Gene Finding using HMMs - UTK-EECS
... Exons, introns, intergenic regions, splice sites, etc. Exon HMM Model ...
... Exons, introns, intergenic regions, splice sites, etc. Exon HMM Model ...
Simultaneous digital counting of DNA, RNA, and Protein
... FIGURE 4: (A) Workflow of multiplexed RNA and protein analysis.(B) Correlation of RNA and protein measurements between the universal cell capture and centrifugation methods. 50,000 PBMCs (universal cell capture) or 500,000 PBMCs (centrifugation method) were used. (C) Correlation between CD3E and CD2 ...
... FIGURE 4: (A) Workflow of multiplexed RNA and protein analysis.(B) Correlation of RNA and protein measurements between the universal cell capture and centrifugation methods. 50,000 PBMCs (universal cell capture) or 500,000 PBMCs (centrifugation method) were used. (C) Correlation between CD3E and CD2 ...
Movement through cell membranes
... oxygen is high due to homeostatic mechanisms. Concentration gradient always favors oxygen diffusing into the cell. • CO2 is a waste product of metabolism, and thus is high inside cells; homeostasis maintains lower levels of CO2 outside the cell. Concentration gradient always favors CO2 to diffuse ou ...
... oxygen is high due to homeostatic mechanisms. Concentration gradient always favors oxygen diffusing into the cell. • CO2 is a waste product of metabolism, and thus is high inside cells; homeostasis maintains lower levels of CO2 outside the cell. Concentration gradient always favors CO2 to diffuse ou ...
Bacterial Genetics
... more stretches of hydrophobic amino acids. Many of these proteins transport molecules in and out of the cell. The transport proteins are very selective: each type of molecule needs its own ...
... more stretches of hydrophobic amino acids. Many of these proteins transport molecules in and out of the cell. The transport proteins are very selective: each type of molecule needs its own ...
Lecture 7: Life`s Information Molecule II
... • The genetic code is universal, shared by the simplest bacteria to the most complex animals • This is why genes can be transcribed and translated after being transplanted from one species to another (recombinant DNA technology) ...
... • The genetic code is universal, shared by the simplest bacteria to the most complex animals • This is why genes can be transcribed and translated after being transplanted from one species to another (recombinant DNA technology) ...
E. coli Inducible Expression Vectors E. coli Expression Vectors with
... Fluorescent and chromogenic Protein Paintbox genes are available in T5 vectors to serve as controls. In addition, any E. coli-optimized Protein Paintbox gene in an Electra MOTHER vector can be cloned into any Electra T5 DAUGHTER vector. ...
... Fluorescent and chromogenic Protein Paintbox genes are available in T5 vectors to serve as controls. In addition, any E. coli-optimized Protein Paintbox gene in an Electra MOTHER vector can be cloned into any Electra T5 DAUGHTER vector. ...
Poster PreDetector_new
... of maximal distances upstream and downstream the translational start wherein functional regulatory motifs could be found), as well as bounds of co-directionally transcribed genes. ...
... of maximal distances upstream and downstream the translational start wherein functional regulatory motifs could be found), as well as bounds of co-directionally transcribed genes. ...
Bionic-Human-Final-Paper - Temple University Sites
... findings revealed the depths in which virus actually altered inherited DNA. It was Edward Tatum who, in 1966, aroused the link between virus and somatic-cell genetics and its possible effectiveness in genetic therapy. Genetic therapy, as we see it today, was first envisioned by Stanfield Roger’s in ...
... findings revealed the depths in which virus actually altered inherited DNA. It was Edward Tatum who, in 1966, aroused the link between virus and somatic-cell genetics and its possible effectiveness in genetic therapy. Genetic therapy, as we see it today, was first envisioned by Stanfield Roger’s in ...
E. coli Inducible Expression Vectors E. coli Expression Vectors with
... Fluorescent and chromogenic Protein Paintbox genes are available in T5 vectors to serve as controls. In addition, any E. coli-optimized Protein Paintbox gene in an Electra MOTHER vector can be cloned into any Electra T5 DAUGHTER vector. ...
... Fluorescent and chromogenic Protein Paintbox genes are available in T5 vectors to serve as controls. In addition, any E. coli-optimized Protein Paintbox gene in an Electra MOTHER vector can be cloned into any Electra T5 DAUGHTER vector. ...
Mutations
... Chromosome mutations can result in changes in the number of chromosomes in a cell or changes in the structure of a chromosome. ...
