...
File
... DNA is transcribed and mRNA is translated; transcription produces RNA and translation produces polypeptides / protein; RNA polymerase for transcription and ribosomes for translation / ribosomes in translation only; transcription in the nucleus (of eukaryotes) and translation in the cytoplasm / at ER ...
... DNA is transcribed and mRNA is translated; transcription produces RNA and translation produces polypeptides / protein; RNA polymerase for transcription and ribosomes for translation / ribosomes in translation only; transcription in the nucleus (of eukaryotes) and translation in the cytoplasm / at ER ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 6. Acclimatization is induced by adding growth hormones. 7. Cybrids are produced by protoplast fusion. 8. nod gene is responsible for nitrogen fixation. 9. Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer is brought about by Ag plasmid. 10. Blue green algae is used as biofertilizer to fix atmospheric nitrogen. ...
... 6. Acclimatization is induced by adding growth hormones. 7. Cybrids are produced by protoplast fusion. 8. nod gene is responsible for nitrogen fixation. 9. Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer is brought about by Ag plasmid. 10. Blue green algae is used as biofertilizer to fix atmospheric nitrogen. ...
The Cell
... • The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. – The cells structural anatomy will determine its overall function. • All cells contains organelles which are the equivalent to organs of an organism. – They provide a specific function within the cell. • produces different types of pro ...
... • The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. – The cells structural anatomy will determine its overall function. • All cells contains organelles which are the equivalent to organs of an organism. – They provide a specific function within the cell. • produces different types of pro ...
Word version - Birkbeck, University of London
... cannot be grown or deliver the gene of interest. Two basic methods are available for this. In the first method, the HSV is inactivated by removing a gene encoding a protein which is essential for it to replicate in all cell types. Although this will prevent the virus having damaging effects when inf ...
... cannot be grown or deliver the gene of interest. Two basic methods are available for this. In the first method, the HSV is inactivated by removing a gene encoding a protein which is essential for it to replicate in all cell types. Although this will prevent the virus having damaging effects when inf ...
PPT - gserianne.com
... • heat, light, sound, electricity, mechanical energy, chemical energy • changed from one form to another, but NEVER destroyed (law of conservation of energy) • involved in all metabolic reactions Release of chemical energy • most metabolic processes depend on chemical energy • oxidation of glucose g ...
... • heat, light, sound, electricity, mechanical energy, chemical energy • changed from one form to another, but NEVER destroyed (law of conservation of energy) • involved in all metabolic reactions Release of chemical energy • most metabolic processes depend on chemical energy • oxidation of glucose g ...
Todd Eckdahl - Davidson College
... Minor Groove Binding Drugs Anti-tumor properties Conformational change in the 3D structure of DNA Prior Knowledge of MGBD/DNA interaction As models for minor groove binding proteins ...
... Minor Groove Binding Drugs Anti-tumor properties Conformational change in the 3D structure of DNA Prior Knowledge of MGBD/DNA interaction As models for minor groove binding proteins ...
Document
... Old gene copy can serve original function. New gene copy can serve similar but novel function (neofunctionalization). Following duplication mutation/genetic drift cause sequences to diverge. Gene conversion between paralogous genes can maintain similarity of structure and function over evolutionary ...
... Old gene copy can serve original function. New gene copy can serve similar but novel function (neofunctionalization). Following duplication mutation/genetic drift cause sequences to diverge. Gene conversion between paralogous genes can maintain similarity of structure and function over evolutionary ...
General Biochemistry Exam – 2002 Excess Acetyl
... b. The amino acid T has a higher affinity for substrate as opposed to S or V c. The protein will change is spatial structure due to the replacement with V d. All the above are likely ...
... b. The amino acid T has a higher affinity for substrate as opposed to S or V c. The protein will change is spatial structure due to the replacement with V d. All the above are likely ...
HUWEL LIFESCIENCES PVT. LTD. BETA THALESSEMIA Disease
... Transport: To be transported at 4 degrees Methodology: Genomic DNA was isolated from Buffy coat cells of EDTA-Blood samples. PCR amplification was carried out using specific primers designed for Beta globin gene. The resultant product was gel eluted and sequenced. Limitations: Rare diagnostic errors ...