... Chromosome mutations can result in changes in the number of chromosomes in a cell or changes in the structure of a chromosome. ...
6.unknown-genes
... 1. There are good BLASTx matches with phylogenetically close organisms, but all the reasonably close hits are things like ‘Theoretical ..’ or ‘Predicted …’ or ‘Riken ..’ or ‘ORF285, chromosome 9’ – we find plenty of evidence for orthologous genes, but these are just different ways of saying but we k ...
... 1. There are good BLASTx matches with phylogenetically close organisms, but all the reasonably close hits are things like ‘Theoretical ..’ or ‘Predicted …’ or ‘Riken ..’ or ‘ORF285, chromosome 9’ – we find plenty of evidence for orthologous genes, but these are just different ways of saying but we k ...
Genetics - LLI Manassas
... scaffold attachment regions (SARs).5 It also controls the cell by regulating genes, serving as gene promoters/enhancers, protein splicing, controlling protein switches, etc. o According to evolutionary biologist, J.S. Mattick: “The failure to recognize the full implications of this . . . may well go ...
... scaffold attachment regions (SARs).5 It also controls the cell by regulating genes, serving as gene promoters/enhancers, protein splicing, controlling protein switches, etc. o According to evolutionary biologist, J.S. Mattick: “The failure to recognize the full implications of this . . . may well go ...
Topic 2 - Wolfgang Hess
... model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 acclimation to N-limiting conditions involves both, the activation of multiple uptake systems for combined N-sources and of enzymes involved in specific routes of the N-assimilation. The Nand energetic status is sensed by the PII-protein which regulate ...
... model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 acclimation to N-limiting conditions involves both, the activation of multiple uptake systems for combined N-sources and of enzymes involved in specific routes of the N-assimilation. The Nand energetic status is sensed by the PII-protein which regulate ...
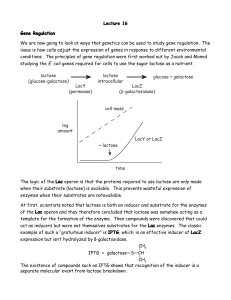
Lecture 16 Gene Regulation
... We are now going to look at ways that genetics can be used to study gene regulation. The issue is how cells adjust the expression of genes in response to different environmental conditions. The principles of gene regulation were first worked out by Jacob and Monod studying the E. coli genes required ...
... We are now going to look at ways that genetics can be used to study gene regulation. The issue is how cells adjust the expression of genes in response to different environmental conditions. The principles of gene regulation were first worked out by Jacob and Monod studying the E. coli genes required ...
DNA AND PROTIEN SYNTHESIS-
... Specifically how and when to make proteins passed from one cell generation to the next; from parent to child (gametes/sex cells) From one cell to the next within an individual ...
... Specifically how and when to make proteins passed from one cell generation to the next; from parent to child (gametes/sex cells) From one cell to the next within an individual ...
Chapter 9 Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA Introduction to
... • Used in commercial production of _______________________________________ • Pre-1980, products made by naturally occurring cells o Naturally occurring cell found, large-scale production developed • Post-1980, microbes, animals, plants engineered to produce array of chemicals • Recombinant DNA, rDNA ...
... • Used in commercial production of _______________________________________ • Pre-1980, products made by naturally occurring cells o Naturally occurring cell found, large-scale production developed • Post-1980, microbes, animals, plants engineered to produce array of chemicals • Recombinant DNA, rDNA ...
Scholarly Interest Report
... pressure, osmolarity, or mechanical forces. Most of our research employs the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a model system for understanding the molecular mechanisms required for sensing and responding to changes in external osmolarity and other stresses. Genetic and biochemical analysis of mutan ...
... pressure, osmolarity, or mechanical forces. Most of our research employs the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a model system for understanding the molecular mechanisms required for sensing and responding to changes in external osmolarity and other stresses. Genetic and biochemical analysis of mutan ...
6 - 1 - Youk Lab
... equations were deterministic equations. They were ordinary differential equations whose solutions are deterministic. This means that if you know the concentration of relevant molecules (mRNA or proteins) at a particular time point, then the equation tells you what the concentrations of those molecul ...
... equations were deterministic equations. They were ordinary differential equations whose solutions are deterministic. This means that if you know the concentration of relevant molecules (mRNA or proteins) at a particular time point, then the equation tells you what the concentrations of those molecul ...
Organization: The 6 Essential Elements
... continue. Enzymes speed up reactions, making an enzyme a biological catalyst. Metabolism (each reaction) has a small range of temperature and pH at which it can proceed. Each reaction also needs some energy to begin. This is called activation energy. Enzymes allow reactions to occur at lower activat ...