... Transport: To be transported at 4 degrees Methodology: Genomic DNA was isolated from Buffy coat cells of EDTA-Blood samples. PCR amplification was carried out using specific primers designed for Beta globin gene. The resultant product was gel eluted and sequenced. Limitations: Rare diagnostic errors ...
Chapter 17 Presentation
... saved because they have important functions such as ribosome binding. ...
... saved because they have important functions such as ribosome binding. ...
TOPIC 4.4 Genetic Engineering Worksheet
... 7. Use the gel electrophoresis results below to answer the following questions: In this case, a DNA sample was taken from a cigarette at a crime scene (in a no ...
... 7. Use the gel electrophoresis results below to answer the following questions: In this case, a DNA sample was taken from a cigarette at a crime scene (in a no ...
Bacteria - Rochester Community Schools
... • Immunoevasion, evasion of the host's immune response • Immunosuppression, inhibition of the host's immune response ...
... • Immunoevasion, evasion of the host's immune response • Immunosuppression, inhibition of the host's immune response ...
S1 Text.
... Table S6), this phosphatase might play a general role in signaling associated with the loss of FAX1 function. Interestingly only one gene, KCS16, functioning in fatty acid elongation and wax biosynthesis, was reciprocally regulated in the overlap with ARALIP, i.e. down in FAX1 over-expressors, but u ...
... Table S6), this phosphatase might play a general role in signaling associated with the loss of FAX1 function. Interestingly only one gene, KCS16, functioning in fatty acid elongation and wax biosynthesis, was reciprocally regulated in the overlap with ARALIP, i.e. down in FAX1 over-expressors, but u ...
2014 lecture 5
... • Cloned animals often have serious health problems with fetal overgrowth being commonplace – attributable to misexpression of important genes • Analysis of cloned mice indicate up to 4% of genes misexpressed • In cloned mouse blastocysts activation of pluripotency genes is often incomplete and high ...
... • Cloned animals often have serious health problems with fetal overgrowth being commonplace – attributable to misexpression of important genes • Analysis of cloned mice indicate up to 4% of genes misexpressed • In cloned mouse blastocysts activation of pluripotency genes is often incomplete and high ...
2014 lecture 5
... • Cloned animals often have serious health problems with fetal overgrowth being commonplace – attributable to misexpression of important genes • Analysis of cloned mice indicate up to 4% of genes misexpressed • In cloned mouse blastocysts activation of pluripotency genes is often incomplete and high ...
... • Cloned animals often have serious health problems with fetal overgrowth being commonplace – attributable to misexpression of important genes • Analysis of cloned mice indicate up to 4% of genes misexpressed • In cloned mouse blastocysts activation of pluripotency genes is often incomplete and high ...
Protein RNA DNA - Molecular Systems Biology
... A| Proteomics and transcriptomics data can be used for generating and improving contextspecific biological networks including protein– protein interaction, regulatory, signaling, and metabolic networks in order to gain further insights into the differences in cellular functions across tissues. Genom ...
... A| Proteomics and transcriptomics data can be used for generating and improving contextspecific biological networks including protein– protein interaction, regulatory, signaling, and metabolic networks in order to gain further insights into the differences in cellular functions across tissues. Genom ...
Gene A - Biology
... polypeptides (the building blocks of proteins) that our cells make. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in polypeptides, and thus the structure of proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) rea ...
... polypeptides (the building blocks of proteins) that our cells make. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in polypeptides, and thus the structure of proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) rea ...
Genes: How few needed for life? | Science News for Students
... are an essential part of all living organisms. They form the basis of living cells, muscle and tissues; they also do the work inside of cells. The hemoglobin in blood and the antibodies that attempt to fight infections are among the better-known, stand-alone proteins.Medicines frequently work by lat ...
... are an essential part of all living organisms. They form the basis of living cells, muscle and tissues; they also do the work inside of cells. The hemoglobin in blood and the antibodies that attempt to fight infections are among the better-known, stand-alone proteins.Medicines frequently work by lat ...
Human EGF / Epidermal Growth Factor Protein
... physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. EGF acts by binding with high affinity to epidermal growth factor receptor on the cell surface and stimulating the intrinsic protein-tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor. The tyrosine kinase activity, in turn, ...
... physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. EGF acts by binding with high affinity to epidermal growth factor receptor on the cell surface and stimulating the intrinsic protein-tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor. The tyrosine kinase activity, in turn, ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... A codon is a 3 base sequence that codes (“signals”) for a specific amino acid ...
... A codon is a 3 base sequence that codes (“signals”) for a specific amino acid ...
Chapter 12
... the aporepressor. The aporepressor becomes active only when a corepressor binds to it The corepressor inhibits transcription by activating the aporepressor ...
... the aporepressor. The aporepressor becomes active only when a corepressor binds to it The corepressor inhibits transcription by activating the aporepressor ...
supplementary information
... array to 0. This is performed so that the data from each array is scaled equivalently. Median centering genes does the same thing for genes and is performed for studies utilizing a common reference so that expression changes become ratios of the median value for that gene across all samples. Data in ...
... array to 0. This is performed so that the data from each array is scaled equivalently. Median centering genes does the same thing for genes and is performed for studies utilizing a common reference so that expression changes become ratios of the median value for that gene across all samples. Data in ...
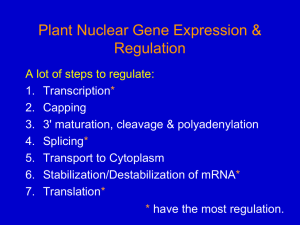
Nuclear gene expression 1
... Enhancers and Silencers 1. Enhancers stimulate transcription, while Silencers inhibit. 2. Orientation-independent – Flip 180 degrees, still work 3. Position-independent (mostly) – Can work at a distance from promoter core – Enhancers have been found all over 4. Bind regulatory transcription factors ...
... Enhancers and Silencers 1. Enhancers stimulate transcription, while Silencers inhibit. 2. Orientation-independent – Flip 180 degrees, still work 3. Position-independent (mostly) – Can work at a distance from promoter core – Enhancers have been found all over 4. Bind regulatory transcription factors ...
Gene regulatory network

A gene regulatory network or genetic regulatory network (GRN) is a collection of regulators thatinteract with each other and with other substances in the cell to govern the gene expression levels of mRNA and proteins.The regulator can be DNA, RNA, protein and their complex. The interaction can be direct or indirect (through their transcribed RNA or translated protein).In general, each mRNA molecule goes on to make a specific protein (or set of proteins). In some cases this protein will be structural, and will accumulate at the cell membrane or within the cell to give it particular structural properties. In other cases the protein will be an enzyme, i.e., a micro-machine that catalyses a certain reaction, such as the breakdown of a food source or toxin. Some proteins though serve only to activate other genes, and these are the transcription factors that are the main players in regulatory networks or cascades. By binding to the promoter region at the start of other genes they turn them on, initiating the production of another protein, and so on. Some transcription factors are inhibitory.In single-celled organisms, regulatory networks respond to the external environment, optimising the cell at a given time for survival in this environment. Thus a yeast cell, finding itself in a sugar solution, will turn on genes to make enzymes that process the sugar to alcohol. This process, which we associate with wine-making, is how the yeast cell makes its living, gaining energy to multiply, which under normal circumstances would enhance its survival prospects.In multicellular animals the same principle has been put in the service of gene cascades that control body-shape. Each time a cell divides, two cells result which, although they contain the same genome in full, can differ in which genes are turned on and making proteins. Sometimes a 'self-sustaining feedback loop' ensures that a cell maintains its identity and passes it on. Less understood is the mechanism of epigenetics by which chromatin modification may provide cellular memory by blocking or allowing transcription. A major feature of multicellular animals is the use of morphogen gradients, which in effect provide a positioning system that tells a cell where in the body it is, and hence what sort of cell to become. A gene that is turned on in one cell may make a product that leaves the cell and diffuses through adjacent cells, entering them and turning on genes only when it is present above a certain threshold level. These cells are thus induced into a new fate, and may even generate other morphogens that signal back to the original cell. Over longer distances morphogens may use the active process of signal transduction. Such signalling controls embryogenesis, the building of a body plan from scratch through a series of sequential steps. They also control and maintain adult bodies through feedback processes, and the loss of such feedback because of a mutation can be responsible for the cell proliferation that is seen in cancer. In parallel with this process of building structure, the gene cascade turns on genes that make structural proteins that give each cell the physical properties it needs.It has been suggested that, because biological molecular interactions are intrinsically stochastic, gene networks are the result of cellular processes and not their cause (i.e. cellular Darwinism). However, recent experimental evidence has favored the attractor view of cell fates.