... continue. Enzymes speed up reactions, making an enzyme a biological catalyst. Metabolism (each reaction) has a small range of temperature and pH at which it can proceed. Each reaction also needs some energy to begin. This is called activation energy. Enzymes allow reactions to occur at lower activat ...
LAB SESSION 1: Bioprocessing
... Fractions collected as the solution passes through the column will contain differing chemicals or proteins based on their characteristics, effectively separating the different components. ...
... Fractions collected as the solution passes through the column will contain differing chemicals or proteins based on their characteristics, effectively separating the different components. ...
LAB SESSION 1: Bioprocessing
... Fractions collected as the solution passes through the column will contain differing chemicals or proteins based on their characteristics, effectively separating the different components. ...
... Fractions collected as the solution passes through the column will contain differing chemicals or proteins based on their characteristics, effectively separating the different components. ...
Parallel Data Mining of microarray biological data
... The microarrays are usually used to compare the gene expression of two sample of cells, e.g. cells of the same kind grown under different environments, or ill and healthy cells. In those applications, the mRNA coming from the two samples is extracted and it is labelled by means of different fluoresc ...
... The microarrays are usually used to compare the gene expression of two sample of cells, e.g. cells of the same kind grown under different environments, or ill and healthy cells. In those applications, the mRNA coming from the two samples is extracted and it is labelled by means of different fluoresc ...
PowerPoint
... Finding relationships between genes and gene products of different species, including those at large evolutionary distances ...
... Finding relationships between genes and gene products of different species, including those at large evolutionary distances ...
UNIT 8 NOTES – MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND EMBRYONIC
... – one enzyme hypothesis” with a set of experiments followed the procedure below: ...
... – one enzyme hypothesis” with a set of experiments followed the procedure below: ...
Gene regulatory network

A gene regulatory network or genetic regulatory network (GRN) is a collection of regulators thatinteract with each other and with other substances in the cell to govern the gene expression levels of mRNA and proteins.The regulator can be DNA, RNA, protein and their complex. The interaction can be direct or indirect (through their transcribed RNA or translated protein).In general, each mRNA molecule goes on to make a specific protein (or set of proteins). In some cases this protein will be structural, and will accumulate at the cell membrane or within the cell to give it particular structural properties. In other cases the protein will be an enzyme, i.e., a micro-machine that catalyses a certain reaction, such as the breakdown of a food source or toxin. Some proteins though serve only to activate other genes, and these are the transcription factors that are the main players in regulatory networks or cascades. By binding to the promoter region at the start of other genes they turn them on, initiating the production of another protein, and so on. Some transcription factors are inhibitory.In single-celled organisms, regulatory networks respond to the external environment, optimising the cell at a given time for survival in this environment. Thus a yeast cell, finding itself in a sugar solution, will turn on genes to make enzymes that process the sugar to alcohol. This process, which we associate with wine-making, is how the yeast cell makes its living, gaining energy to multiply, which under normal circumstances would enhance its survival prospects.In multicellular animals the same principle has been put in the service of gene cascades that control body-shape. Each time a cell divides, two cells result which, although they contain the same genome in full, can differ in which genes are turned on and making proteins. Sometimes a 'self-sustaining feedback loop' ensures that a cell maintains its identity and passes it on. Less understood is the mechanism of epigenetics by which chromatin modification may provide cellular memory by blocking or allowing transcription. A major feature of multicellular animals is the use of morphogen gradients, which in effect provide a positioning system that tells a cell where in the body it is, and hence what sort of cell to become. A gene that is turned on in one cell may make a product that leaves the cell and diffuses through adjacent cells, entering them and turning on genes only when it is present above a certain threshold level. These cells are thus induced into a new fate, and may even generate other morphogens that signal back to the original cell. Over longer distances morphogens may use the active process of signal transduction. Such signalling controls embryogenesis, the building of a body plan from scratch through a series of sequential steps. They also control and maintain adult bodies through feedback processes, and the loss of such feedback because of a mutation can be responsible for the cell proliferation that is seen in cancer. In parallel with this process of building structure, the gene cascade turns on genes that make structural proteins that give each cell the physical properties it needs.It has been suggested that, because biological molecular interactions are intrinsically stochastic, gene networks are the result of cellular processes and not their cause (i.e. cellular Darwinism). However, recent experimental evidence has favored the attractor view of cell fates.